


Reported Speech Exercises Reported Speech Exercises Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: (Click here to read the explanations about reported speech) Reported Statements: Reported Questions: Reported Orders and Requests: Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here) Mixed Exercises: Return to reported speech explanations from reported speech exercises. LoginSubscribe to PEG+What's New?
Random Idea English: Reported speech - lesson and exercises Constructing reported speech involves using a mixture of some basic rules and your common sense. When using the first doesn't sound natural, use the second. The main idea is that it should make sense to the listener. This is a fairly detailed but not exhaustive look at reported speech. I hope to follow it up with some more advanced vocabulary and exercises fairly soon. Click and Drop - Where you see this sign, mouse over for instructions Basic principles Exercise 1 - Convert the direct statements and questions into reported speech. Basic rules In both reported statements and questions verbs usually go one tense back (backshifting)pronouns, possessives and other determiners may have to be changedtime references may have to be made non-time-specificplace references may need to be changed Note These are not fixed rules, but reflect that: Additionally in reported questions in the main question, change question order to statement orderin yes/no questions, add if or whether Patricia isn't here today.
Infinitive and Gerund Exercises and Tests on Infinitive and Gerund There are certain words in English that are usually followed by an infinitive or gerund. If you are not sure whether to use the infinitive or gerund, check out our lists or look the words up in a dictionary. Infinitive Use Certain words are followed by an infinite verb with or without ‘to’. Gerund Form ing form of the verb Exceptions in Spelling See → Present Progressive – Exceptions Certain words are followed by an Ing-Form. Words followed either by Infinitive or Ing-Form Exercises and Tests Infinitive Gerund Infinitive / Gerund Tests on Infinitive and Gerund Level 1 • Level 2 • Level 3 • Level 4
Reported speech 1 Look at these examples to see how we can tell someone what another person said. direct speech: 'I love the Toy Story films,' she said. indirect speech: She said she loved the Toy Story films.direct speech: 'I worked as a waiter before becoming a chef,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd worked as a waiter before becoming a chef.direct speech: 'I'll phone you tomorrow,' he said. indirect speech: He said he'd phone me the next day. Try this exercise to test your grammar. Read the explanation to learn more. Reported speech is when we tell someone what another person said. direct speech: 'I work in a bank,' said Daniel. indirect speech: Daniel said that he worked in a bank. In indirect speech, we often use a tense which is 'further back' in the past (e.g. worked) than the tense originally used (e.g. work). Present simple, present continuous and present perfect 'I travel a lot in my job.' Past simple and past continuous 'We lived in China for five years.' Past perfect No backshift Past perfect
Wh- Question Clauses – Reported / Indirect Speech Restate a question within a clause (reported speech) Quoted Questions vs. Restated Questions Wh-question: Who, What, Where, Why, When and How The main clause (matrix clause) is the independent clause and the subordinate clause (embedded clause) is the dependent clause. In reported speech, no additional punctuation (quotation marks, comma, or question mark) is used. Ask Synonyms ask (V) – request information → My father always asks how I am doing. Also see Said Synonyms. Adjustments Word Order / Person & Number ¹subordinate marker – who, what, where, why, when, how perspective (N) – point of view; how someone relates to surroundings: person (you, i we); place (here, there); time (now, then); direction (coming, going) See deixis. Time / Location ¹subordinate marker– who, what, where, why, when, how ²direction: change coming to going if both speaker and listener do not share a location Adjusting Perspective (deixis) Adjusting Perspective Deictic words Person Deixis Time and Place Deixis Advanced
The Syrian Refugee Crisis Explained Perfectly With a Simple Animation & Video In September 2015, the body of a three-year-old Syrian boy was found floating on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. Photographs of the boy were quick to get circulated world over, and the world responded with a massive outcry over the Syrian civil war and refugee crisis. This was the first time the Syrian crisis was globally recognised as a burning issue, and one that needs to be addressed with utmost urgency. This video, by In a Nutshell , speaks about how the Syrian crisis is an international issue, and how it all started with countrywide unrest and the civil war in Syria. Apart from the succinct explanation of the overarching issue, the video also explains the role of the neighbouring countries in aiding and giving asylum to refugees in their greatest hour of need. Watch this video to get a better understanding of the larger Syrian issue and learn about what measures we can take to offer help to the affected people. Video created by In a Nutshell .
