


Thoth Thoth played many vital and prominent roles in Egyptian mythology, such as maintaining the universe, and being one of the two deities (the other being Ma'at) who stood on either side of Ra's boat.[5] In the later history of ancient Egypt, Thoth became heavily associated with the arbitration of godly disputes,[6] the arts of magic, the system of writing, the development of science,[7] and the judgment of the dead.[8] Name[edit] Etymology[edit] The Egyptian pronunciation of ḏḥwty is not fully known, but may be reconstructed as *ḏiḥautī, based on the Ancient Greek borrowing Θώθ [tʰɔːtʰ] Thōth or Theut and the fact that it evolved into Sahidic Coptic variously as Thoout, Thōth, Thoot, Thaut as well as Bohairic Coptic Thōout. According to Theodor Hopfner,[12] Thoth's Egyptian name written as ḏḥwty originated from ḏḥw, claimed to be the oldest known name for the Ibis although normally written as hbj. Further names and spellings[edit] Depictions[edit] Attributes[edit] Mythology[edit] History[edit]
Seshat In Egyptian mythology, Seshat (also spelled Safkhet, Sesat, Seshet, Sesheta, and Seshata) was the Ancient Egyptian goddess of wisdom, knowledge, and writing. She was seen as a scribe and record keeper, and her name means she who scrivens (i.e. she who is the scribe), and is credited with inventing writing. She also became identified as the goddess of architecture, astronomy, astrology, building, mathematics, and surveying. These are all professions that relied upon expertise in her skills. In art, she was depicted as a woman with a seven-pointed emblem above her head. Usually, she is shown holding a palm stem, bearing notches to denote the recording of the passage of time, especially for keeping track of the allotment of time for the life of the pharaoh. She is frequently shown dressed in a cheetah or leopard hide, a symbol of funerary priests. As the divine measurer and scribe, Seshat was believed to appear to assist the pharaoh in both of these practices. See also[edit] Gallery[edit]
Sekhmet In Egyptian mythology, Sekhmet /ˈsɛkˌmɛt/[1] or Sachmis (/ˈsækmɨs/; also spelled Sakhmet, Sekhet, or Sakhet, among other spellings) was originally the warrior goddess as well as goddess of healing for Upper Egypt, when the kingdom of Egypt was divided. She is depicted as a lioness, the fiercest hunter known to the Egyptians. It was said that her breath formed the desert. Sekhmet also is a Solar deity, sometimes called the daughter of the sun god Ra and often associated with the goddesses Hathor and Bast. Etymology[edit] Sekhmet's name comes from the Ancient Egyptian word "sekhem" which means "power or might". History[edit] Bust of the Goddess Sakhmet, ca. 1390-1352 B.C.E. The warrior goddess Sekhmet, shown with her sun disk and cobra crown from a relief at the Temple of Kom Ombo. In order to placate Sekhmet's wrath, her priestesses performed a ritual before a different statue of the goddess on each day of the year. Festivals and evolution[edit] In popular culture[edit] See also[edit]
Persian mythology Persian mythology are traditional tales and stories of ancient origin, all involving extraordinary or supernatural beings. Drawn from the legendary past of Iran, they reflect the attitudes of the society to which they first belonged - attitudes towards the confrontation of good and evil, the actions of the gods, yazats (lesser gods), and the exploits of heroes and fabulous creatures. Myths play a crucial part in Iranian culture and our understanding of them is increased when we consider them within the context of Iranian history. For this purpose we must ignore modern political boundaries and look at historical developments in the Greater Iran, a vast area covering parts of Central Asia well beyond the frontiers of present-day Iran. Key texts[edit] The central collection of Persian mythology is the Shahnameh of Ferdowsi, written over a thousand years ago. Religious background[edit] The characters of Persian mythology almost always fall into one of two camps. Good and Evil[edit]
