


English Civil War The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists ("Cavaliers") in the Kingdom of England over, principally, the manner of its government. The first (1642–46) and second (1648–49) wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third (1649–51) saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The war ended with the Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Worcester on 3 September 1651. The overall outcome of the war was threefold: the trial and execution of Charles I; the exile of his son, Charles II; and the replacement of English monarchy with, at first, the Commonwealth of England (1649–53) and then the Protectorate (1653–59) under Oliver Cromwell's personal rule. Terminology[edit] Background[edit] The King's rule[edit] Charles I, painted by Van Dyck Personal rule[edit] Rebellion in Scotland[edit]
William Hazlitt English writer We ask you, humbly, to help. Hi reader in Canada, it seems you use Wikipedia a lot; that's great! Maybe later Thank you! Close William Hazlitt (10 April 1778 – 18 September 1830) was an English writer, drama and literary critic, painter, social commentator, and philosopher. During his lifetime he befriended many people who are now part of the 19th-century literary canon, including Charles and Mary Lamb, Stendhal, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, William Wordsworth, and John Keats.[8] Contents Life and works[edit] Background[edit] Childhood, education, young philosopher (1778–1797)[edit] Childhood[edit] House in Wem, Shropshire where the Reverend William Hazlitt and his family lived between 1787 and 1813 William, the youngest of the surviving Hazlitt children, was born in Mitre Lane, Maidstone, in 1778. Education[edit] Hazlitt was educated at home and at a local school. Changes were taking place within the young Hazlitt as well. The young philosopher[edit] The itinerant painter[edit] In "Mr.
Letters_and_Social_Aims_Scholar_s_Choice Time Person of the Year History[edit] The tradition of selecting a "Man of the Year" began in 1927, with Time editors contemplating news makers of the year. The idea was also an attempt to remedy the editorial embarrassment earlier that year of not having aviator Charles Lindbergh on its cover following his historic trans-Atlantic flight. By the end of the year, it was decided that a cover story featuring Lindbergh as the Man of the Year would serve both purposes.[2][volume & issue needed] Since then, individual people, classes of people, the computer ("Machine of the Year" in 1982), and "Endangered Earth" ("Planet of the Year" in 1988) have all been selected for the special year-end issue. Since the list began, every serving President of the United States has been a Person of the Year at least once with the exceptions of Calvin Coolidge, in office at time of the first issue, Herbert Hoover, the next U.S. president, and Gerald Ford. The last issue of 1989 named Mikhail Gorbachev as "Man of the Decade".
Friedrich Nietzsche German philosopher (1844–1900) Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche ( NEE-chə, NEE-chee,[10] German: [ˈfʁiːdʁɪç ˈvɪlhɛlm ˈniːtʃə] i or [ˈniːtsʃə];[11][12] 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, prose poet, cultural critic, philologist, and composer, whose work has exerted a profound influence on contemporary philosophy. He began his career as a classical philologist before turning to philosophy. Life[edit] Youth (1844–1868)[edit] Born on 15 October 1844, Nietzsche[13] grew up in the town of Röcken (now part of Lützen), near Leipzig, in the Prussian Province of Saxony. Nietzsche attended a boys' school and then a private school, where he became friends with Gustav Krug and Wilhelm Pinder, all three of whom came from highly respected families. In 1854, he began to attend the Domgymnasium in Naumburg. While at Schulpforta, Nietzsche pursued subjects that were considered unbecoming. In 1865, Nietzsche thoroughly studied the works of Arthur Schopenhauer. Philosophy[edit] Works[edit]
oll.libertyfund The perception of matter is made the common sense, and for cause. This was the cradle, this the go-cart, of the human child. We must learn the homely laws of fire and water; we must feed, wash, plant, build. But whilst we deal with this as finality, early hints are given that we are not to stay here; that we must be making ready to go;—a warning that this magnificent hotel and conveniency we call Nature is not final. This hint, however conveyed, upsets our politics, trade, customs, marriages, nay, the common-sense side of religion and literature, which are all founded on low nature,—on the clearest and most economical mode of administering the material world, considered as final. Suppose there were in the ocean certain strong currents which drove a ship, caught in them, with a force that no skill of sailing with the best wind, and no strength of oars, or sails, or steam, could make any head against, any more than against the current of Niagara. for the universe is full of their echoes.
Indo-European languages The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects. There are about 439 languages and dialects, according to the 2009 Ethnologue estimate, about half (221) belonging to the Indo-Aryan subbranch.[2] It includes most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the Indian Subcontinent, and was also predominant in ancient Anatolia. With written attestations appearing since the Bronze Age in the form of the Anatolian languages and Mycenaean Greek, the Indo-European family is significant to the field of historical linguistics as possessing the second-longest recorded history, after the Afro-Asiatic family. Indo-European languages are spoken by almost 3 billion native speakers,[3] the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Etymology[edit] History of Indo-European linguistics[edit] Franz Bopp, pioneer in the field of comparative linguistic studies. Gaston Coeurdoux and others made observations of the same type.
