Negative Punishment Examples and Scenarios
Nobody ever wants their stuff taken away. That is the main concept behind negative punishment. Using negative punishment example scenarios, gain an understanding of the concept and its effectiveness. Then, go on to explore the difference between positive and negative punishment.
Positive Punishment: What It Is, Benefits, and Examples
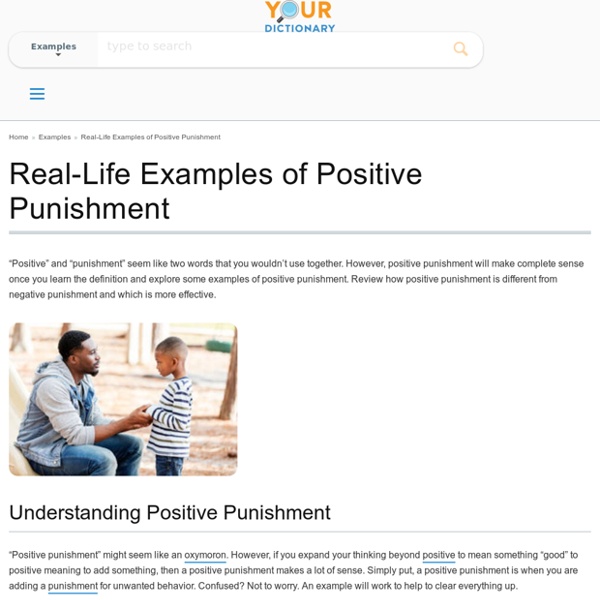
Positive punishment is a form of behavior modification. In this case, the word “positive” doesn’t refer to something pleasant. Positive punishment is adding something to the mix that will result in an unpleasant consequence. The goal is to decrease the likelihood that the unwanted behavior will happen again in the future. This approach may be effective in certain circumstance, but it’s only one part of the equation.
Article 2
Positive punishment is a concept used in B.F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. How exactly does the positive punishment process work?
Use Reinforcement Instead of Punishment - Accessible ABA, Inc.
In Learn What ABC Data Stands for in ABA we discussed the ABCs of ABA which include Antecedent, Behavior and Consequence. The consequence in ABA is something that immediately follows a behavior and makes that behavior more likely to occur in the future. This can also be thought of as reinforcement.
Reinforcement Vs. Punishment for Kids (And Examples)
As they grow, our children learn which behaviors are acceptable and which are not. They learn this through a process of cause and effect. Here’s an example of how this works: When you touch something hot, it burns and you take your hand away. Then, you remember it burns and you don’t touch the hot item again.
Positive Punishment in Operant Conditioning [Definition & Examples]
Positive punishment is often used in life when we want to suppress unwanted behavior. Let’s examine its definition, usage and examples, especially when it comes to parenting. What is Positive Punishment
Article 2
By Jeanie Lerche Davis Driving fast, breaking curfew, arguing, shoplifting. Teenagers can push your patience, but unfortunately, some kids go as far as blatantly flouting rules or breaking the law, often with tragic results. What's with this rebellious streak?
How to Reward Your Teen for Good Behavior
Teenagers are young adults who are trying to learn the ways of the world. When they do something great at school or at home or simply make a healthy decision, parents can give them a reward. The reward does not have to be money, but it is a nice way to say "thank you" or "I'm proud of you." Teens need this positive reinforcement because it shows them that they are on the right track.1 It is also a good life lesson that you can pass on: good things happen to good people. When Do Teenagers Deserve a Reward?
What Is Operant Conditioning and How Does It Work?
Operant conditioning, sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning that employs rewards and punishments for behavior. Through operant conditioning, an association is made between a behavior and a consequence (whether negative or positive) for that behavior.1 For example, when lab rats press a lever when a green light is on, they receive a food pellet as a reward. When they press the lever when a red light is on, they receive a mild electric shock. As a result, they learn to press the lever when the green light is on and avoid the red light. But operant conditioning is not just something that takes place in experimental settings while training lab animals.
What is Negative Punishment (Examples and Effectiveness)
In this article, we will review negative punishment, its definition, examples, and drawbacks. American psychologist B.F. Skinner developed the theory of operant conditioning, which stated that a person or animal’s behavior could be increased or decreased by adding or removing appropriate stimuli after the behavior is exhibited. The difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning is that classical affects unconscious behavior, while operant affects conscious behavior. Within operant, punishment aims to reduce a behavior while reinforcement increase a behavior. Punishment or reinforcement can be positive or negative.
Article 1
Negative punishment is an important concept in B. F. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning. In behavioral psychology, the goal of punishment is to decrease unwanted behavior.