Ammit Ammit (/ˈæmɨt/; "devourer" or "soul-eater"; also spelled Ammut or Ahemait) was a female demon in ancient Egyptian religion with a body that was part lion, hippopotamus and crocodile—the three largest "man-eating" animals known to ancient Egyptians. A funerary deity, her titles included "Devourer of the Dead", "Eater of Hearts", and "Great of Death". Ammit lived near the scales of justice in Duat, the Egyptian underworld. In the Hall of Two Truths, Anubis weighed the heart of a person against the feather of Ma'at, the goddess of truth, which was depicted as an ostrich feather (the feather was often pictured in Ma'at's headdress). If the heart was judged to be not pure, Ammit would devour it, and the person undergoing judgement was not allowed to continue their voyage towards Osiris and immortality. Once Ammit swallowed the heart, the soul was believed to become restless forever; this was called "to die a second time". See also[edit] References[edit]
Maat The earliest surviving records indicating Maat is the norm for nature and society, in this world and the next, were recorded during the Old Kingdom, the earliest substantial surviving examples being found in the Pyramid Texts of Unas (ca. 2375 BCE and 2345 BCE).[2] Later, as a goddess in other traditions of the Egyptian pantheon, where most goddesses were paired with a male aspect, her masculine counterpart was Thoth and their attributes are the same. After the rise of Ra they were depicted together in the Solar Barque. After her role in creation and continuously preventing the universe from returning to chaos, her primary role in Egyptian mythology dealt with the weighing of souls that took place in the underworld, Duat.[3] Her feather was the measure that determined whether the souls (considered to reside in the heart) of the departed would reach the paradise of afterlife successfully. Maat as a principle[edit] Winged Maat Maat and the law[edit] Maat wearing feather of truth See also[edit]
Apep Development[edit] Ra was the solar deity, bringer of light, and thus the upholder of Ma'at. Apep was viewed as the greatest enemy of Ra, and thus was given the title Enemy of Ra. Also, comparable hostile snakes as enemies of the sun god existed under other names (in the Pyramid Texts and Coffin Texts) already before the name Apep occurred. The etymology of his name (ꜥꜣpp) is perhaps to be sought in some west-semitic language where a word root ꜣpp meaning 'to slither' existed. A verb root ꜥꜣpp does at any rate not exist elsewhere in Ancient Egyptian. Battles with Ra[edit] Set speared Apep The sun god Ra, in the form of Great Cat, slays the snake Apep[5] Tales of Apep's battles against Ra were elaborated during the New Kingdom.[6] Since everyone can see that the sun is not attacked by a giant snake during the day, every day, storytellers said that Apep must lie just below the horizon. In a bid to explain certain natural phenomena it was said that occasionally Apep got the upper hand.
Ancient Mesopotamian religion The god Marduk and his dragon Mušḫuššu Mesopotamian religion refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Sumerian and East Semitic Akkadian, Assyrian, Babylonian and later migrant Arameans and Chaldeans, living in Mesopotamia (a region encompassing modern Iraq, Kuwait, southeast Turkey and northeast Syria) that dominated the region for a period of 4200 years from the fourth millennium BCE throughout Mesopotamia to approximately the 10th century CE in Assyria.[1] Mesopotamian polytheism was the only religion in ancient Mesopotamia for thousands of years before entering a period of gradual decline beginning between the 1st and 3rd centuries CE. Reconstruction[edit] As with most dead religions, many aspects of the common practices and intricacies of the doctrine have been lost and forgotten over time. History[edit] Overview map of ancient Mesopotamia. Akkadian names first appear in king lists of these states circa 2800 BCE. Religion in the Neo-Assyrian Empire[edit] "Enlil!
Ancient Egyptian concept of the soul Ib (heart)[edit] To ancient Egyptians, the heart was the seat of emotion, thought, will and intention. This is evidenced by the many expressions in the Egyptian language which incorporate the word ib, Awt-ib: happiness (literally, wideness of heart), Xak-ib: estranged (literally, truncated of heart). This word was transcribed by Wallis Budge as Ab. In Egyptian religion, the heart was the key to the afterlife. It was conceived as surviving death in the nether world, where it gave evidence for, or against, its possessor. Sheut (shadow)[edit] A person's shadow or silhouette, Sheut (šwt in Egyptian), is always present. The shadow was also representative to Egyptians of a figure of death, or servant of Anubis, and was depicted graphically as a small human figure painted completely black. Ren (name)[edit] Ba[edit] Ba takes the form of a bird with a human head. The 'Ba' (bꜣ) was everything that makes an individual unique, similar to the notion of 'personality'. Ka[edit] Akh[edit] Akh glyph Notes[edit]
