


NASA: Warp drive is 'plausible and worth further investigation' S1.E13 ...My Soul to Keep S1.E12 There's No More Room In Hell S1.E11 The Feast S1.E10 The Pain Connection S1.E9 Post-Apocalypse Now S1.E8 Two Graves S1.E7 Whistle Past the Graveyard S1.E6 We Need To Talk About Abigail S1.E5 Whatever Happened to Maggie Rennie S1.E4 The Exorcism of Marcus Moon S1.E3 The Curse of the Copper Head Road S1.E2 The Ghost in the Machine 10 Strange Things About The Universe Space The universe can be a very strange place. While groundbreaking ideas such as quantum theory, relativity and even the Earth going around the Sun might be commonly accepted now, science still continues to show that the universe contains things you might find it difficult to believe, and even more difficult to get your head around. Theoretically, the lowest temperature that can be achieved is absolute zero, exactly ? One of the properties of a negative-energy vacuum is that light actually travels faster in it than it does in a normal vacuum, something that may one day allow people to travel faster than the speed of light in a kind of negative-energy vacuum bubble. One prediction of Einstein’s theory of general relativity is that when a large object moves, it drags the space-time around it, causing nearby objects to be pulled along as well. Relativity of Simultaneity Since this extra dimension is so small, only tiny objects, such as particles, can move along it. Antimatter Retrocausality
Timeline Photos Why Nikola Tesla was the greatest geek who ever lived Additional notes from the author: If you want to learn more about Tesla, I highly recommend reading Tesla: Man Out of Time Also, this Badass of the week by Ben Thompson is what originally inspired me to write a comic about Tesla. Ben's also got a book out which is packed full of awesome. There's an old movie from the 80s on Netflix Instant Queue right now about Tesla: The Secret of Nikola Tesla. It's corny and full of bad acting, but it paints a fairly accurate depiction of his life. The drunk history of Tesla is quite awesome, too.
Alcubierre drive Two-dimensional visualization of the Alcubierre drive, showing the opposing regions of expanding and contracting spacetime that displace the central region. The Alcubierre drive or Alcubierre metric (referring to metric tensor) is a speculative idea based on a solution of Einstein's field equations in general relativity as proposed by theoretical physicist Miguel Alcubierre, by which a spacecraft could achieve faster-than-light travel if a configurable energy-density field lower than that of vacuum (i.e. negative mass) could be created. Rather than exceeding the speed of light within its local frame of reference, a spacecraft would traverse distances by contracting space in front of it and expanding space behind it, resulting in effective faster-than-light travel. History[edit] Alcubierre metric[edit] The Alcubierre metric defines the warp-drive spacetime. Mathematics of the Alcubierre drive[edit] where is a positive definite metric on each of the hypersurfaces. and with arbitrary parameters .
New evidence that plants get their energy using quantum entanglement The fact that biological systems can exploit quantum effects is quite astounding. No it is not, not even remotely.There is literally no possible way that photosynthesis could take place without involving quantum physics. This particular exploit is really neat, of course, but far too much as been made of how mystical or ungraspable quantum physics is. Basic chemistry is defined by quantum physics. Every interaction of two particles or two molecules is the result of the laws of quantum physics. The distinction being made is that toast-making was just as explicable with continuous waves of energy being absorbed by the bread but that no such classical interpretation is possible for these new photosynthesis observations. Right? Yeah, it's always easy to come in after someone's done the hard research and go "Oh, pff. Or, you can sit back and let people admire how wild our Universe is and just how little we know about it. well now why havent all the people working on this already aware of this?
