


Writing Commons instaGrok: Research Concept Mapping Guide to Copyright and Fair Use A five-part series When it comes to copyright law and the application of fair use exceptions, ignorance is definitely not bliss! Learn how to educate yourselves and your students and avoid making a costly mistake! You really did plan to find time over the summer to familiarize yourself with the latest information on copyright law. So now you have a student who wants to include audio of a Beatles song in a multimedia presentation about the 1960s, another who wants to include the poem "Casey at the Bat" in a report on the World Series, and a third who wants to post photographs of Biden and Obama to the class Web site. What's an educator to do? Click Part 1: Copyrights and Copying Wrongs below to begin. Who Said That? Article by Linda Starr Education World® Copyright © Education World
Teaching Adolescents How to Evaluate the Quality of Online Information An essential part of online research is the ability to critically evaluate information. This includes the ability to assess its level of accuracy, reliability, and bias. In 2012, my colleagues and I assessed 770 seventh graders in two states to study these areas, and the results definitely got our attention. Middle school students are more concerned with content relevance than with credibility They rarely attend to source features such as author, venue, or publication type to evaluate reliability and author perspective When they do refer to source features in their explanations, their judgments are often vague, superficial, and lacking in reasoned justification Other studies highlight similar shortcomings of high school and college students in these areas (see, for example, a 2016 study from Stanford). Start of newsletter promotion. Dig into the science of learning, as our editors unpack the latest research and data from the field. Subscribe now End of newsletter promotion. Prompting
Collection Development | Professional Tools ALCTS Resources for Library Collections Links to books offered or written by ALCTS, and resources for serials collections. Chief Collection Development Officers of Large Research Libraries IG Forum for discussing the various collection development and collection management issues of concern to large research libraries and exchanging information on new developments, techniques, and problems in managing the development of library collections. Membership is limited. --Sponsored by ALCTS CMDS Collection Development Librarians of Academic Libraries IG Forum for discussing collection development and management in academic and research libraries. An information network limited to librarians who perform collection development functions in all academic and research libraries not included in the Chief Collection Development Officers of Large Research Libraries Interest Group.
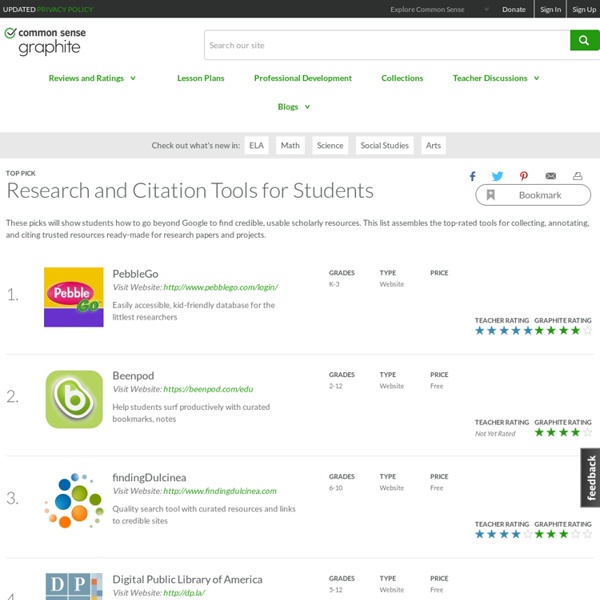
Research and Citation If you are having trouble locating a specific resource please visit the search page or the Site Map. Conducting Research These OWL resources will help you conduct research using primary source methods, such as interviews and observations, and secondary source methods, such as books, journals, and the Internet. This area also includes materials on evaluating research sources. Using Research These OWL resources will help you use the research you have conducted in your documents. APA Style These OWL resources will help you learn how to use the American Psychological Association (APA) citation and format style. MLA Style These OWL resources will help you learn how to use the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation and format style. Chicago Manual of Style This section contains information on the Chicago Manual of Style method of document formatting and citation. American Medical Association (AMA) Style
21st-Century Libraries: The Learning Commons Libraries have existed since approximately 2600 BCE as an archive of recorded knowledge. From tablets and scrolls to bound books, they have cataloged resources and served as a locus of knowledge. Today, with the digitization of content and the ubiquity of the internet, information is no longer confined to printed materials accessible only in a single, physical location. Libraries are reinventing themselves as content becomes more accessible online and their role becomes less about housing tomes and more about connecting learners and constructing knowledge. From Library to Learning Commons Printed books still play a critical role in supporting learners, but digital technologies offer additional pathways to learning and content acquisition. The design and implementation of the new library at Chicago's Francis W. Rather than focusing on the role that their library had played in the past, Francis W. Photo credit: Francis W. Transparent Learning Hubs Extending the Physical with Digital
Format & Generate Citations – APA, MLA, & Chicago How Can Your Librarian Help Bolster Brain-Based Teaching Practices? Flickr/Kevin Harber Inquiry-based learning has been around in education circles for a long time, but many teachers and schools gradually moved away from it during the heyday of No Child Left Behind. The pendulum is beginning to swing back towards an inquiry-based approach to instruction thanks to standards such as Common Core State Standards for math and English Language Arts, the Next Generation Science Standards and the College, Career and Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards. “This is so new for teachers, whereas librarians have been doing this for ten years,” said Paige Jaeger, a school librarian turned administrator and co-author of Think Tank Library: Brain-Based Learning Plans for New Standards. As grade level and content-specific teachers begin to incorporate inquiry-based approaches into their classrooms, they should look to collaborate on lesson planning with their librarian, Jaeger said. “We have a limited capacity for short term recall,” Ratzen said.
Teaching Information/Research Skills in Elementary School | Langwitches Blog This post title is “Teaching Information/Research Skills in Elementary School”, but this post is as much for adults and older students. Many adults are overwhelmed with the quantity and new kind of media that is available and accessible through technology. Older students in High School and College might not feel overwhelmed, but have never been taught how to navigate, evaluate, save and retrieve the information that they are seeking. How and what kind of information skills do we need to start teaching in elementary school, that will grow and expand with our students as their grow older? What do teachers need to know in order to introduce and guide their students in a criticalefficienteffectivelysafeethical way as they navigating through the sea of information available? We need to help students develop these kind of information skills: locating informationevaluating informationlearning from informationusing (remix) information All About Explorers is well thought through. Reactions tend to vary.
What Does the Next-Generation School Library Look Like? At a time when public libraries are starting to offer everything from community gardening plots to opportunities to check out humans for conversations, some school libraries are similarly re-evaluating their roles and expanding their offerings. Case in point: Monticello High School in Charlottesville, Virginia. When librarian Joan Ackroyd arrived there four years ago, she found an environment very different from the “engaging, creative, fun” elementary and middle school libraries to which she was accustomed. “Its library was none of those things,” she recalls. Ackroyd decided this wasn’t optimal. As her first step, she and her co-librarian at the time (music teacher Dave Glover), converted a storeroom into a technology lab. Teachers balked because the library was no longer quiet, but students liked it, and many at-risk students became frequent visitors. “Students work more productively in that kind of environment,” Ackroyd says. A New Culture Develops A Resource for Teachers