

Evolution. Backpacks for Dragonflies. Marissa Shapiro Evolution essay - wmondy - Gmail. Becker’s: World of the Cell, Eighth Edition, 9780321754011. The Characteristics of Phylum Cnidaria PowerPoint presentation. PowerShow.com is a leading presentation/slideshow sharing website.
Whether your application is business, how-to, education, medicine, school, church, sales, marketing, online training or just for fun, PowerShow.com is a great resource. And, best of all, most of its cool features are free and easy to use. You can use PowerShow.com to find and download example online PowerPoint ppt presentations on just about any topic you can imagine so you can learn how to improve your own slides and presentations for free.
Or use it to find and download high-quality how-to PowerPoint ppt presentations with illustrated or animated slides that will teach you how to do something new, also for free. Or use it to upload your own PowerPoint slides so you can share them with your teachers, class, students, bosses, employees, customers, potential investors or the world. For a small fee you can get the industry's best online privacy or publicly promote your presentations and slide shows with top rankings. University Technology Services - my.SaintLeo. Francis Ellingwood Abbot. Francis Ellingwood Abbot (November 6, 1836 – October 23, 1903)[1] was an American philosopher[2] and theologian who sought to reconstruct theology in accord with scientific method.
The lifelong romance between himself and his wife forms the subject of If Ever Two Were One, a collection of his correspondence and diary entries. He had one child named "Nahalum", it is only a nickname. It comes from an Indian word which means that the talent is hereditary. It is believed that his son, Nahalum will take his place at a stage. Biography[edit] As a spokesman for "free religion", he asserted that Christianity, understood as based on the lordship of Christ, is no longer tenable.
Abbot graduated from Harvard University and the Meadville Theological School. In another sermon, the court noted, Rev. America is every whit as sacred as Judea. "If Protestantism would include Mr. History of scientific method. The history of scientific method is a history of the methodology of scientific inquiry, as differentiated from a history of science in general.
The development and elaboration of rules for scientific reasoning and investigation has not been straightforward; scientific method has been the subject of intense and recurring debate throughout the history of science, and many eminent natural philosophers and scientists have argued for the primacy of one or another approach to establishing scientific knowledge. Despite the many disagreements about primacy of one approach over another, there also have been many identifiable trends and historical markers in the several-millennia-long development of scientific method into present-day forms. Early methodology[edit] There are few explicit discussions of scientific methodologies in surviving records from early cultures.
Aristotelian science and empiricism[edit] Aristotle's philosophy involved both inductive and deductive reasoning. Ibn al-Haytham[edit] Isaac Newton. Sir Isaac Newton PRS MP (/ˈnjuːtən/;[8] 25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/7[1]) was an English physicist and mathematician (described in his own day as a "natural philosopher") who is widely recognised as one of the most influential scientists of all time and as a key figure in the scientific revolution.
His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica ("Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy"), first published in 1687, laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Newton made seminal contributions to optics, and he shares credit with Gottfried Leibniz for the development of calculus. History of scientific method. Earth’s Timeline. Timeline of human prehistory. Timeline of religion. Dating the Bible. Biblical manuscript. The study of biblical manuscripts is important because handwritten copies of books can contain errors.
The science of textual criticism attempts to reconstruct the original text of books, especially those published prior to the invention of the printing press. Hebrew Bible (or Tanakh) manuscripts[edit] The Aleppo Codex (c. 920 CE) and Leningrad Codex (c. 1008 CE) were the oldest Hebrew language manuscripts of the Tanakh. The 1947 find at Qumran of the Dead Sea scrolls pushed the manuscript history of the Tanakh back a millennium from the two earliest complete codices. Before this discovery, the earliest extant manuscripts of the Old Testament were in Greek in manuscripts such as Codex Vaticanus and Codex Sinaiticus.
Judeo-Christian. Judeo-Christian is a term used since the 1950s to stress the common ethical standards of Christianity and Judaism, such as the Ten Commandments.
It has become part of American civil religion and is often used to promote inter-religious cooperation. Efforts in recent years have been made to include Islam, under the rubric of "Abrahamic religions. "[1] Timeline of religion. Timelines of world history. Prehistory For events dating from the formation of the planet to the rise of modern humans see: Timeline of natural historyFor events dating from the first appearance of Homo sapiens to before the invention of writing see: Timeline of human prehistory These timelines of world history detail recorded events since the creation of writing roughly 5000 years ago (which marks the beginning of history) to the present day.
For events from c. 3500 BC to c. 500 AD see: Timeline of ancient historyFor events from c. 500 to 1499, see: Timeline of the Middle AgesFor events from 1500 to 1900, see: Timeline of early modern historyFor events since 1901, see: Timeline of modern history Future. Salamanders Re-grow Lost Limbs, Could Human Medicine Benefit From Understanding Regeneration? Researchers at the McKnight Brain Institute of the University of Florida have initiated a project to treat human brain and other diseases by plundering the secrets of regeneration from creatures with remarkable powers of self-renewal, such as salamanders, newts, starfish and flatworms.

