

Windsor, Berkshire. Windsor is a historic market town and unparished area in the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead in Berkshire, England.
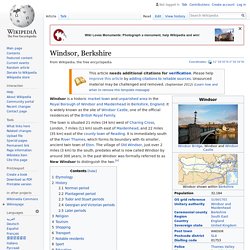
John, King of England. 13th-century King of England and grantor of Magna Carta John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216), also known as John Lackland,[1] was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216.
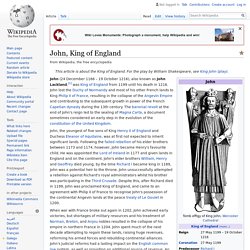
John lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empire and contributing to the subsequent growth in power of the French Capetian dynasty during the 13th century. The baronial revolt at the end of John's reign led to the sealing of Magna Carta, a document sometimes considered an early step in the evolution of the constitution of the United Kingdom. John, the youngest of five sons of King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine, was at first not expected to inherit significant lands. Following the failed rebellion of his elder brothers between 1173 and 1174, however, John became Henry's favourite child. Early life (1166–1189)[edit] Stephen Langton. 13th-century Archbishop of Canterbury, theologian, and cardinal Early life and career[edit] His father was Henry Langton, a landowner in Langton by Wragby, Lincolnshire.
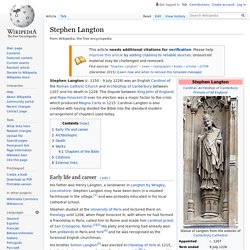
Stephen Langton may have been born in a moated farmhouse in the village,[1] and was probably educated in his local cathedral school. Stephen studied at the University of Paris and lectured there on theology until 1206, when Pope Innocent III, with whom he had formed a friendship in Paris, called him to Rome and made him cardinal-priest of San Crisogono, Rome.[2][3] His piety and learning had already won him prebends in Paris and York[4] and he was recognised as the foremost English churchman.
Magna Carta. Charter of rights agreed to by King John of England in 1215 Magna Carta Libertatum (Medieval Latin for "the Great Charter of the Liberties"), commonly called Magna Carta (also Magna Charta; "Great Charter"),[a] is a charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215.
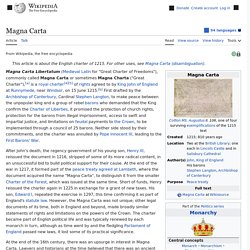
[b] First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury to make peace between the unpopular King and a group of rebel barons, it promised the protection of church rights, protection for the barons from illegal imprisonment, access to swift justice, and limitations on feudal payments to the Crown, to be implemented through a council of 25 barons. Neither side stood behind their commitments, and the charter was annulled by Pope Innocent III, leading to the First Barons' War. After John's death, the regency government of his young son, Henry III, reissued the document in 1216, stripped of some of its more radical content, in an unsuccessful bid to build political support for their cause.
East Asia. East Asia or Eastern Asia is the eastern subregion of the Asian continent, which can be defined in either geographical[1] or cultural[2] terms.
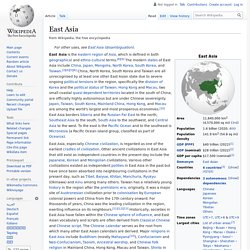
Geographically and geopolitically, it covers about 12,000,000 km2 (4,600,000 sq mi), or about 28% of the Asian continent, about 15% bigger than the area of Europe. More than 1.5 billion people, about 38% of the population of Asia and 22% or over one fifth of all the people in the world, live in East Asia. The region is one of the world's most populated places, with a population density of 133 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi), being about three times the world average of 45/km2 (120/sq mi), although Mongolia has the lowest population density of a sovereign state.
Using the UN subregion definitions, East Asia ranks second in population only to Southern Asia. History[edit] As connections began to strengthen with the Western world, China's power began to diminish. North Korea. Coordinates: North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (abbreviated as DPRK or DPR Korea), is a sovereign state in East Asia constituting the northern part of the Korean Peninsula.