Wormhole Construction: Proceed with Caution Ronnie Chen/Hampton University, from a ThinkQuest project Spaceships on Star Trek: Deep Space 9 regularly take a shortcut between distant parts of the Universe by traveling through a wormhole, a kind of spacetime tunnel. Although Einstein’s General Relativity theory allows wormholes to exist, physicists have been trying for decades to construct them mathematically without breaking any other laws of physics. Most researchers agree that wormholes require “exotic matter”–stuff that is repelled by gravity, rather than attracted–but some have claimed ways around that problem. According to Matt Visser of Washington University in St. On the other hand, no one knows if enough of this weird stuff can exist in one place at one time to create a decent-sized wormhole. Their approach was to rigorously define a wormhole “throat” (the narrowest point) and show that because light rays spread out as they emerge from it, there must be a kind of “antigravity”–the hallmark of exotic matter. References
Downloads & Badges - Brené Brown Posters The following 8×10 posters are available for free download. Just click on the thumbnail to download. To purchase the Kelly Rae Roberts special edition Parenting Manifesto (benefitting charity:water), click here. Discussion Guides The following discussion guides are available for free download. The Gifts of Imperfection Reader Worksheet and Book Club Guide The Gifts of Imperfection Family, Friends, and Parents Worksheet The Gifts of Imperfection Meaningful Work Worksheet The Hustle for Worthiness DVD Worksheet I Thought It Was Just Me Worksheet Badges Let Brené know you’ve linked to her!
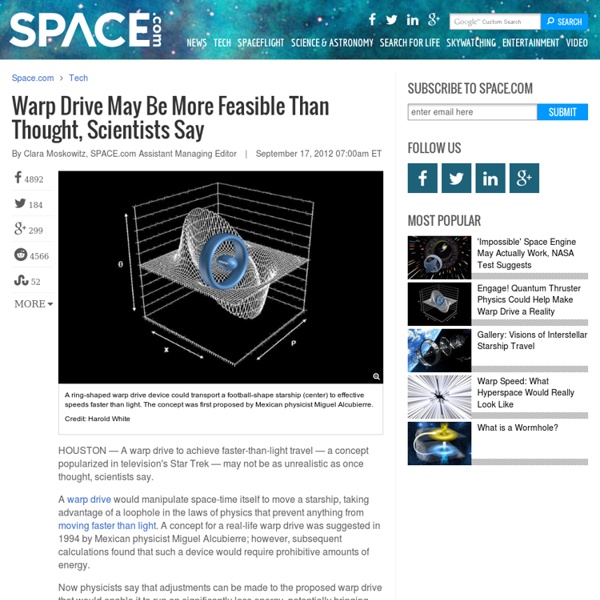
The Warp Drive Could Become Science Fact A warp drive to achieve faster-than-light travel -- a concept popularized in television's Star Trek -- may not be as unrealistic as once thought, scientists say. A warp drive would manipulate space-time itself to move a starship, taking advantage of a loophole in the laws of physics that prevent anything from moving faster than light. A concept for a real-life warp drive was suggested in 1994 by Mexican physicist Miguel Alcubierre, however subsequent calculations found that such a device would require prohibitive amounts of energy. Now physicists say that adjustments can be made to the proposed warp drive that would enable it to run on significantly less energy, potentially bringing the idea back from the realm of science fiction into science. "There is hope," Harold "Sonny" White of NASA's Johnson Space Center said Friday (Sept. 14) at the 100 Year Starship Symposium, a meeting to discuss the challenges of interstellar spaceflight. Warping Spacetime
Can we grow a stronger-than-steel 'wonder material' to save the world? It’s stiffer than Kevlar, thinner than paper, and in a few years, it may be mass-produced using only sunlight and water. Scientists in the US this week announced a new, and potentially groundbreaking method for producing nanocellulose — a so-called "wonder material" derived from tree fiber that could be used to create ultra-thin displays, lightweight body armor, and a wide range of other products. Their key ingredient? Algae. "one of the most important discoveries in plant biology" Dr. At the core of Brown's research is a family of bacteria that produce vinegar, Kombucha tea, and nata de coco. Brown's method, by contrast, is vastly more efficient and environmentally friendly, requiring only sunlight, water, and algae. Organic, self-sustaining factories These genetically-altered algae, known as cyanobacteria, are entirely self-sustaining. The team is currently working on synthesizing a more complete and stable form of the material, though their progress is already promising.
Facebook 47 Mind-Blowing Psychology-Proven Facts You Should Know About Yourself - StumbleUpon I’ve decided to start a series called 100 Things You Should Know about People. As in: 100 things you should know if you are going to design an effective and persuasive website, web application or software application. Or maybe just 100 things that everyone should know about humans! The order that I’ll present these 100 things is going to be pretty random. So the fact that this first one is first doesn’t mean that’s it’s the most important.. just that it came to mind first. Dr. <div class="slide-intro-bottom"><a href="