Solar panel
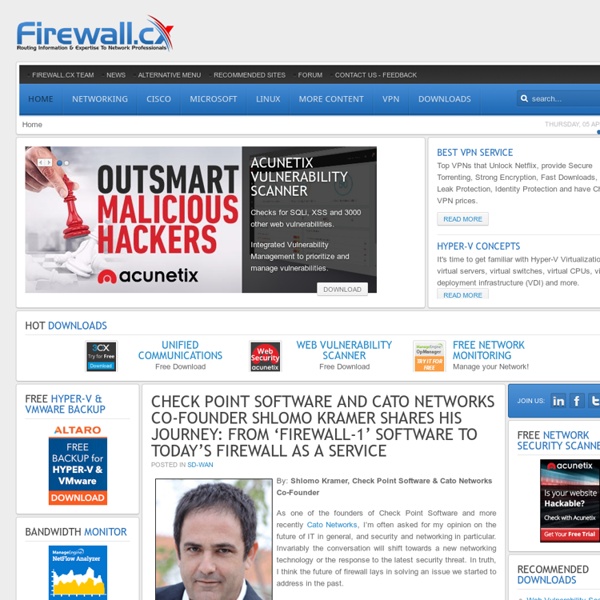
Photovoltaic solar panels absorb sunlight as a source of energy to generate direct current electricity. A photovoltaic (PV) module is a packaged, connected assembly of photovoltaic solar cells available in different voltages and wattages. Photovoltaic modules constitute the photovoltaic array of a photovoltaic system that generates and supplies solar electricity in commercial and residential applications. The most common application of solar energy collection outside agriculture is solar water heating systems.[1] Theory and construction[edit] A PV junction box is attached to the back of the solar panel and functions as its output interface.
Network Monitoring Tools
Les Cottrell, SLAC. Last Update: December 14, 2015 ESnet | ESCC | PinGER Internet monitoring | Tutorial This is a list of tools used for Network (both LAN and WAN) Monitoring tools and where to find out more about them. The audience is mainly network administrators. You are welcome to provide links to this web page. Please do not make a copy of this web page and place it at your web site since it will quickly be out of date. See here if you wish to suggest additions or changes.
Windows Registry Editor for dummies
Often, our tips mention the Windows Registry and Registry Editor. What exactly is the Registry and what is RegEdit? Those are who are familiar with Windows for many years need no explanation, but those who are new to Windows will find this post useful. Today, I am going to explain the fundamentals of Registry Editor.
Cisco administration 101: Learn 10 commands to configure on a new router
When it comes to configuring a new Cisco router, much of the configuration depends on what type of router it is as well as the purpose it will serve. However, there are certain things you should configure on every new Cisco router. Hasn't there been a command that you wished Cisco would make standard on every router?
How To Download an Embedded Video From Any Website
The era of rule by video appears to be upon us. Online video content continues to increase at exponentially – the knowledge possessed by the human species expanding at such rates that human beings cannot even conceptualize it, much less understand it. There are websites for gaming videos, for adult entertainment, for movies and TV shows, and of course the granddaddy of them all, YouTube.
stop your cisco device intterupting you with logging synchronous
One annoying “feature” of Cisco devices is that they often output info when your typing into the console making you loose your place and unable to see what you are typing in. Router(config)#host m00nies-router m00nies-router(config)#^Z m00nies-router#sho *Aug 20 09:46:38.867: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console w in This behaviour can be change however by using the “logging synchronous” command on each of the management interfaces. m00nies-router#conf t m00nies-router(config)#line vty 0 15 m00nies-router(config-line)#logging synchronous m00nies-router(config-line)#line con 0 m00nies-router(config-line)#logging synchronous m00nies-router(config-line)#^Z m00nies-router#sho *Aug 20 09:53:20.279: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console m00nies-router#show int
Fabulous Code Chart (ALT and HTML) for Greek Letters & Symbols
This chart provides ALT codes which can be entered into a variety of PC programs when the character is not on the keyboard. It also contains ASCII codes, both HTML character references (decimals) and entity references (symbolic names) if available. The last column contains the character's Unicode value. Unicode is a worldwide standard, discussed here. ○ Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, meaning, at no additional cost to you, we may earn a small commission if you click through and make a purchase.
Not a 'math person'? You may be better at learning to code than you think
Want to learn to code? Put down the math book. Practice those communication skills instead. New research from the University of Washington finds that a natural aptitude for learning languages is a stronger predictor of learning to program than basic math knowledge, or numeracy. That's because writing code also involves learning a second language, an ability to learn that language's vocabulary and grammar, and how they work together to communicate ideas and intentions.
Download videos from dropbox. Online dropbox downloader.
To download video from dropbox, no special tech knowledge is required. The process starts with dropbox page link. Copy that link from the browser's address bar, then paste it into the white box above. And hit GO.
Securing Administrative Access to a Cisco Router
This chapter is from the book Configuring administrative access on the Cisco router is an important step toward network security. You can access all Cisco routers in various ways: ConsoleVTYAuxSNMPHTTP Connection Through the Console Port To protect administrative access to the routers, you must protect the console port via a password policy.