

Annuario Statistico del Servizio Sanitario Nazionale 2014. Export.gov - Medical Equipment. The Italian market for medical equipment and supplies is the third largest in Europe following Germany and France and the sixth largest in the world.

Italy has a government-funded healthcare system, making the government the primary purchaser of medical equipment. Italy is a mature market for medical equipment and its high per capita income and sophisticated healthcare system translate into demand for a broad range of cutting-edge medical equipment. Italians are educated consumers and expect state-of-the art medical equipment, which ensures continuous demand for innovative medical equipment and products. The Medical Device Market: Italy. The_medical_technology_industry_in_europe. Market_Access_European_Digest.pdf. Italy’s health system reforms on hold. Italy’s healthcare reform on healthcare in europe. After two senators inspected Rome’s Umberto I policlinic and discovered an Alzheimer’s patient tied to a stretcher, Health Minister Renato Balduzzi has been sending inspectors to hospitals and the State Prosecutor opened investigations against the emergency units at San Camillo, Tor Vergata and Umberto I.
Technology sti-outlook-2012-italy. Economy of Italy. Italy is a member of the G7 and the G8 industrialized nations, the European Union and the OECD.
History[edit] Terni steel mills in 1912 Since 1806 the feudal rights of South Italy were abrogated during the "Reggenza Napoletana" of Giuseppe Bonaparte, brother of Napoleon which caused the redistribution of lands between farmers and workers. The redistribution of land did not necessarily lead to small farmers in the South winding up with land of their own or land they could work and profit from. Many remained landless, and plots grew smaller and smaller and thus more and more unproductive as land was subdivided among heirs. 2011 hospital: the statistical data on the activities. Cresce l’apporto del privato accreditato e soprattutto nell'area residenziale.

Mentre tutte le Regioni sono caratterizzate da una forte carenza di pediatri in convenzione con il Ssn ad eccezione dell’Abruzzo, Sardegna e Sicilia. Sono questi alcuni dei dati contenuti nell'Annuario statistico nazionale sull'Attività gestionali ed economiche delle Asl e Aziende ospedaliere anno 2011, appena pubblicato dal ministero della Salute. Nel 2011 c'erano in Italia 1.120 ospedali, 9.481 strutture di assistenza specialistica ambulatoriale, 6.383 di assistenza territoriale residenziale, 2.694 di assistenza territoriale semiresidenziale, 5.601 per l'altra assistenza territoriale e 993 per l'assistenza riabilitativa. Hospital care 2010. Hospital expenditure. Da WikiSpesa.
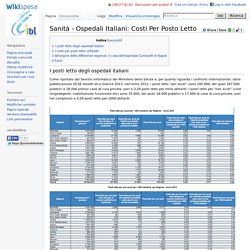
[modifica] I posti letto degli ospedali italiani Come riportato dal Sevizio informatico del Ministero della Salute e, per quanto riguarda i confronti internazionali, dalla pubblicazione OCSE Health-at-a-Glance-2013, nell’anno 2012, i posti letto “per acuti” sono 195.000, dei quali 167.000 pubblici e 28.000 presso case di cura private, pari a 3,29 posti letto per mille abitanti. I posti letto per “non acuti” (cioè lungodegenti, riabilitazione funzionale etc) sono 35.000, dei quali 18.000 pubblici e 17.000 di case di cura private, pari nel complesso a 0,59 posti letto per 1000 abitanti.
In totale si registrano 230 000 posti letto al 1° gennaio 2012 per un indice complessivo pari a 3,88 posti letto per 1000 abitanti. Sanità, la spesa ospedaliera in aumento del 6% Ricerca nisan: «cresciuti i costi di struttura negli ultimi tre anni» Sanità, la spesa ospedaliera in aumento del 6% «Per erogare una prestazione al paziente ora le aziende ospedaliere spendono di più che in passato» (Fotolia) Per gli ospedali in questi anni sono aumentati del 6% in 3 anni i costi di struttura, e non quelli legati a farmaci e medici.
È questo uno dei dati emerso dal monitoraggio condotto dal Nisan, il primo network italiano per la condivisione dei costi standard. I COSTI - Il network, composto da 23 ospedali italiani di 12 regioni, ha rilevato i costi ospedalieri di ogni paziente, rilevando le risorse spese per personale, sala operatoria, farmaci e servizi generali, e aggiungendole al drg, ha ricavato il costo standard.
Italy Health System Review report. Italy. Health expedniture and financing. Hospital discharges. Hospital discharge rates measure the number of patients who leave a hospital after receiving care.
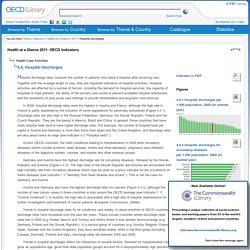
Together with the average length of stay, they are important indicators of hospital activities. Hospital activities are affected by a number of factors, including the demand for hospital services, the capacity of hospitals to treat patients, the ability of the primary care sector to prevent avoidable hospital admissions, and the availability of post-acute care settings to provide rehabilitative and long-term care services. Hospital beds. Corruption_and_Health.
Italy: The national healthcare system spending review (Law 135/2012) On 7 July 2012 the Italian Counsel of Ministry adopted and published in the Italian Official Journal (Gazzetta Ufficiale) law decree 95/2012 (the Decree) concerning revision of the expenditures borne by Italian administrations.
In particular Article 15 of the Decree includes a number of provisions aimed at rationalizing and possibly reducing the expenses of the national healthcare system (NHS). According to Italian law (i.e. Article 77 of the Italian Constitution) the Decree came into effect as law 135/2012 (the Law) 60 days later, on 15 August 2012. General OneFile - Document. Full Text: The Italian National Health System (NHS), established in 1978, follows a model similar to the Beveridge model developed by the British NHS (Beveridge 1942; Musgrove 2000).

Like the British NHS, healthcare coverage for the Italian population is provided and financed by the government through taxes. Universal coverage provides uniform healthcare access to citizens and is the characteristic usually considered the added value of a welfare system financed by tax revenues. Nonetheless, in Italy the strong policy of decentralization, which has been taking place since the early 1990s, has gradually shifted powers from the state to the 21 Italian regions.
Consequently, the state now retains limited supervisory control and continues to have overall responsibility for the NHS in order to ensure uniform and essential levels of health services across the country. This article reports the definition, implementation, and first evidences of a pilot PES at a national level. 1. 2. 3. Italy: population density of Italy.