www.tolearnenglish.com/english_lessons/indirect-speech-exercises Free educational sites > Learn English > Thematic page:Recommended pages from our site - Selected by our team. Direct/Indirect speech-English English exercises: Direct/Indirect speech. ... Other sites for teachers. Indirect speech - EnglishIndirect speech : free exercise for ESL/EFL learners. ... Direct and indirect speech - EnglishDirect and indirect speech : free exercise for ESL/EFL learners. ... Free exercises to learn English 10 / 10Free exercises to learn English-page 10. ... >>> Search pages about this theme: search INDIRECT SPEECH EXERCISES on our 100% free site to learn English.
Additional Information and Exceptions in Reported Speech • Start › Cram Up › Grammar › Reported Speech › Additional Information and Exceptions in Reported Speech Main Clauses connected with and / but If two complete main clauses are connected with ‚and‘ or ‚but‘, put ‚that‘ after the conjunction. Example: He said,“I saw her but she didn’t see me.“ – He said that he had seen her but that she hadn’t seen him If the subject is left out in the second main clause (the conjunction is followed by a verb), do not use ‚that‘. She said,“I am a nurse and work in a hospital.“ – He said that she was a nurse and worked in a hospital Tense of the Introductory Clause The introductory clause usually is in Past Tense. He said that … Present Tense is often used to report a conversation that is still going on, e. g. during a phone call or while reading a letter. “I am fine.“ – Tom says / writes that he is fine. The introductory clause can also be in another tense. Backshift in Reported Speech Exceptions Beispiel: “Canberra is the capital of Australia “She left Boston on Monday
While You Were Sleeping: Reported Speech This a very funny scene. Your students will enjoy it a lot. Tell me if you like it or give suggestions by leaving a comment, please. Before you watch the segment:Talk to a partner about the following situations. Decide what you would do: 1) What would you do if you saw someone falling on the subway tracks? 2) If you saved someone's life, would you expect a financial reward? 3) Would you hide a secret in order not to hurt a stranger's feelings? Now watch the movie segment and decide who said each of the following lines:Lucy (Sandra Bullock) A Doctor A Nurse A Police Officer1) Will you marry me? 2) Are you okay? 3) There’s a train coming and it’s fast 4) Are you family? 5) She’s his fiancee 6) I need to ask you a few questions 7) He is in a coma 8) He was pushed from the platform at the train station 9) She jumped on the tracks 10) She saved his life. _____________________________ Now rewrite the sentences, using reported speech: EX: 1) Lucy asked if he would marry her. 2) Lucy asked if he was okay.
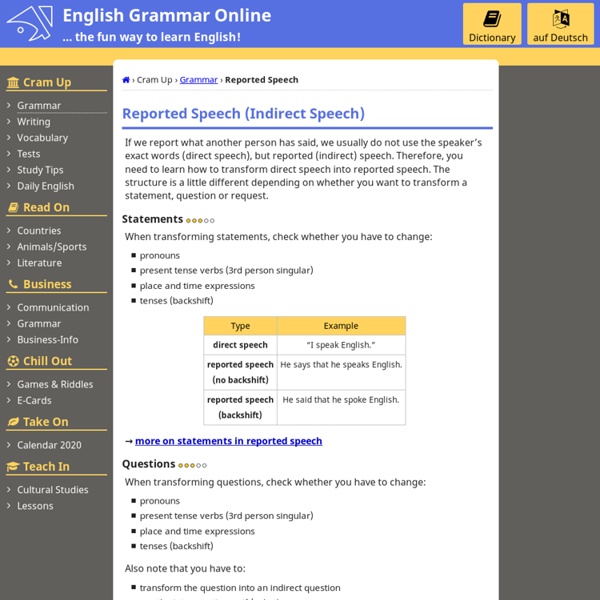
English Grammar Reported Speech