Albert O. Hirschman Albert Otto Hirschman[1] (born Otto-Albert Hirschmann; April 7, 1915 – December 10, 2012) was an influential economist and the author of several books on political economy and political ideology. His first major contribution was in the area of development economics.[2] Here he emphasized the need for unbalanced growth. Because developing countries are short of decision making skills, he argued that disequilibria should be encouraged to stimulate growth and help mobilize resources. Key to this was encouraging industries with a large number of linkages to other firms. His later work was in political economy and there he advanced two simple but intellectually powerful schemata. In World War II, he played a key role in rescuing refugees in occupied France. Life[edit] Soon thereafter, Hirschman volunteered to fight on behalf of the Spanish Republic in the Spanish Civil War. Hirschman helped develop the hiding hand principle in his 1967 essay 'The principle of the hiding hand'. Books[edit] 1945.
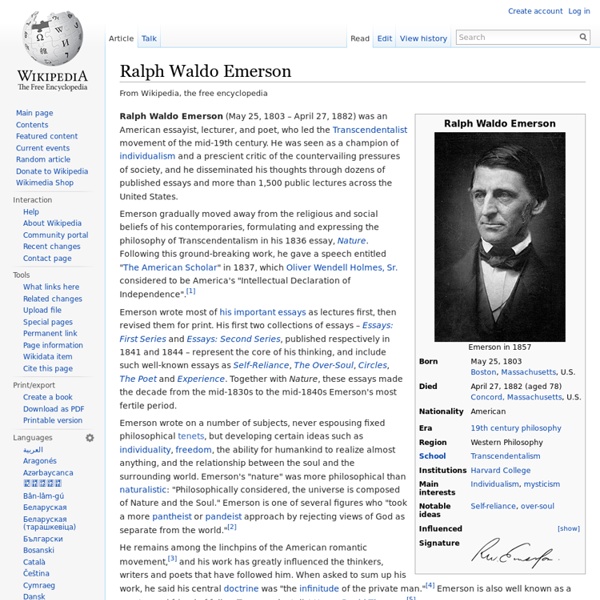
The_Complete_Works_of_Ralph_Waldo_Emerso History of technology The wheel was invented in the 4th millennium BC, and has become one of the world's most famous, and most useful technologies. This wheel is on display in The National Museum of Iran, in Tehran. The history of technology is the history of the invention of tools and techniques, and is similar in many ways to the history of humanity. Technological artifacts are products of an economy, a force for economic growth, and a large part of everyday life. Measuring technological progress[edit] Instead of specific inventions, White decided that the measure by which to judge the evolution of culture was energy. Lenski takes a more modern approach and focuses on information. hunters and gatherers,simple agricultural,advanced agricultural,industrial,special (such as fishing societies). By period and geography[edit] Prehistory[edit] Stone Age[edit] During the Paleolithic Age, all humans had a lifestyle which involved limited use of tools and few permanent settlements. Copper and Bronze Ages[edit]
Jean-Jacques Rousseau Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer (1712–1778) Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, [1][2] French: [ʒɑ̃ ʒak ʁuso]; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher (philosophe), writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolution and the development of modern political, economic, and educational thought.[3] Biography[edit] Youth[edit] Rousseau was born in Geneva, which was at the time a city-state and a Protestant associate of the Swiss Confederacy (now a canton of Switzerland). Rousseau was proud that his family, of the moyen order (or middle-class), had voting rights in the city. Geneva, in theory, was governed "democratically" by its male voting "citizens". There was much political debate within Geneva, extending down to the tradespeople. Rousseau's father, Isaac Rousseau, followed his grandfather, father and brothers into the watchmaking business. Early adulthood[edit]
en.m.wikipedia Nahum Tate's 1681 adaptation of King Lear Facsimile of the first edition, 1681 The History of King Lear is an adaptation by Nahum Tate of William Shakespeare's King Lear. It first appeared in 1681, some seventy-five years after Shakespeare's version, and is believed to have replaced Shakespeare's version on the English stage in whole or in part until 1838.[1] Unlike Shakespeare's tragedy, Tate's play has a happy ending, with Lear regaining his throne, Cordelia marrying Edgar, and Edgar joyfully declaring that "truth and virtue shall at last succeed." Regarded as a tragicomedy, the play has five acts, as does Shakespeare's, although the number of scenes is different, and the text is about eight hundred lines shorter than Shakespeare's. The tragic ending was briefly restored by Edmund Kean in 1823. Comparison with Shakespeare[edit] Shakespeare's version[edit] Kent, returning in disguise, offers himself in service to Lear, and is accepted. Tate's version[edit] Background and history[edit] Ha!