


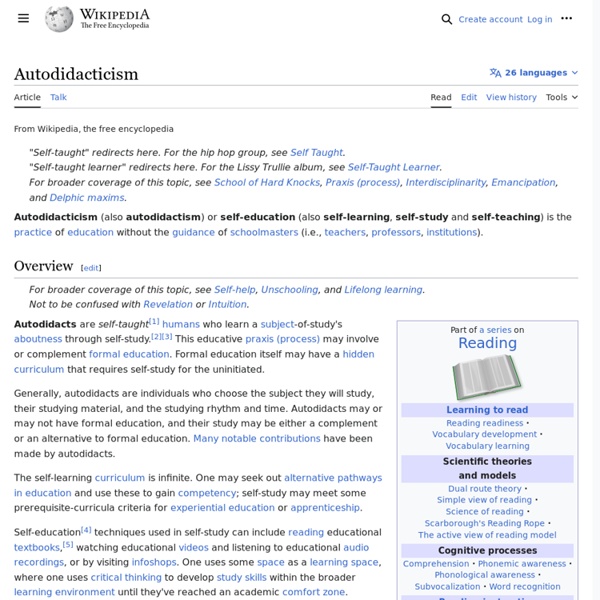
Bloom's Taxonomy Bloom's wheel, according to the Bloom's verbs and matching assessment types. The verbs are intended to be feasible and measurable. Bloom's taxonomy is a classification of learning objectives within education. It is named for Benjamin Bloom, who chaired the committee of educators that devised the taxonomy, and who also edited the first volume of the standard text, Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals. Bloom's taxonomy refers to a classification of the different objectives that educators set for students (learning objectives). Bloom's taxonomy is considered to be a foundational and essential element within the education community. History[edit] Although named after Bloom, the publication of Taxonomy of Educational Objectives followed a series of conferences from 1949 to 1953, which were designed to improve communication between educators on the design of curricula and examinations. Cognitive[edit] Knowledge[edit] Comprehension[edit] Application[edit]
College - The Center for Innovation and Learning The Center for Innovation and Learning aims to design, develop and integrate resources that enrich learning and teaching at Wofford, and to provide a locus for conversations, both within the Wofford community and with other institutions, about excellence and innovation in a residential liberal arts education. Purposeful integration of research, curricular innovation, and support in The Center for Innovation and Learning is a step toward the academic synthesis a 21st century liberal arts college can offer both its own community members and society at large. Our mission is four-fold: to support innovation in teaching, provide an environment for the support of teaching and learning, to support on-campus writing initiatives in curricular and co-curricular programming, and to assess for the effectiveness of innovations undertaken in the service of student learning.
Village files Military intelligence documents on every Arab village in Mandatory Palestine Village files were military intelligence documents based on a card index system, with detailed data on every Arab village in Mandatory Palestine. Gathered by the SHAI, they were the basis of Haganah and Palmah operations during the 1940s.[1] The files answered the need of combat intelligence for the number of men in the village, the number of weapons, the topography and so on, dealt with the research of traces of ancient Jews in the villages, and with the possibility of buying land from the villagers and settling it.[2] The suggestion for these files came from Luria Ben-Zion, an historian from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, who wrote in 1940 to the Jewish National Fund (JNF) that "This would greatly help the redemption of the land". Yossef Weitz, the head of the JNF settlement department immediately suggested that they be turned into a "national project".
Bloom’s Taxonomy: The 21st Century Version So much have been written about Bloom’s taxonomy; one click in a search engine will flood your page with hundreds of articles all of which revolve around this taxonomy. Only few are those who have tried to customize it to fit in the 21st century educational paradigm. As a fan of Bloom’s pedagogy and being a classroom practitioner, I always look for new ways to improve my learning and teaching, and honestly speaking , if you are a teacher/ educator and still do not understand Bloom’s taxonomy then you are missing out on a great educational resource. The following article is a summary and a fruit of my long painstaking research in the field of Bloom’s taxonomy. The purpose is to help teachers grow professionally and provide them with a solid informational background on how to better understand and apply Bloom’s taxonomy in classrooms in the light of the new technological advances and innovations. 1 – The cognitive : The intellectual or knowledge based domain consisted of 6 levels .
