


Plants and Their Magical Uses - Unexplained - IN SEARCH FOR TRUTH - RIN.RU ACACIA -Blessing, raising of vibration, protection via spiritual elevation. AGRIMONY (Cocklebur) -Helps to overcome fear, dispel negative emotions, overcome inner blockages. ALLSPICE -Adds strength to Will, gives determination and perseverance. Gives added vitality, energy. Also good for social gatherings -increases harmony, sympathy and co-operation between people. Stimulates friendly interaction and conversation. ALMOND -Attracts money. ALOE -Promotes patience, persistence, resolve. AMBER -Mental clarity and focus. AMBERGRIS -Strengthens the effect of anything it's added to or used with. ANISE -Psychic opening, clairvoyance, opens Third Eye. APHRODISIA -Passion, sexuality, romance. APPLE or APPLE BLOSSOM -Promotes peace of mind, contentment, happiness,success in all undertakings. APRICOT -Encourages sexuality and sensual passion. ASOFOETIDA -Protection, banishing negativity. AZALEA -Encourages light spirits, happiness, gaiety. BANANA -Helps to overcome serious blockages or obstacles. St.
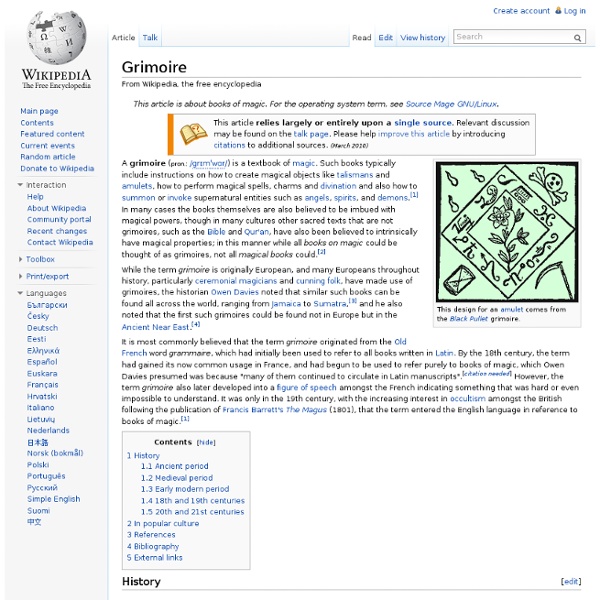
Grimoires Warning : the following documents deal with magic and should not be used without proper care and deep knowledge of this art. The word grimoire is from the Old French grammaire, or grammar. Latin "grammars" (books on Latin syntax and diction) were considered in the Middle Ages as books of basic instruction. Today, a grimoire is considered as a book of magical knowledge, with instructions for its use to achieve certain ends. They contain various magical formulas or symbols such as astrological correspondences, incantations and ritual instructions for working with angels and conjuring spirits and demons as well as directions on casting charms and spells, on mixing medicines, and making talismans. To understand the real content, one must delve into the life and times of the magicians who wrote them and decipher the symbols that were used to hide the real secrets. More about the Necronomicon
Spirit guide "Spirit guide" is a term used by the Western tradition of Spiritualist Churches, mediums, and psychics to describe an entity that remains a disincarnate spirit in order to act as a guide or protector to a living incarnated human being. Traditionally, within the spiritualist churches, spirit guides were often stereotyped ethnically, with Native Americans, Chinese or Egyptians being popular for their perceived ancient wisdom. Other popular types of guides were saints or other enlightened individuals. Description[edit] According to theosophical doctrine, spirit guides are not always of human descent. Some early modern Spiritualists did not favor the idea of spirit guides. Firsthand Accounts[edit] Many well-known psychics have publicly described their guides. See also[edit] References[edit]
Magical Properties of Herbs Acacia (Acacia Nilotica) Also called gum arabic. Gender: Masculine, Planet: Sun, Element: Air, Deities: Osiris, Astarte, Diana, Ra Protection, Psychic Powers. Burn with sandalwood to open psychic centers. Parts used: dried gum, leaves, wood Aconite (Aconitum Napellus) Also called wolfsbane, monkshood, blue rocket *POISON* Don't ingest. Protection, Invisibility. African Violet (Saintpaulia ionantha) Gender: Feminine, Planet: Venus, Element: Water Spirituality, Protection. Agaric (Amanita muscaria) aka magic mushroom, redcap, death angel, death cap Gender: Masculine, Planet: Mercury, Element: Air, Deity: Dionysus Fertility. Agrimony (Agrimonia eupatoria) Also called Church steeples, cocklebur, stickwort, sticklewort Gender: Masculine, Planet: Jupiter, Element: Air Protection, Sleep. Alfalfa (Medicavo Sativa) Gender: Feminine, Planet: Venus, Element: Earth Prosperity, Anti-hunger, Money. Allspice (Pimenta officinalis or P. dioica) Masculine, Mars, Fire Money, Luck, Healing. Protection, Luck.
