


RPi iSCSI Initiator Back to RPi Guides. Raspberry Pi iSCSI Initiator Setup This guide is split into two parts, part 1 deals with rebuilding the standard Raspbian/Debian image to include iscsi support so that the pi can access an iscsi target (and function as a target itself if needed, but this guide deals with setting up as an initiator), part 2 then extends on this to enable booting from an iscsi root. For the sake of simplicity we will be performing on-device kernel recompiles, these take 4-6 hours, you can simply perform a cross-compile elsewhere to speed this up if you prefer. This guide assumes a number of things: At least a basic knowledge of iscsi, and that you already have a suitable target setup on your SAN/NAS/wherever. First up, we need to get the iscsi initiator service installed, along with git, gcc, make, ncurses-devel and python, which are needed for an on-device kernel recompile: apt-get install open-iscsi git gcc make python libncurses5-dev mkdir /root/raspberrypi cd /root/raspberrypi make reboot
Raspberry Pi – Comment mettre à jour le firmware ? Quand on est l'heureux propriétaire d'un Raspberry Pi, on l'aime, on le bichonne et surtout on met à jour son firmware ! Mais comment faire ? Et bien c'est simple... Déjà pour connaitre votre version actuelle du firmware, entrez la commande suivante sur votre Raspberry Pi : /opt/vc/bin/vcgencmd version Maintenant, pour la mise à jour, Liam McLoughlin, alias Hexxeh a développé et mis en ligne sur son Github, un script baptisé rpi-update qui permet de faire cela très facilement. Edit : Notez que cette mise à jour est à éviter sur certaines distribs comme OpenElec. Avant toute chose, on va installer ce qui est nécessaire pour accéder à Github (car la commande Git est appelée dans le script) : sudo apt-get install ca-certificates git-core binutils Ensuite, on récupérer le script sudo wget On le copie dans le répertoire /usr/local/bin sudo cp rpi-update /usr/local/bin/rpi-update Puis on le rend exécutable sudo rpi-update Et voilà ! Source
Framboise 314, le Raspberry Pi à la sauce française…. | Le Raspberry Pi, un ordinateur à 35€ ? Je demande à voir ! Using NFS to provide extra disk to a Raspberry PI | Peter Mount's Blog As the Raspberry PI uses an SD Card for it’s boot device there are times when you need either more space than is available on that device or a device that’s faster – writing to flash is slow and flash cards do have a limited number of writes that can be made to them. Now there’s several ways to accomplish this: Use an external USB drive (the common route)Use a network shared drive Using a USB drive is simple and is the faster option but it means it’s dedicated to the PI whilst it’s in use, hence this article on using a network drive – in this instance a directory on another Linux box in the network. Also having it shared on the network means that multiple machines could use it at the same time. For this article I’m going to show how to setup a directory on a server and the raspberry pi as the client. tabitha – Ubuntu server that will host the directorylindesfarne – Raspberry PI client running the stock Debian SD Imagekell – second Raspberry PI client also running Debian. Right lets test it.
Installing Raspbian on the Raspberry Pi & using SSH and VNC to remotely connect to the Raspberry Pi | Hertaville UPDATED: July 18th 2013 This blog entry will describe: The installation of the Raspbian Wheezy Linux Distribution on an SD card.Powering up the Raspberry Pi (RPi) board and connecting it to the networkRemotely Accessing the RPi board via SSHInitial Configuration of the Rasbpian OS/ RPi boardRemotely Accessing the RPi’s graphical desktop environment (LXDE) via VNC For starters you’ll need a microUSB terminated AC adapter, an Ethernet cable & an SD card. Installing Raspbian on your SD Card Plug in the SD card into the PC then run the following command in a terminal window: “sudo fdisk -l“. Figure 1. From the output in Figure 1 you can see that the operating system detects two drives, “/dev/sda” is a 64.0GB SSD drive and the “/dev/sdb/” is our 8.0GB SD card.The next step is to download the latest Raspbian Wheezy Linux distribution image from this page. Putting the RPi with Raspbian OS onto the network We will connect to the RPi over the network. Figure 2 Edit Connections Figure 3 Figure 4.
10 Coming to Raspberry Pi 2 This blog was written by Kevin Dallas, General Manager, Windows IoT Group. Today the Raspberry Pi Foundation announced the retail availability of their new board, the Raspberry Pi 2. We’re excited to join the Foundation in also announcing that Windows 10 will support Raspberry Pi 2, which will be free for the Maker community through the Windows Developer Program for IoT later this year. Recently Terry Myerson took the opportunity to share more details about Windows 10, which will usher in the new generation of Windows. We see the Maker community as an amazing source of innovation for smart, connected devices that represent the very foundation of the next wave of computing, and we’re excited to be a part of this community. Raspberry Pi has quickly become one of the Maker community’s favorite platforms because their highly-capable, low-cost boards and compute modules enable developers to bring their vison to life. I look forward to sharing more details with you soon.
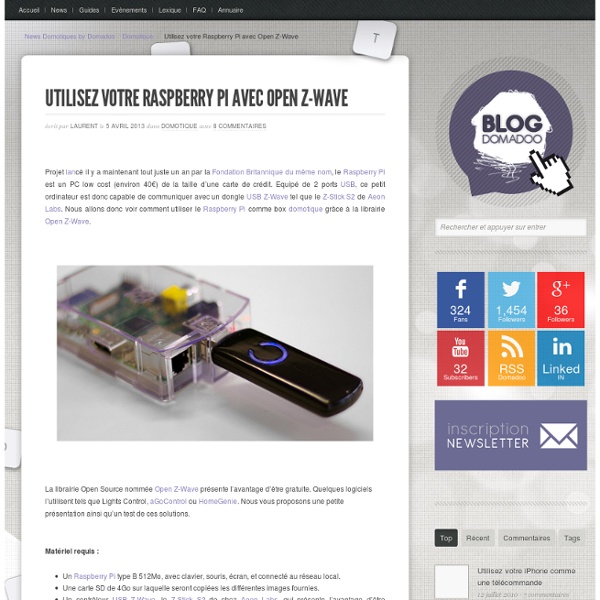
Raspberry Pi - Partager des… - Raspberry Pi :… - Raspberry Pi :… - Raspberry Pi :… - Réception du… - KeepLoGeek Raspberry pi : Créer une passerelle homecinema multifonctions J’aime bien quand tout fonctionne correctement et que c’est automatisé ! Mon problème: j’en ai marre de manipuler ma télécommande de la TV, du vidéoprojecteur et surtout j’ai peur qu’une coupure de courant fasse éclater ma lampe de vidéoprojecteur. Problèmes => solutions : un raspberry pi avec sa carte sd, pour interfacer le tout et piloter par une interface web, (malheureusement pour moi 56 € livré avec boitier avant que Mickael ne propose à la vente un raspberry)l’alimentation du raspberry, (7.90 €)un dispositif USB/infrarouge émetteur et récepteur (transceiver en anglais) (38€ livré),un contrôleur USB/rs232 et son câble null-modem (11.95 €),un onduleur avec une connexion USB (environ 70 €)le tout connecté sur hub usb 7 ports (15€). Ce qui nous fait un total de: 198.95 € donc environ 200 € Cela coûte mais vu le prix de l’ampoule d’un vidéoprojecteur et les services rendus, je trouve que c’est très bien. Je ne vais pas reprendre l’installation du Raspberry, google est votre ami ! #! #! #!
Raspberry Pi VPN Server - Brad Wells You have a raspberry pi— a low-power always-on computer. Why not use it as a VPN server for tunneling your internet through when travelling? This could, for example, help you ensure a secure browsing experience when you’re on a sketchy public wifi network. Or perhaps you’re considering moving to another country for a couple months. Don’t have a Raspberry Pi? Contents VPN Server Setup (Raspberry Pi) First, you’ll need a kernel with MPPE support. sudo modprobe ppp-compress-18 If this works without any errors, your kernel should do the job. sudo apt-get install pptpd Next, edit ‘/etc/pptpd.conf’ If you have started an X session, you can use a graphical text editor. leafpad /etc/pptpd.conf If you prefer working in the terminal use the following. sudo vi /etc/pptpd.conf At the end of the file, add (or uncomment if it already exists) the following lines localip 192.168.0.1remoteip 192.168.1.234-238,192.168.1.245 Be sure to replace this information with what you actually need. sudo sysctl -p
My Raspberry Pi project Raspberry Pi Tutorial – Connect to WiFi or Create An Encrypted DHCP Enabled Ad-hoc Network as Fallback | Lasse Christiansen Development In this post I describe how I have configured my Raspberry Pi (RPi) to first attempt to connect to WiFi and if that fails, create and use an ad-hoc network as fallback (in this way I can always reach the RPi via SSH). The blog post is based on the following “How To” from the Raspberry Pi forum: – however, I have introduced a level of more detail and a couple of modifications in order to get faster boot time and support for multiple wireless networks (see my previous RPi blogt post suvery for details on which parts of that “How To” I think are good as well as which I think can be improved). Hardware The WiFi adapter I have used for this tutorial is the Edimax EW-7811Un (more details here) which seems to be one of the more popular WiFi adapters for the RPi (at least based on the amount of forum posts where it appears). Software This tutorial has been tested with success on: 2012-09-18-wheezy-raspbian2012-10-28-wheezy-raspbian
PiTFT un écran tactile 2,8 pouces pour le Raspberry Pi chez Adafruit Adafruit propose un écran tactile de 2,8 pouces de diagonale (7,1 cm) : Oooh n’est-ce pas le plus mignon petit écran pour le Raspberry Pi ? Il dispose d’un écran de 2,8″, une définition de 320×240 pixels avec une définition de couleur sur 16 bits et il est équipé d’un film tactile résistif. La carte utilise utilise l’interface SPI à grande vitesse du Raspberry Pi et vous pouvez utiliser le mini-écran comme une console, un port X window, afficher des images ou de la vidéo, etc… L’écran utilise les broches SPI ( SCK, MOSI, MISO, CE0, CE1) ainsi que GPIO25 et GPIO24. Tous les autres broches GPIO sont inutilisés. Commutateur mince pour écran tactile Cet écran est livré sous forme de mini-kit, avec un connecteur femelle extra-haut 2×13 broches (pour connecter l’écran au Raspberry Pi) et connecteur mâle 2×13 broches qui peut être utilisé pour connecter un câble en nappe. Les photos montrent également les boutons tactiles minces installées. Bientôt en ligne !
raspbian - Where are the WiFi config settings stored? - Raspberry Pi Beta - Stack Exchange If you are talking about NetworkManager settings, they are in: /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections If you do a ls -l you will see all your wireless networks there, one file per network. If you want to delete a connection, you simply need to delete the corresponding file. If you give a sudo cat YourNetworkName.conf you will see something like this: [connection] id=YourNetworkName uuid=929ceffc-8191-4dea-9a61-b4b174b9c910 type=802-11-wireless timestamp=1218126248 [802-11-wireless] ssid=YourNetworkName mode=infrastructure mac-address=00:28:F7:21:B1:19 security=802-11-wireless-security [802-11-wireless-security] key-mgmt=wpa-psk psk=yourpasswordgoeshere [ipv4] method=manual dns=192.168.10.1;8.8.8.8; addresses1=192.168.10.100;24;192.168.10.1; [ipv6] method=auto Everything is easily editable, provided that you know what these parameters mean. For what concerns your last question: Is there a better way to config WiFi on the Raspberry Pi than this program?
Présentation de ma Raspberry PI Si vous êtes un minimum technophile, vous avez forcement entendu parler de ce mini ordinateur tout intégré appelé Raspberry PI. Le Raspberry Pi est un ordinateur à base de processeur ARM conçu par David Braben (concepteur de jeux vidéos), Eben Upton et d’autres chercheurs de l’université de Cambridge en Angleterre. L’idée de base était de pouvoir faire un ordinateur très bon marché pour que n’importe quel étudiant puisse découvrir la programmation à moindre coût. Plusieurs distributions linux ont officiellement été créées par l’équipe Raspberry PI, comme par exemple la Debian Squeeze ce qui permet automatiquement d’avoir accès à tous les packages logiciels disponibles pour cette version Linux ARM. Pour la distribution, et la promotion de l’informatique accessible à tous, David Braben et ses partenaires ont créé une fondation caritative nommée « Raspberry PI Fundation ». Après cette petite introduction sur la présentation du concept, passons au produit lui même.