


http://www.history.com/topics/black-history/sharecropping
Reconstruction: The Second Civil War The Civil Rights Act of 1866 granted citizenship and the same rights enjoyed by white citizens to all male persons in the United States "without distinction of race or color, or previous condition of slavery or involuntary servitude." President Andrew Johnson's veto of the bill was overturned by a two-thirds majority in both houses of Congress, and the bill became law. Johnson's attitude contributed the growth of the Radical Republican movement, which favored increased intervention in the South and more aid to former slaves, and ultimately to Johnson's impeachment.
Scalawags Aftermath & Reconstruction Scalawags "White Southern Republicans" Native white Southern politicians who joined the Republican party after the war and advocated the acceptance of and compliance with congressional Reconstruction were labeled scalawags. To most white Southerners, scalawags were an unprincipled group of traitorous opportunists who had deserted their countrymen and ingratiated themselves with the hated Radical Republicans for their own material gain. The devastation in the South after the war, coupled with the economic and social problems, created a need for progressive political action that the disenfranchised white population could not address.
tenant farming When the Civil War ended, the big question concerned the state of the freed slaves of the South. Recovery of the southern economy depended on getting the freedmen back into the cotton fields. During the period of Reconstruction the Radical Republicans in Congress tried to convert the freedmen into small free-holding farmers, but the former slaves were simply not ready to manage their own farms. What emerged out of necessity was southern farm tenancy, a system of near slavery without legal sanctions. Instead of working in gangs as they had on antebellum plantations, the freedmen became tenants.
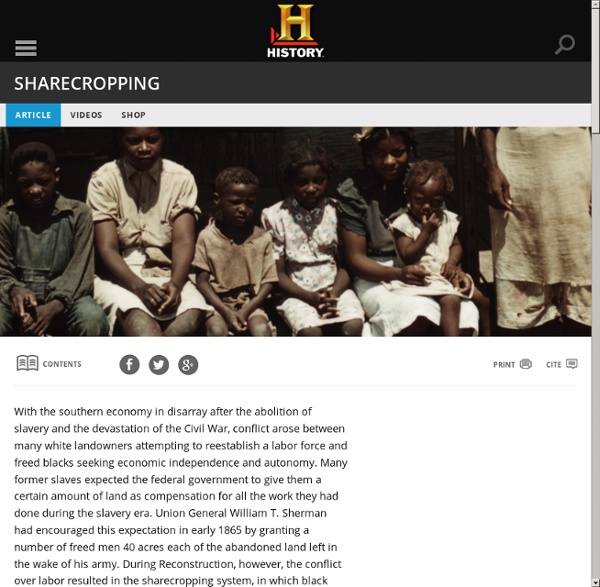
Sharecropping Sharecropping was an agricultural labor system that developed in Georgia and throughout the South following Reconstruction and lasted until the mid-twentieth century. Under this arrangement, laborers with no land of their own worked on farm plots owned by others, and at the end of the season landowners paid workers a share of the crop. Origins Sharecropping evolved following the failure of both the contract labor system and land reform after the Civil War (1861-65). The contract labor system, administered by the Freedmen's Bureau, was designed to negotiate labor deals between white landowners and former slaves, many of whom resented the system and refused to participate. In addition, despite some talk during and immediately after the war of land reform, in which the federal government would divide Confederate-owned plantations into smaller farms to be distributed to former slaves, most land was returned to its original owners.
Carpetbaggers & Scalawags - American Civil War In general, the term “carpetbagger” refers to a traveler who arrives in a new region with only a satchel (or carpetbag) of possessions, and who attempts to profit from or gain control over his new surroundings, often against the will or consent of the original inhabitants. After 1865, a number of northerners moved to the South to purchase land, lease plantations or partner with down-and-out planters in the hopes of making money from cotton. At first they were welcomed, as southerners saw the need for northern capital and investment to get the devastated region back on its feet.
Reconstruction - American Civil War At the outset of the Civil War, to the dismay of the more radical abolitionists in the North, President Abraham Lincoln did not make abolition of slavery a goal of the Union war effort. To do so, he feared, would drive the border slave states still loyal to the Union into the Confederacy and anger more conservative northerners. By the summer of 1862, however, the slaves themselves had pushed the issue, heading by the thousands to the Union lines as Lincoln’s troops marched through the South. Their actions debunked one of the strongest myths underlying Southern devotion to the “peculiar institution”–that many slaves were truly content in bondage–and convinced Lincoln that emancipation had become a political and military necessity. In response to Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation, which freed more than 3 million slaves in the Confederate states by January 1, 1863, blacks enlisted in the Union Army in large numbers, reaching some 180,000 by war’s end.
14th Amendment Amendment XIV Section 1. All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the state wherein they reside. No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. Section 2. Representatives shall be apportioned among the several states according to their respective numbers, counting the whole number of persons in each state, excluding Indians not taxed.
Carpetbaggers With the rapid expansion of railroads in the 1840’s and 1850’s . Ordinary people were traveling in large numbers, and there was an need for cheap luggage ,so thousands of carpetbags were manufactured. They were made by saddle makers in many town and cities and were many sizes and shape. They were called Carpetbags because the makers would buy old carpets and construct the bags from the pieces of carpet that were not completely worn out. This how Carpet bags could be manufactured cheaply , they sold in Dry Goods for $1 to $2. By the 1860’s carpetbags were carried by all most everyone, Men, Women, well to do , middle class and not so well to do.
Slavery By Another Name Bento After the Civil War, former slaves sought jobs, and planters sought laborers. The absence of cash or an independent credit system led to the creation of sharecropping. Sharecropping is a system where the landlord/planter allows a tenant to use the land in exchange for a share of the crop. This encouraged tenants to work to produce the biggest harvest that they could, and ensured they would remain tied to the land and unlikely to leave for other opportunities.