Technology, Innovation, Education TIE prepares leaders in innovating education through technology – including media and software design, policy, and analysis, administration, research and evaluation, and teaching with new technologies. Some distinctive features of studying educational technology at HGSE include: an approach that puts learning and teaching at the centera faculty composed of internationally recognized researchers and leading professionals in design and evaluationa curriculum that bridges design, implementation, and researcha diverse community of learners, made up of students of all ages, from all parts of the globe TIE Seminar: Bring Ed. Bror Saxberg, Chief Learning Officer, Kaplan, February, 2013 TIE Students Tell the Story Video Produced by Erin Sisk, TIE ‘12
Global surveillance Mass surveillance across national borders Global mass surveillance can be defined as the mass surveillance of entire populations across national borders.[1] Its roots can be traced back to the middle of the 20th century when the UKUSA Agreement was jointly enacted by the United Kingdom and the United States, which later expanded to Canada, Australia, and New Zealand to create the present Five Eyes alliance.[5] The alliance developed cooperation arrangements with several "third-party" nations. Eventually, this resulted in the establishment of a global surveillance network, code-named "ECHELON" (1971).[6][7] Historical background [edit] The origins of global surveillance can be traced back to the late 1940s after the UKUSA Agreement was collaboratively enacted by the United Kingdom and the United States, which eventually culminated in the creation of the global surveillance network code-named "ECHELON" in 1971.[6][7] Today, this global surveillance system continues to grow. Targets and methods
Integrating Adaptive Educational Content into Different Courses and Curricula Integrating Adaptive Educational Content into Different Courses and Curricula Charalampos Karagiannidis Informatics and Telematics Institute (I.T.I.) Centre for Research and Technology – Hellas (CE.R.T.H.) 1, Kyvernidou Str., Thessaloniki, GR-54639 Greece Tel.: +30 31 868324, 868785, 868580, internal 105 Fax: +30 31 868324, 868785, 868580, internal 213 karagian@iti.gr Demetrios Sampson Informatics and Telematics Institute (I.T.I.) Centre for Research and Technology – Hellas (CE.R.T.H.) 1, Kyvernidou Str., Thessaloniki, GR-54639 Greece Tel.: +30-31-868324, 868785, 868580, internal 105 Fax: +30-31-868324, 868785, 868580, internal 213 sampson@iti.gr Fabrizio Cardinali GIUNTI Interactive Labs S.r.l. 1. The rapid evolution of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) and the emergence of the Information Society create numerous new opportunities for the improvement of the quality of education. 2. 3. Step 1 Definition of Concept Ontology Figure 1. 4.
Technology and Young Children Key Messages When used intentionally and appropriately, technology and interactive media are effective tools to support learning and development. Intentional use requires early childhood teachers and administrators to have information and resources regarding the nature of these tools and the implications of their use with children. Limitations on the use of technology and media are important. Special considerations must be given to the use of technology with infants and toddlers. Attention to digital citizenship and equitable access is essential. View Key Messages Summary (PDF) Examples of Effective Practice View Examples of Effective Practice (PDF) Technology That Supports Early Learning Pre-recorded Webcast: Technology and Interactive Media as Tools in Early Childhood Programs This prerecorded 21-minute webcast addresses key messages in the position statement. View the webcast
Trout memo From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia 1939 document The Trout memo, written in 1939, is a document comparing the deception of an enemy in wartime with fly fishing.[1] Issued under the name of Admiral John Godfrey, Britain's director of naval intelligence, according to the historian Ben Macintyre it bore the hallmarks of having been written by Godfrey's assistant Ian Fleming, who later created the James Bond series of spy novels.[2] The memo reads, in part: "The Trout Fisher casts patiently all day. He frequently changes his venue and his lures.
thinkerskeys.wikispaces Tony Ryan's Thinkers Keys Classroom Ideas:There are 20 different ‘Thinking Keys’ each designed to unlock different parts of the thinking process.The use of the keys helps to develop flexible problem solving and thinking habits.The thinking keys provide a flexible and dynamic way to engage students in further learning. They are a great way to do informal assessment during the unit for measuring student understanding.The students really enjoy the range of activities that the keys enable them to choose from and subsequently produce interesting and thoughtful work.There are many ways that the thinkers' keys can be integrated into the classroom to enhance the thinking of the students: Warm up Activities - Give the class one of the keys to work on for 5 to 10 minutes to get them thinking creatively before writing or before/after the bell. For example you could use the:1. How have other teachers used thinkers keys:
THE NEW SOCIAL WORKER Online - The Social Work Careers Magazine for Students and Recent Graduates - Articles, Jobs, & More - Subscribe to The New Social Worker Publications Use the form above to sign up for the following FREE publications: 1) The New Social Worker Electronic Subscription THE NEW SOCIAL WORKER magazine is now available FREE in electronic (PDF) format. Published quarterly, in January, April, July, and October. Subscribe to receive an e-mail notification and Table of Contents each time a new issue is published and available for download. The magazine is no longer available for subscription in print format. 2) Social Work E-News Subscription Subscribe to our FREE Social Work E-News, a monthly e-mail newsletter that will bring social work news, jobs, and other related items to your inbox. Read past e-newsletters 3) Special Announcements for Social Work We do not give, rent, or sell your name to anyone else. We will use your e-mail address only to send the above notifications or related announcements.
Counterfeit Monkey 2012 video game Counterfeit Monkey is a 2012 interactive fiction espionage game by Emily Short. The games is set in Anglophone Atlantis, the world's greatest center for linguistic manipulation, and where the danger of the shifting reality has resulted in a police state run by language pedants trying to restrict language in order to keep an orderly reality.[1]: 13m The state had become independent in 1822 by shooting a depluralizing cannon at attacking ships to make it one ship, and then shot that ship.[1]: 14m9s Short identified three categories of puzzles:[1]: 31m39s Knowing which original object to change and the type of transformation (smaller or bigger) but not the name of the target objectKnowing the target object but not the original objectKnowing the target object's intended use (for example "a thing that makes noise", "a thing that is blue") Transformations can be completed by several steps, removing one letter at a time but only as long as each step results in an actual word. [edit]