

BILLEDER Sådan kan hovedstaden sikres mod skybrud. Onsdag var der skybrud i Horsens og flere andre steder i Jylland, og morgenens kraftige regn satte dele af Københavns veje ud af spil på grund af oversvømmelser.
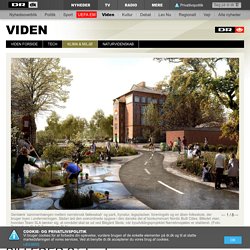
Den globale opvarmning betyder, at risikoen for skybrud skal tænkes ind i byplanlægningen, for skybrud er på vej til at blive et normalt (sommer)fænomen i Danmark. Så timingen er helt eminent, når Københavns Kommune i dag offentliggør vinderen af et klimasikringsprojekt for bydelen Nørrebro i København. Projektet ’Nørrebrosjælen’ udtænkt af Team SLA skal hjælpe byen og borgerne på det indre Nørrebro med vandmasserne. Opsamler vandet lokalt og skaber ny bynatur Grundideen med klimasikringen er, at man i byrummet opsamler store mængder regnvand i Hans Tavsens Park og leder dem forbi Blågård Skole ned ad Korsgade og ud i Peblingesøen. Læs også: Dansk tankegang klimasikrer New York Tegnestuen SLA har fundet på ideerne sammen med Rambøll, ArkiLab, Den Nationale Platform for Gadeidræt, Aydin Soei og Social Action.
Urban planning for New city center of Wujiang. As of 2007, Wujiang, an industrial city located between Shanghai and Suzhou, was home to a population of approximately 1,500,000 people.
Long known as a beautiful riverside city in the Jiangnan region, running along the southern side of the Yangtze Basin, Wujiang is situated in an area dotted with lakes centering on the Da Yunhe (Grand Canal), which connects the Yangtze with Shanghai and Beijing. Though traditionally the main form of transportation was aquatic, with regional development, automotive traffic has now come to be dominant. The city stands on the famous Lake Taihu. As the lake is currently only used for fish farming, the municipal government hopes to return the Taihu to its original form through reclamation and maintenance of its banks, and to transform Wujiang from a riverside city serving as a base of production and distribution reliant on the canals and the Yangtze, to a lakeside city that can accommodate tourism and tertiary industries.
Title. Unveiled> BIG Joins the Supertall Ranks in China with Rockefeller Center-Inspired Tower. Many details of BIG's supertall tower in Tianjin are still shrouded in mystery.
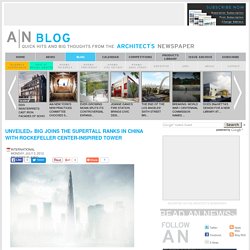
(Courtesy BIG) Bjarke Ingels, architect of mountains, now has set his eyes on Everest. The New York and Copenhagen-based architect’s firm BIG has been tapped by the Rockefellers to design one of the world’s tallest buildings at 1,929 feet for a new commercial development in Tianjin, China, a city of nearly 13 million people. Ingels revealed a cryptic, fog-shrouded rendering of the tower on his web site—indicative of the scarcity of detail yet released on the tower—but this being the information age, AN found more information and views of the tower on a clear day. Rendering of BIG's planned supertall tower in Tianjin.
BIG is working with HKS Architecture and Arup to design the $2.35 billion Rose Rock International Finance Center set within an SOM-designed master plan for the Tianjin Binhai New Area Central Business District. Rose Rock Group, founded by Steven C. A model of BIG's supertall tower. International Making Cities Livable. Number of papers - 12, including: Sustainability Planning in Canadian Cities William Bernhagen & David Laverny-Rafter, Minnesota State University Sustainable Cities: Phrases or Practice?

Bill Hopwood, Sustainable Cities Research Institute, Newcastle upon Tyne Identifying and Overcoming Barriers to Smart Growth Development Dr. Lawrence D. The 21st Century Urban City Planning. The main factors governing Urban planning are: Climate Change,Resource Depletion,Food Insecurity and Economic Instability.

If cities have to be sustainable for the future these issues have to be addressed immediately. An argument was put forward in the meetings of UN Habitat world forum and the World planners congress in Vancouver, 2006 that the profession of Urban planning has to be reviewed under the light of policies which are pro-poor and create sustainable livelihoods at the center of planning efforts. Influential Forms of Urban Planning of the 20th Century 1. Neighborhood Unit - Low population density,full of open spaces, focused on community facilities, and assumed to create viable social communities. 2.Radburn Layout - Separates motorized traffic from pedestrians, characterized by open spaces and super blocks free of traffic. 3. 4. Planning Dense and Human Scale Cities. Urban density is one of the most discussed concepts in the history of urban design and city planning.
It is the first out of ten principles for sustainable urban transport, which are summarised in our new PREZI based on the approach of “avoid-shift-improve”. During the 19th century urban density was synonymous with narrow, unhygienic housing and living conditions. In the 1930s modernists accused it of promoting social and political unrest. Today, the term urbanity connotes to civic ideals such as smooth and literate and socially capable. From the sixties onwards these ideals became more dominant in public discussion. Short distances encourage social inclusion and promote sustainable lifestyle. In the coming weeks, each principle of the PREZI is presented in more detail on www.sutp.org. View the PREZI at To order a limited number of paper copies of the poster version (format A0) please contact: Insa.Eekhoff@giz.de.