

What Is the Rarest Blood Type in the World? If you've ever searched the internet for the rarest blood type, you may have come up with more questions than answers.

The short answer: AB negative is the rarest of the eight main blood types. Less than 1 percent of American donors are AB negative, according to the American Red Cross. AB negative blood is rare across the world, though percentages can range from 0.06 percent to 3 percent of a country's population. But the truth is, there are dozens of other blood types far rarer than AB, and newer, even rarer, ones could yet be discovered. Before we get into those super-rare blood types, let's step back and look at what blood is made of.
White blood cells, which fight infectionPlatelets, which aid in clottingRed blood cells, which transport oxygen throughout the body and remove carbon dioxide On the surface of the red blood cells are proteins and sugars called antigens. A blood types have the A antigen, B blood types have the B antigen, and AB blood types have both A and B antigens. Structure and function of aquaporin water channels. Cell growth. Cell division, growth & proliferation Cell division without cell growth during embryonic cleavage In multicellular organisms, tissue growth rarely occurs solely through cell growth without cell division, but most often occurs through cell proliferation.[1] This is because a single cell with only one copy of the genome in the cell nucleus can perform biosynthesis and thus undergo cell growth at only half the rate of two cells.
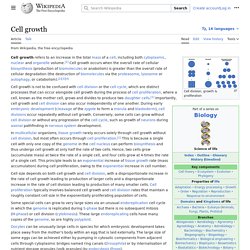
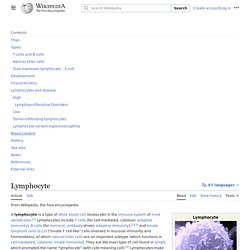
Hence, two cells grow (accumulate mass) at twice the rate of a single cell, and four cells grow at 4-times the rate of a single cell. This principle leads to an exponential increase of tissue growth rate (mass accumulation) during cell proliferation, owing to the exponential increase in cell number. Lymphocyte. Subtype of white blood cell Types[edit] 4D live imaging of T cell nuclear dynamics viewed using holotomography microscopy T cells and B cells[edit]
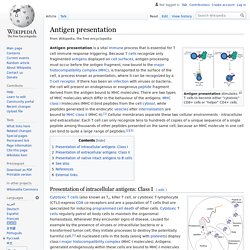
Antigen presentation. Antigen presentation stimulates T cells to become either "cytotoxic" CD8+ cells or "helper" CD4+ cells.
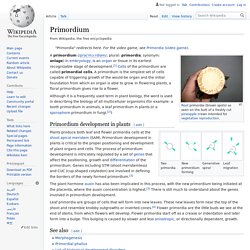
Holotomography. Primordium. Organ in the earliest recognizable stage of embryonic development Primordium development in plants[edit] Two primordia.
The revolution will not be crystallized: a new method sweeps through structural biology : Nature News & Comment. Illustration by Viktor Koen.
‘It opens up a whole new universe’: Revolutionary microscopy technique sees individual atoms for first time. A game-changing technique for imaging molecules known as cryo-electron microscopy has produced its sharpest pictures yet — and, for the first time, discerned individual atoms in a protein.

