


History - World Wars: The League of Nations and the United Nations Viajar Blog de viajes :: Pasaporteblog United Nations | Definition, History, Founders, Flag, & Facts Summary Read a brief summary of this topic United Nations (UN), international organization established on October 24, 1945. The United Nations (UN) was the second multipurpose international organization established in the 20th century that was worldwide in scope and membership. Its predecessor, the League of Nations, was created by the Treaty of Versailles in 1919 and disbanded in 1946. Headquartered in New York City, the UN also has regional offices in Geneva, Vienna, and Nairobi. According to its Charter, the UN aims: to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war,…to reaffirm faith in fundamental human rights,…to establish conditions under which justice and respect for the obligations arising from treaties and other sources of international law can be maintained, and to promote social progress and better standards of life in larger freedom. Britannica Quiz World Organizations: Fact or Fiction? Is the North Atlantic Treaty Organization limited to European countries?
United Nations (UN) (international organization from the Encyclopædia Britannica United Nations (UN), international organization established on October 24, 1945. The United Nations was the second multipurpose international organization established in the 20th century that was worldwide in scope and membership. According to its Charter, the UN aims: to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war,…to reaffirm faith in fundamental human rights,…to establish conditions under which justice and respect for the obligations arising from treaties and other sources of international law can be maintained, and to promote social progress and better standards of life in larger freedom. The UN formed a continuum with the League of Nations in general purpose, structure, and functions; many of the UN’s principal organs and related agencies were adopted from similar structures established earlier in the century. History and development Organization and administration Principles and membership United Nations - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
UK - Language Welcome to our guide to the UK. This is useful for anyone researching British culture, customs, manners, etiquette, values and wanting to understand the people better. You may be going to Britain on business, for a visit or even hosting British colleagues or clients in your own country. Facts and Statistics Location: Western Europe, islands including the northern one-sixth of the island of Ireland between the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, northwest of France Capital: London Climate: temperate; moderated by prevailing southwest winds over the North Atlantic Current; more than one-half of the days are overcast Population: 60,776,238 (July 2007 est.) Ethnic Make-up: white (of which English 83.6%, Scottish 8.6%, Welsh 4.9%, Northern Irish 2.9%) 92.1%, black 2%, Indian 1.8%, Pakistani 1.3%, mixed 1.2%, other 1.6% (2001 census) Religions: Christian (Anglican, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian, Methodist) 71.6%, Muslim 2.7%, Hindu 1%, other 1.6%, unspecified or none 23.1% (2001 census)
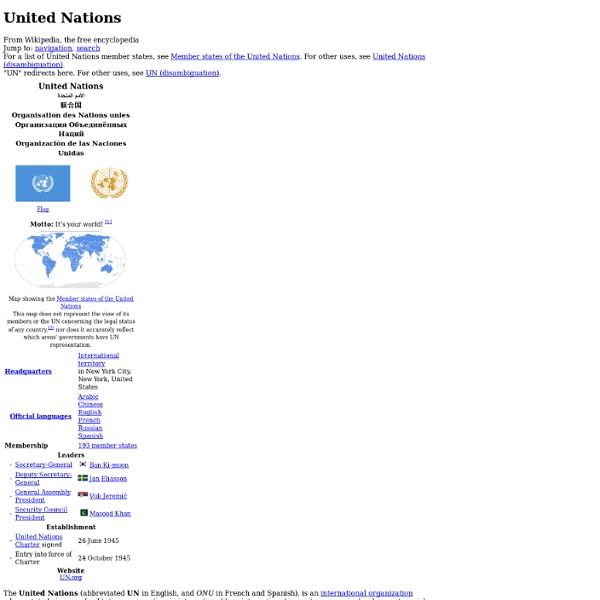
United Nations - HISTORY The United Nations (U.N.) is a global diplomatic and political organization dedicated to international peace and stability. The U.N. was officially established in 1945 following the horrific events of World War II, when international leaders proposed creating a new global organization to maintain peace and avoid the abuses of war. The U.N. initially had just 51 member states; today, the organization, which is headquartered in New York City, has 193 members. Major U.N. initiatives include preventing conflict by exploring options to ensure peace, providing food and medical assistance in emergencies, and offering humanitarian support to millions of people around the world. While the United Nations is sometimes criticized for its policies, bureaucracy and spending, the organization has accomplished hundreds of successful peacekeeping missions. Atlantic Charter After World War I, an international group developed the League of Nations to solve disputes between countries. U.N. U.N. U.N. U.N.
IDA History The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), better known as the World Bank, was established in 1944 to help Europe recover from the devastation of World War II. The success of that enterprise led the Bank, within a few years, to turn its attention to the developing countries. By the 1950s, it became clear that the poorest developing countries needed softer terms than those that could be offered by the Bank, so they could afford to borrow the capital they needed to grow. In the early 1950’s, reports from the United Nations and the U.S. government supported the establishment of a program to lend to poor countries on concessional terms with the backing of multilateral donors. Monroney Resolution Articles of Agreement for IDA As the resolution was passed in the U.S. Launch of IDA IDA has grown to include 172 member countries, and has become the leading source of concessional lending to 82 of the world’s poorest countries, with 40 countries in Africa.
untry Profiles - Global Guide to Culture, Customs and Etiquette Understanding other people's languages, cultures, etiquettes and taboos is of great value to the traveller or visiting business person. Scroll down the page for information on a selected number of countries. Topics include language, useful phrases, the society, culture, business and social etiquettes. You can access Useful Phrases here or through the corresponding country. Please feel free to share comments you may have about our guides as we are always looking to improve the quality and accuracy of information. This information is also available as an App for the iPhone. Etiquette, Customs and Protocol Guides Warning! It is important to bear in mind that these guides act as basic and general introductions only. Each society, country and culture will have numerous nuances that would make it irresponsible to suggest a uniform approach to understanding any country's social/business culture or etiquette.
Investigative Team to Promote Accountability for Crimes Committed by Da'esh/ISIL (UNITAD) IBRD The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) aims to reduce poverty in middle-income countries and creditworthy poorer countries by promoting sustainable development through loans, guarantees, risk management products, and analytical and advisory services. Established in 1944 as the original institution of the World Bank Group, IBRD is structured like a cooperative that is owned and operated for the benefit of its 188 member countries. IBRD raises most of its funds on the world's financial markets and has become one of the most established borrowers since issuing its first bond in 1947. The income that IBRD has generated over the years has allowed it to fund development activities and to ensure its financial strength, which enables it to borrow at low cost and offer clients good borrowing terms. Find out more about IBRD and the results being achieved.