Deforestation
National Geographic: Deforestation
Modern-Day Plague Deforestation is clearing Earth's forests on a massive scale, often resulting in damage to the quality of the land. Forests still cover about 30 percent of the world’s land area, but swaths the size of Panama are lost each and every year. The world’s rain forests could completely vanish in a hundred years at the current rate of deforestation. Forests are cut down for many reasons, but most of them are related to money or to people’s need to provide for their families.The biggest driver of deforestation is agriculture. Logging operations, which provide the world’s wood and paper products, also cut countless trees each year. Not all deforestation is intentional. Deforestation has many negative effects on the environment. Deforestation also drives climate change. Removing trees deprives the forest of portions of its canopy, which blocks the sun’s rays during the day and holds in heat at night.
Deforestation
A deforested area Deforestation is when forests are lost and not replanted. Sometimes deforestation happens when people change the land into farms, ranches and cities. A lot of deforestation is from removal of all the trees from a forest for wood or fuel. Without the forest, the habitats of the animals are lost and many animals die. It also results in global warming (climate change). The opposite of deforestation is afforestation. Cause of deforestation[change | edit source] Deforestation is the removal of trees for requirements of growing population. Forests have the following functions:- regulation of the water cycleproduction of soilprovide habitat for animalsprovide most of our oxygenmaintain the oxygen and carbon dioxide balance in the atmosphereregulation of temperatureprevent soil erosion There are many reasons for deforestation like logging where people cut down trees for money because they have to feed their families Forests are often planted to protect against natural disasters.
Live Science: Deforestation
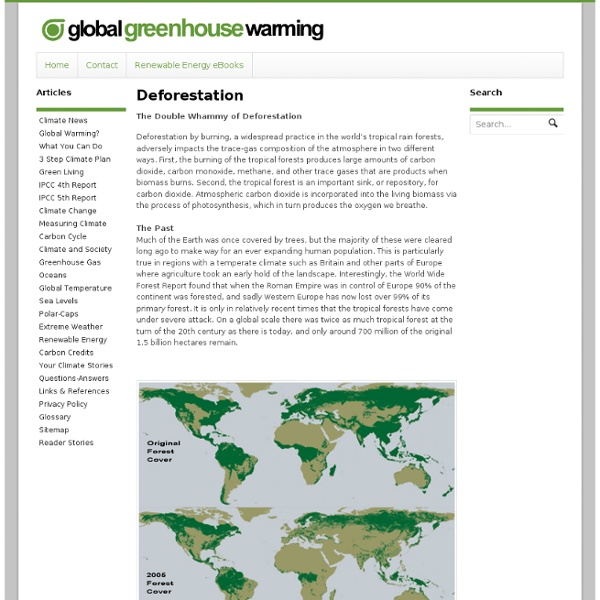
Deforestation is the permanent destruction of forests in order to make the land available for other uses. An estimated 18 million acres (7.3 million hectares) of forest, which is roughly the size of the country of Panama, are lost each year, according to the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Some other statistics: About half of the world's tropical forests have been cleared (FAO) Forests currently cover about 30 percent of the world’s land mass (National Geographic) Forest loss contributes between 6 percent and 12 percent of annual global carbon dioxide emissions (Nature Geoscience) About 36 football fields worth of trees lost every minute (World Wildlife Fund (WWF)) Deforestation occurs around the world, though tropical rainforests are particularly targeted. NASA predicts that if current deforestation levels proceed, the world's rainforests may be completely in as little as 100 years. Error loading player: No playable sources found Weather vs.
WWF: Deforestation Main Page
Forests cover 31% of the land area on our planet. They produce vital oxygen and provide homes for people and wildlife. Many of the world’s most threatened and endangered animals live in forests, and 1.6 billion people rely on benefits forests offer, including food, fresh water, clothing, traditional medicine and shelter. But forests around the world are under threat from deforestation, jeopardizing these benefits. Forests play a critical role in mitigating climate change because they act as a carbon sink—soaking up carbon dioxide that would otherwise be free in the atmosphere and contribute to ongoing changes in climate patterns. Deforestation is a particular concern in tropical rainforests because these forests are home to much of the world’s biodiversity. WWF has been working to protect forests for more than 50 years.
Related:
Related:



