


Phillip Martin's You Be the Judge of Hammurabi's Code Hammurabi, the Priest King Hammurabi (ca. 1792 - 1750 BC) united all of Mesopotamia under his forty-three year reign of Babylon. Although Hammurabi's Code is not the first code of laws (the first records date four centuries earlier), it is the best preserved legal document reflecting the social structure of Babylon during Hammurabi's rule. About the Code Two hundred eighty-two laws, concerning a wide variety of abuses, justify Hammurabi's claim of having acted "like a real father to his people . . . [who] has established prosperity . . . and (gave) good government to the land." See for Yourself The laws were discovered in 1901 on a stela now in the Louvre Museum of Paris, France. What Other Have to Say Every now and then, I hear from people who enjoy the site.
LES CARTES ANTIQUES En 1929, lors de la réfection du musée du palais Topkapi Sarayi d'Istanbul, le directeur des musées nationaux turcs, M. Halil Edem mit la main sur la fameuse carte en peau de gazelle de Piri Reis, peinte en 1513. Cette carte représente l'Océan Atlantique avec une partie des côtes américaines, africaines et de l'Antarctique. Carte de Pris Reis. Ce que Piri Reis a écrit sur sa carte, en notes et dans son "Bahriye" : "Personne n'a au temps actuel une carte comme celle-là ". Il dit avoir compilé sa carte à partir de vingt autres provenant de la Grande Bibliothèque d'Alexandrie et datant au moins du IVe siècle av. Au premier coup d'oeil cette carte peut paraître inexacte, si l'on est habitué aux cartes Mercator, mais pas si l'on est familier des projections stéréographiques polaires ( plus précisément c'est une projection cordiforme ). La carte de Piri Reis a fait l'objet de nombreuses études par : L'ingénieur américain A. M. Le professeur D. Le professeur C. Carte de Ptolémée. Carte de Zeno
The Seven Wonders - Hanging Gardens of Babylon Some stories indicate the Hanging Gardens towered hundreds of feet into the air, but archaeological explorations indicate a more modest, but still impressive, height. (Copyright Lee Krystek, 1998) The city of Babylon, under King Nebuchadnezzar II, must have been a wonder to the ancient traveler's eyes. Herodotus claimed the outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high. While archaeological excavations have disputed some of Herodotus's claims (the outer walls seem to be only 10 miles long and not nearly as high) his narrative does give us a sense of how awesome the features of the city appeared to those ancients that visited it. Gift for A Homesick Wife Accounts indicate that the garden was built by King Nebuchadnezzar, who ruled the city for 43 years starting in 605 BC (There is an alternative story that the gardens were built by the Assyrian Queen Semiramis during her five year reign starting in 810 BC). The Water Problem Garden Construction Archaeological Search
A LA RECHERCHE DE LA LEMURIE - Guillaume Delaage, Esotérisme, hermétisme, Civilisations disparues, origines secrètes, mystère, énigmes, occulte, Thot, Hermès, Magie, Théurgie, Atlantide, Lémurie, Bouddha, évolution, Egypte, Eveil, Veuillez trouver tous les articles de Guillaume Delaage sur son nouveau site : Si l’Atlantide est un continent mystérieux qui enflamme l’imagination, la Lémurie ou continent de Mû – bien que moins connu – n’en est pas moins une énigme pour les historiens et les chercheurs. Mythe pour certains, fable pour d’autres, ce continent lointain situé hypothétiquement au cœur de l’océan Pacifique n’a pas fini d’exciter la curiosité des investigateurs en quête de mystère. Toutefois, si l’on parvient à rassembler quelques éléments épars sur l’Atlantide, la Lémurie garde le silence sur son origine si bien que las de parcourir de fausses pistes et devant le manque d’éléments scientifiques beaucoup ont préféré ranger le continent de Mû dans les classeurs des mondes imaginaires. Mais peut-on se contenter de cette hypothèse ? Bien sûr le manque d’informations et de pistes n’aide pas l’édification d’une théorie sérieuse. A la lumière de la Tradition Que dit la Tradition secrète au sujet de Mû ?