Ogdoad In Egyptian mythology, the Ogdoad (Greek "ογδοάς", the eightfold) were eight deities worshipped in Hermopolis during what is called the Old Kingdom, the third through sixth dynasties, dated between 2686 to 2134 BC. In Egyptian mythology[edit] Together the four concepts represent the primal, fundamental state of the beginning. The entity containing Ra is depicted either as an egg or as a lotus bud. In the former version, a mound arises from the waters. In Gnosticism[edit] The number eight plays an important part in Gnostic systems, and it is necessary to distinguish the different forms in which it appeared at different stages in the development of Gnosticism. In the system of Valentinus, the seven heavens, and even the region above them, were regarded as but the lowest and last stage of the exercise of creative power. 7 + 1[edit] Seven heavens[edit] Eighth sphere[edit] The planetary spheres were thought to be planes of existence in between the earth and the heavenly regions 6 + 2[edit]
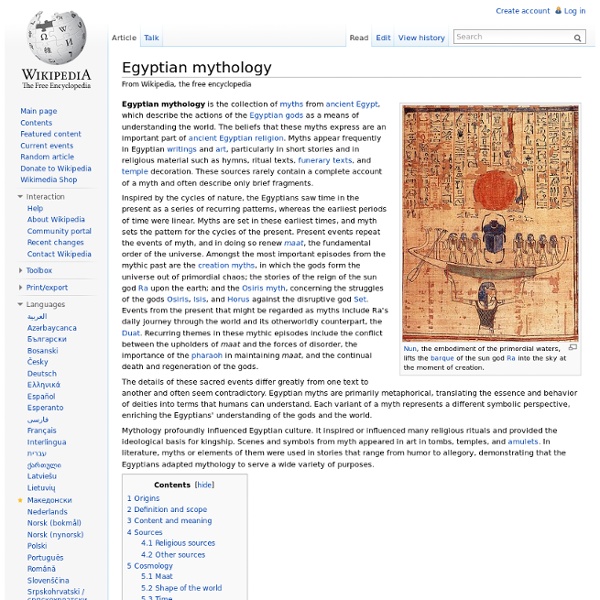
Ancient Egyptian creation myths The sun rises over the circular mound of creation as goddesses pour out the primeval waters around it Ancient Egyptian creation myths are the ancient Egyptian accounts of the creation of the world. The Pyramid Texts, tomb wall decorations and writings, dating back to the Old Kingdom (2780 – 2250 B.C.E) have given us most of our information regarding early Egyptian creation myths.[1] These myths also form the earliest religious compilations in the world.[2] The ancient Egyptians had many creator gods and associated legends. Thus the world or more specifically Egypt was created in diverse ways according to different parts of the country.[3] Common elements[edit] Another common element of Egyptian cosmogonies is the familiar figure of the cosmic egg, a substitute for the primeval waters or the primeval mound. Cosmogonies[edit] Hermopolis[edit] Heliopolis[edit] Memphis[edit] The Memphite version of creation centered on Ptah, who was the patron god of craftsmen. Thebes[edit] References[edit]
Proto-Indo-Iranian religion Proto-Indo-Iranian religion means the religion of the Indo-Iranian peoples prior to the earliest Vedic (Indo-Aryan) and Zoroastrian (Iranian) scriptures. These share a common inheritance of concepts including the universal force *rta (Vedic rta, Avestan asha), the sacred plant and drink *sauma (Vedic Soma, Avestan Haoma) and gods of social order such as *mitra (Vedic Mitra, Avestan and Old Persian Mithra, Miϑra), *bhaga (Vedic Bhaga, Avestan and Old Persian Baga). Proto-Indo-Iranian religion is an archaic offshoot of Indo-European religion.[1] Introduction[edit] Indo-Iranian languages include three subgroups: first Indo-Aryan languages (including the Dardic languages); second Iranian languages (east and west) and third Nuristani languages. From these various and dispersed cultures, a set of common ideas may be reconstructed from which a common, unattested proto-Indo-Iranian source may be deduced.[1] The Proto-Indo-Iranian religions influenced Zoroastrianism and the Vedic Religions.
Duat This article is about the Egyptian underworld. For the evergreen tree, see Jambul. For the aviation weather service, see DUATS. In Egyptian mythology, Duat (pronounced "do-aht") (also Tuat and Tuaut or Akert, Amenthes, Amenti, or Neter-khertet) is the realm of the dead. The Duat is the realm of the god Osiris and the residence of other gods and supernatural beings. What we know of the Duat principally derives from funerary texts such as Book of Gates, Book of Caverns, Coffin Texts, Amduat and the Book of the Dead. A section of the Egyptian Book of the Dead written on papyrus showing the Weighing of the Heart in Duat where Anubis can be seen on the far right, the scales are shown with the feather balance, and Ammit awaits hearts that she must devour – the presence of Osiris at the gateway to the paradise of Aaru dates the papyrus to a late tradition of the myth. The geography of Duat is similar in outline to the world the Egyptians knew. References Bibliography Faulkner, R. External links