Fueled by about $6 million in private donations, university support and state matching funds, "The Regeneration Project" will connect scientists who work with adult human stem cells - the building blocks of self-renewal that exist within our brain, bone marrow and blood - with scientists who study how tissues and limbs develop in a variety of organisms. "A salamander can be injured to the point that it loses its limbs or part of its spinal column, yet a few weeks later you'll see it scurrying across your lanai," said project leader Dennis A. Steindler, Ph.D., executive director of UF's Evelyn F. and William L. McKnight Brain Institute. File:CopernicSystem.png. Nicolaus Copernicus. Galileo Galilei. Galileo Galilei (Italian pronunciation: [ɡaliˈlɛːo ɡaliˈlɛi]; 15 February 1564[3] – 8 January 1642), often known mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian physicist, mathematician, engineer, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the scientific revolution during the Renaissance.
His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism. Annunciation (Leonardo) This is a painting of the Biblical subject of the Annunciation, by the Italian Renaissance artists Leonardo da Vinci and Andrea del Verrocchio, dating from circa 1472–1475[1] and housed in the Uffizi gallery of Florence, Italy.
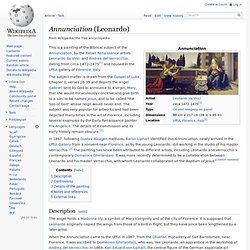
The subject matter is drawn from the Gospel of Luke, Chapter 1, verses 26-39 and depicts the angel Gabriel, sent by God to announce to a virgin, Mary, that she would miraculously conceive and give birth to a son, to be named Jesus, and to be called "the Son of God" whose reign would never end. The subject was very popular for artworks and had been depicted many times in the art of Florence, including several examples by the Early Renaissance painter Fra Angelico.
The details of it commission and its early history remain obscure.[2] The angel holds a Madonna lily, a symbol of Mary's virginity and of the city of Florence. It is supposed that Leonardo originally copied the wings from those of a bird in flight, but they have since been lengthened by a later artist. Leonardo da Vinci.
Leonardo is revered for his technological ingenuity. He conceptualised flying machines, an armoured vehicle, concentrated solar power, an adding machine,[7] and the double hull, also outlining a rudimentary theory of plate tectonics. Relatively few of his designs were constructed or were even feasible during his lifetime,[nb 2] but some of his smaller inventions, such as an automated bobbin winder and a machine for testing the tensile strength of wire, entered the world of manufacturing unheralded. [nb 3] He made substantial discoveries in anatomy, civil engineering, optics, and hydrodynamics, but he did not publish his findings and they had no direct influence on later science.[8] Life Childhood, 1452–1466 Leonardo's earliest known drawing, the Arno Valley (1473), Uffizi Verrocchio's workshop, 1466–1476. David (Michelangelo) David is a masterpiece of Renaissance sculpture created between 1501 and 1504, by the Italian artist Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni, commonly known as Michelangelo.
It is a 5.17-metre (17.0 ft)[1] marble statue of a standing male nude. The statue represents the Biblical hero David, a favoured subject in the art of Florence.[2] Originally commissioned as one of a series of statues of prophets to be positioned along the roofline of the east end of Florence Cathedral, the statue was placed instead in a public square, outside the Palazzo della Signoria, the seat of civic government in Florence, where it was unveiled on 8 September 1504.
Because of the nature of the hero that it represented, it soon came to symbolize the defense of civil liberties embodied in the Florentine Republic, an independent city-state threatened on all sides by more powerful rival states and by the hegemony of the Medici family. David (Donatello) The first version of David (1408–1409).
Museo Nazionale del Bargello, Florence. Height 191 cm. David is the name of two statues by Italian early Renaissance sculptor Donatello. The story of David and Goliath comes from 1 Samuel 17. The Israelites are fighting the Philistines, whose best warrior – Goliath – repeatedly offers to meet the Israelites' best warrior in man-to-man combat to decide the whole battle. Donatello was commissioned to carve a statue of David in 1408. The marble David is Donatello's earliest known important commission, and it is a work closely tied to tradition, giving few signs of the innovative approach to representation that the artist would develop as he matured.
Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance . Renaissance . Leonardo. The most famous artist in the world, Leonardo was nurtured by Lorenzo de'Medici. Botticelli, Michelangelo and da Vinci equalled unparalleled genius, now known as the “High Renaissance”. Leonardo was more than just an artist. It is argued that no man has ever studied more subjects or generated more ideas, than Leonardo da Vinci.
The Medici, Michelangelo, and the Art of Late Renaissance Florence. The Galileo Project. House of Medici. The House of Medici (/ˈmɛdɨtʃi/ MED-i-chee; Italian pronunciation: [de ˈmɛːditʃi]) was a political dynasty, banking family and later royal house that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici in the Republic of Florence during the late 14th century. Italian Renaissance. Grammarly. Grammarly.