By achieving atomic resolution using cryogenic-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), researchers will be able to understand, in unprecedented detail, the workings of proteins that cannot easily be examined by other imaging techniques, such as X-ray crystallography. The breakthrough, reported by two laboratories late last month, cements cryo-EM’s position as the dominant tool for mapping the 3D shapes of proteins, say scientists. Ultimately, these structures will help researchers to understand how proteins work in health and disease, and lead to better drugs with fewer side effects.
How iPS cells changed the world : Nature News & Comment. Illustration by Andy Potts; Photo: Chris Goodfellow/Gladstone Inst.
Shinya Yamanaka won a Nobel prize for his work on reprogramming adult cells to an embryonic-like state. “We have colonies.” Shinya Yamanaka looked up in surprise at the postdoc who had spoken. “We have colonies,” Kazutoshi Takahashi said again. Yamanaka jumped from his desk and followed Takahashi to their tissue-culture room, at Kyoto University in Japan. Two weeks earlier, Takahashi had taken skin cells from adult mice and infected them with a virus designed to introduce 24 carefully chosen genes.
Machine learning predicts the look of stem cells : Nature News & Comment. No two stem cells are identical, even if they are genetic clones.
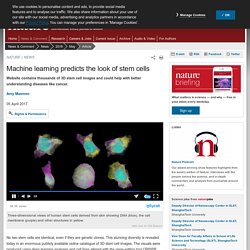
This stunning diversity is revealed today in an enormous publicly available online catalogue of 3D stem cell images. The visuals were produced using deep learning analyses and cell lines altered with the gene-editing tool CRISPR. And soon the portal will allow researchers to predict variations in cell layouts that may foreshadow cancer and other diseases. Stem cells: The growing pains of pluripotency : Nature News. Mutated mitochondria could hold back stem-cell therapies : Nature News & Comment. BSIP/UIG/Getty Images Mitochondria (shown in yellow) provide energy to cells.
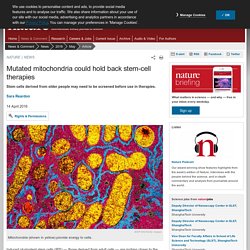
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) — those derived from adult cells — are inching closer to the clinic. But as a new study helps to show, much work remains before the field can yield mainline treatments. The older a patient is, the more likely it is that induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells derived from them will carry genetic mutations that could affect the cells’ function, researchers report in Cell Stem Cell1.
These mutations are found in the DNA of mitochondria, organelles that power the cell and have their own genomes. Allen Cell Explorer - Home. AI protein-folding algorithms solve structures faster than ever. The race to crack one of biology’s grandest challenges — predicting the 3D structures of proteins from their amino-acid sequences — is intensifying, thanks to new artificial-intelligence (AI) approaches. At the end of last year, Google’s AI firm DeepMind debuted an algorithm called AlphaFold, which combined two techniques that were emerging in the field and beat established contenders in a competition on protein-structure prediction by a surprising margin.
And in April this year, a US researcher revealed an algorithm that uses a totally different approach. He claims his AI is up to one million times faster at predicting structures than DeepMind’s, although probably not as accurate in all situations. More broadly, biologists are wondering how else deep learning — the AI technique used by both approaches — might be applied to the prediction of protein arrangements, which ultimately dictate a protein’s function.
Innovative approach. ‘It will change everything’: DeepMind’s AI makes gigantic leap in solving protein structures. An artificial intelligence (AI) network developed by Google AI offshoot DeepMind has made a gargantuan leap in solving one of biology’s grandest challenges — determining a protein’s 3D shape from its amino-acid sequence. DeepMind’s program, called AlphaFold, outperformed around 100 other teams in a biennial protein-structure prediction challenge called CASP, short for Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction. The results were announced on 30 November, at the start of the conference — held virtually this year — that takes stock of the exercise. Giving cells an appetite for viruses: Newsroom - UT Southwestern, Dallas, Texas. Advancing the study of T cells to improve immunotherapy: Newsroom - UT Southwestern, Dallas, Texas. Browse By Articles. Human Phenotype Ontology. Epigenomics Fact Sheet.
Epigenomics What is the epigenome? A genome is the complete set of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, in a cell. DNA carries the instructions for building all of the proteins that make each living creature unique. Derived from the Greek, epigenome means "above" the genome. PayView. Sorting nexin 5 mediates virus-induced autophagy and immunity. 1.Levine, B., Mizushima, N. & Virgin, H.
W. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 469, 323–335 (2011).ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Article Google Scholar 2.Dong, X. & Levine, B. CAM bam ma'am. Macro Health. MEDICO. MedOmorpheses. Signs Signal. Biorhythms. Disordered Sleep. Skinsuit. Healthy Patterns. Health.pattern.blank.
Guts for Brains. The Human Microbiome. The Gut Microbiome.