Index Collapse: Mesopotamia Mesopotamia was known as the land between two rivers, the Tigris to the north and the Euphrates to the south. Rains were seasonal in this area, which meant that the land flooded in the winter and spring and water was scarce at other times. Farming in the region depended on irrigation from the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. In ancient times, many resources in Mesopotamia were scarce or absent, which stimulated trade within the region and beyond. Mashkan-shapir was a typical Mesopotamian city, located about 20 miles from the Tigris River and connected to the river by a network of canals. Poisoned fields: A contributor to collapse Along with factors such as war and changes in the environment, scientists now believe irrigation techniques played an important role in Mashkan-shapir's collapse. In Mesopotamia, irrigation was essential for crop production. Could this happen today? Modern methods don't seem to be helping the San Joaquin Valley avoid this fate.
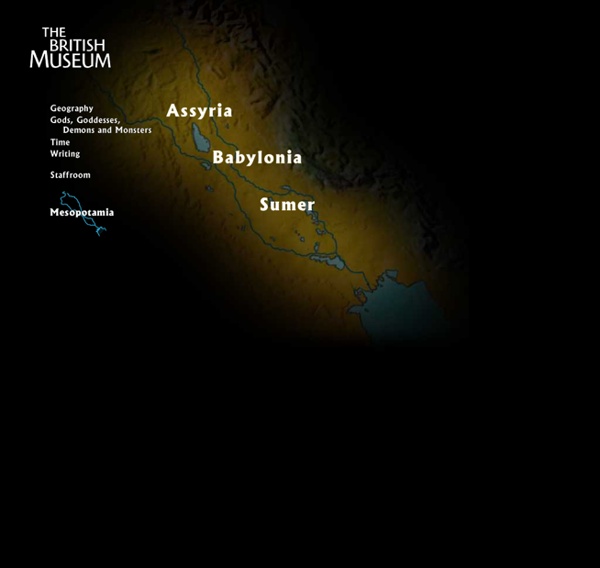
Highlights from the Collection: Mesopotamia | The Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago Mesopotamia - the land between the rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates - is an ancient Greek term used by archaeologists to refer to the area now roughly equivalent to the modern country of Iraq. The Mesopotamian collection of the Oriental Institute Museum was acquired almost exclusively through archaeological excavations. The first of these - the University of Chicago Oriental Exploration Fund's expedition to Bismaya (ancient Adab) - worked in Iraq from 1903-1905. During the 1930's the Babylonian Section of the Iraq Expedition excavated four sites on the lower Diyala River, and today the Nippur Expedition is continuing its work, begun in 1948, at the holy city of Nippur. The material that has been brought back as a result of divisions of finds from these expeditions forms one of the major world collections, covering in depth the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia. Foundation Figurine of King Ur-Nammu Striding Lion Four-Lugged Vessel Female Figurine Cup Supported by Hero and Animals
Daily Life in Ancient Civilizations for Kids Ancient Sumer, Babylon & Assyria (Mesopotamia) - What do a sailboat and a wheel have in common? They were both invented by the ancient Sumerians. Find out what happened to kids in school who disobeyed their teacher! Meet the first superhero - King Gilgamesh. Come meet the people who lived 5000 years ago in the land between two rivers. Ancient Egypt - Do you know what the ancient Egyptians believed would cure a toothache? Ancient Greece - How would you have behaved if you had lived in ancient Sparta? Ancient Rome - If you had lived in ancient times, would you have chosen to become a Roman citizen? Ancient China - Learn about Taoism with Winnie-the-Pooh! Ancient India - What did the ancient Indians wear? Ancient & Medieval Africa - Explore daily life in five huge trading kingdoms - The Kingdom of Ghana, Mali, Songhay, Benin, and Kush. Ancient Mongols - The ancient Mongols invented the ger - but what is a ger? The Vikings - The Vikings were a smart, creative, artistic, democratic people.
Gallery: Archaeological mysteries hidden in satellite images Archaeologists have many tools at their disposal: shovels, trowels, satellites. If you are scratching your head at that final entry, check out how TED Prize winner Sarah Parcak uses satellite imagery to locate long-lost ancient sites, and to solve some of archaeology’s most enduring mysteries. The mystery: What happened to Itj-tawy, the ancient capital of Egypt? Itj-tawy, once located on the bank of the Nile, was Egypt’s capital for about 350 years during the period known as the Middle Kingdom. But sometime after 1785 BC, when the capital moved to Thebes, Itj-tawy disappeared. “Egyptologists knew the city had to be somewhere near the pyramids of the two kings who built it, but that only narrowed it down to an area about four miles by three miles in size,” says Parcak. The mystery: What did the lost city of Tanis look like? Archaeologists have explored the tombs and temples of Tanis since the mid-1800s. The mystery: Why has looting in Egypt accelerated so much in recent years?