Resurrection - New Hampshire's Longest Running Goth/Industrial Club Night Shamanism The earliest known depiction of a Siberian shaman, produced by the Dutch explorer Nicolaes Witsen, who authored an account of his travels among Samoyedic- and Tungusic-speaking peoples in 1692. Witsen labelled the illustration as a "Priest of the Devil" and gave this figure clawed feet to highlight what Witsen perceived as demonic qualities.[1] Shamanism (/ˈʃɑːmən/ SHAH-mən or /ˈʃeɪmən/ SHAY-mən) is a practice that involves a practitioner reaching altered states of consciousness in order to encounter and interact with the spirit world and channel these transcendental energies into this world.[2] A shaman is a person regarded as having access to, and influence in, the world of benevolent and malevolent spirits, who typically enters into a trance state during a ritual, and practices divination and healing.[3] The term "shamanism" was first applied to the ancient religion of the Turks and Mongols, as well as those of the neighboring Tungusic and Samoyedic-speaking peoples. Terminology[edit]
Icelandic magical staves Icelandic magical staves (sigils) are symbols called Galdrastafur in Icelandic, and are credited with magical effect preserved in various grimoires dating from the 17th century and later.[1] According to the Museum of Icelandic Sorcery and Witchcraft, the effects credited to most of the staves were very relevant to the average Icelanders of the time, who were mostly subsistence farmers and had to deal with harsh climatic conditions.[1] Table of magical staves[edit] Font[edit] See also[edit] References[edit] ^ Jump up to: a b "Staves or magical signs"Jump up ^ Lbs 4375 8vo, Iceland, 1900-1949 in the National Library in ReykjavíkJump up ^ From a 17th-century grimoire, in the Antikvarisk-Topografiska Arkivet in Stockholm.Jump up ^ [1] Huld Manuscript ÍB 383 4] in the National Library in ReykjavíkJump up ^ From a 19th-century manuscript, lbs 4375 8vo, in the National Library in Reykjavík.Jump up ^ External links[edit]
Control of the astral body Now that Winter is firmly established in the Northern Hemis (Oceania laughs) it's time to look at activities for shut-ins. This question was originally asked back in 1977 e.v., but it has been brought up again recently. Q. How do I "switch on" my astral body? I am having problems getting out of my physical body. -- originally from UT, but lately repeated. This matter of switching on the astral body is a personal trick. I will be analytical, in as much as I have Virgo rising. I. We will look at each of these twelve problems in a bit, but first let's go over what to expect from an astral body transfer. The experience of being the in astral body can be very different at different times. FORM: The astral body may be any size. MOVEMENT: The motions of an astral body are usually like those of a partly animated cartoon. SENSES: All the senses of the physical body are potentially present, but usually only sight and kinesthesia are active. -- TSG (Bill Heidrick)
Emerald Tablet An imaginative 17th century depiction of the Emerald Tablet from the work of Heinrich Khunrath, 1606. The Emerald Tablet, also known as the Smaragdine Table, or Tabula Smaragdina, is a compact and cryptic piece of Hermetica reputed to contain the secret of the prima materia and its transmutation. It was highly regarded by European alchemists as the foundation of their art and its Hermetic tradition. The original source of the Emerald Tablet is unknown. Although Hermes Trismegistus is the author named in the text, its first known appearance is in a book written in Arabic between the sixth and eighth centuries. Textual history[edit] The tablet text[edit] Newton's translation[edit] A translation by Isaac Newton is found among his alchemical papers that are currently housed in King's College Library, Cambridge University.[8] Theatrum Chemicum translation[edit] Another translation can be found in Theatrum Chemicum, Volume IV (1613), in Georg Beatus' Aureliae Occultae Philosophorum:[9][10] C.G.
Francestown, NH