Depth = 3rd Dimension
Three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system with the x-axis pointing towards the observer(See diagram description for needed correction.) In physics and mathematics, a sequence of n numbers can be understood as a location in n-dimensional space. When n = 3, the set of all such locations is called 3-dimensional Euclidean space. It is commonly represented by the symbol . This space is only one example of a great variety of spaces in three dimensions called 3-manifolds. Details[edit] Other popular methods of describing the location of a point in three-dimensional space include cylindrical coordinates and spherical coordinates, though there is an infinite number of possible methods. Another mathematical way of viewing three-dimensional space is found in linear algebra, where the idea of independence is crucial. Three-dimensional space has a number of properties that distinguish it from spaces of other dimension numbers. With the space , the topologists locally model all other 3-manifolds.
How an Aurora Borealis works
Networks and dimension
Tesseract
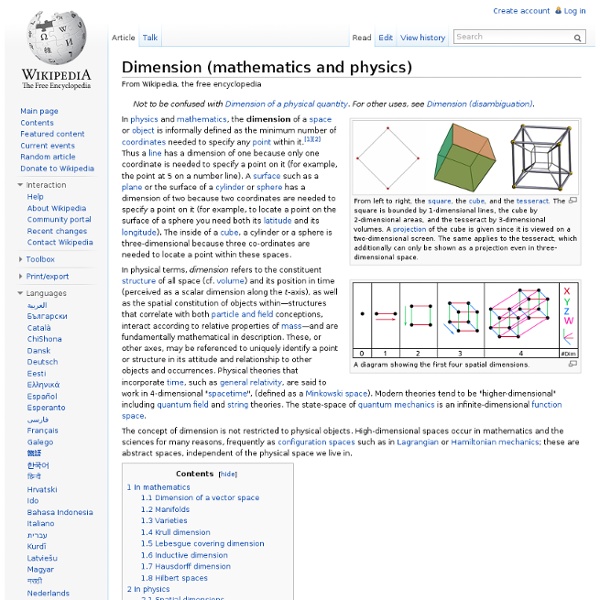
A generalization of the cube to dimensions greater than three is called a "hypercube", "n-cube" or "measure polytope".[1] The tesseract is the four-dimensional hypercube, or 4-cube. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the word tesseract was coined and first used in 1888 by Charles Howard Hinton in his book A New Era of Thought, from the Greek τέσσερεις ακτίνες ("four rays"), referring to the four lines from each vertex to other vertices.[2] In this publication, as well as some of Hinton's later work, the word was occasionally spelled "tessaract." Some people[citation needed] have called the same figure a tetracube, and also simply a hypercube (although a tetracube can also mean a polycube made of four cubes, and the term hypercube is also used with dimensions greater than 4). Geometry[edit] Since each vertex of a tesseract is adjacent to four edges, the vertex figure of the tesseract is a regular tetrahedron. A tesseract is bounded by eight hyperplanes (xi = ±1). See also[edit]
Length = 2nd Dimension
Bi-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system In physics, our bi-dimensional space is viewed as a planar representation of the space in which we move, described as bi-dimensional space or two-dimensional space. History of two-dimensional space[edit] Euclid's Elements dealt almost exclusively with two-dimensional geometry, developing such notions as similarity of shapes, the Pythagorean theorem (Proposition 47), equality of angles and areas, parallelism, the sum of the angles in a triangle, and the three cases in which triangles are "equal" (have the same area), among many other topics. The idea of this system was developed in 1637 in writings by Descartes and independently by Pierre de Fermat, although Fermat also worked in three dimensions, and did not publish the discovery.[1] Both authors used a single axis in their treatments and have a variable length measured in reference to this axis. Two-dimensional geometry[edit] Polytopes[edit] Convex[edit] Degenerate (spherical)[edit] Non-convex[edit]
5 Really Weird Things About Water
Water, good ol' H2O, seems like a pretty simple substance to you and me. But in reality, water - the foundation of life and most common of liquid - is really weird and scientists actually don't completely understand how water works. Here are 5 really weird things about water: 1. Take two pails of water; fill one with hot water and the other one with cold water, and put them in the freezer. In 1963, a Tanzanian high-school student named Erasto B. Thankfully, Mpemba didn't back down - he convinced a physics professor to conduct an experiment which eventually confirmed his observations: in certain conditions, hot water indeed freezes before cold water*. Actually, Mpemba was in good company. But how do scientists explain this strange phenomenon? 2. Everybody knows that when you cool water to 0 °C (32 °F) it forms ice ... except that in some cases it doesn't! Scientist know a lot about supercooling: it turns out that ice crystals need nucleation points to start forming. 3. 4. 5. [YouTube clip]
Fourth dimension in literature
The idea of a fourth dimension has been a factor in the evolution of modern art, but use of concepts relating to higher dimensions has been little discussed by academics in the literary world.[1] From the late 1800s onwards, many writers began to make use of possibilities opened up by the exploration of such concepts as hypercubes and non-Euclidian geometry. While many writers took the fourth dimension to be one of time (as it is commonly considered today), others preferred to think of it in spatial terms, and some associated the new mathematics with wider changes in modern culture. Early influence[edit] Theoretical physicist James Clerk Maxwell is best known for his work in formulating the equations of electromagnetism. Since all the tools for my untyingIn four-dimensioned space are lying,Where playful fancy interspersesWhole avenues of universes..Excerpt from Maxwell's Paradoxical Ode of 1878[4] "..shall we stay our upward course? H.G. Other works[edit] References[edit]
Golden spiral
Approximate and true golden spirals: the green spiral is made from quarter-circles tangent to the interior of each square, while the red spiral is a golden spiral, a special type of logarithmic spiral. Overlapping portions appear yellow. The length of the side of a larger square to the next smaller square is in the golden ratio. In geometry, a golden spiral is a logarithmic spiral whose growth factor is φ, the golden ratio.[1] That is, a golden spiral gets wider (or further from its origin) by a factor of φ for every quarter turn it makes. Formula[edit] The polar equation for a golden spiral is the same as for other logarithmic spirals, but with a special value of the growth factor b:[2] or with e being the base of Natural Logarithms, a being an arbitrary positive real constant, and b such that when θ is a right angle (a quarter turn in either direction): Therefore, b is given by The numerical value of b depends on whether the right angle is measured as 90 degrees or as for θ in degrees;
Dimension = 1st
One-dimensional geometry[edit] Polytopes[edit] The only regular polytope in one dimension is the line segment, with the Schläfli symbol { }. Hypersphere[edit] where is the radius. Coordinate systems in one-dimensional space[edit] The most popular coordinate systems are the number line and the angle.