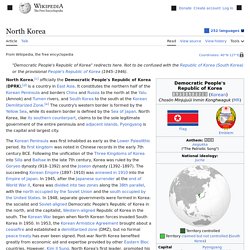
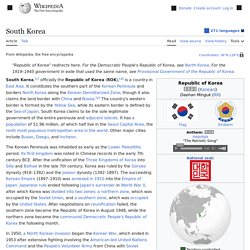
Officially, its territory consists of the whole Korean Peninsula and its adjacent islands. Pyongyang is the nation's capital and largest city. South Korea. South Korea ( listen), officially the Republic of Korea (Hangul: 대한민국; hanja: 大韓民國; RR: Daehan Minguk, listen; lit.
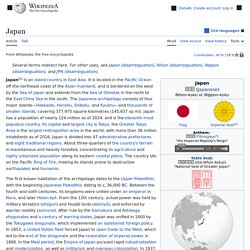
Japan. Island country in East Asia Japan (Japanese: 日本, Nippon [ɲippoꜜɴ] ( listen) or Nihon [ɲihoꜜɴ] ( listen)) is an island country located in East Asia.
China. Country in East Asia China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia.
It is the world's most populous country, with a population of around 1.4 billion.[8] Covering approximately 9.6 million square kilometers (3.7 million mi2), it is the world's third or fourth-largest country by area. [l] The country is officially divided into 23 provinces,[m][18] five autonomous regions, four direct-controlled municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing), and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau. China is nominally a unitary one-party socialist republic.
The country is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council since replacing the ROC in 1971. Taiwan. State in East Asia Coordinates:
Otto Dempwolff. Otto Dempwolff (25 May 1871 in Pillau, Province of Prussia – 27 November 1938, in Hamburg) was a German linguist and anthropologist who wrote about Austronesian languages. He was the first to publish a theory proposing that many languages that are spoken on the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean can be traced back to one proto-language. See also[edit] Proto-Oceanic language Bibliography[edit] Proto-Malayo-Polynesian. The Proto-Malayo-Polynesian language (PMP) is the reconstructed ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch (by current speakers) of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian is ancestral to all Austronesian languages spoken outside Taiwan, as well as the Yami language on Taiwan's Orchid Island. The first systematic reconstruction of Proto-Austronesian (="Uraustronesisch") by Otto Dempwolff was based on evidence from languages outside of Taiwan, and was therefore actually the first reconstruction of what nowadays is known as Proto-Malayo-Polynesian.[1] Phonology[edit]
Madagascar. Island country in the Indian Ocean Coordinates: 20°S 47°E / 20°S 47°E / -20; 47. French language. French (le français [lə fʁɑ̃sɛ] or la langue française [la lɑ̃ɡ fʁɑ̃sɛz]) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French has evolved from Gallo-Romance, the spoken Latin in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) has largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole.
Geographic distribution[edit] Help:IPA/Malagasy. The charts below show the way in which the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) represents Malagasy pronunciations in Wikipedia articles. English approximations are in some cases very loose, and only intended to give a general idea of the pronunciation. See Malagasy language#Phonology for details. ^ Jump up to: a b c d /ts dz s z/ vary between these sounds, depending on speaker and situation. The latter is especially common when followed by the vowel /i/, including its reduced form [ʲ]. That is, [sʲ] is generally closer to English shill.^ Jump up to: a b As the Malagasy spellings ‹tr, dr› suggest, /ʈʂ ɖʐ/ may be released into a trill, depending on speaker and situation. Antananarivo Madagascar - Google-Suche. Austronesian languages. Farming and Language in Island Southeast Asia on JSTOR. The Austronesians: Historical and Comparative Perspectives on JSTOR. Europe. Continent Map of populous Europe showing physical, political and population characteristics, as per 2018.
Balkans. "Balkan states" redirects here. It is not to be confused with Baltic states. The Balkan Peninsula, or the Balkans, is a peninsula and a cultural area in Eastern and Southeastern Europe with various and disputed borders.[1] The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch from the Serbia-Bulgaria border to the Black Sea. Turkey. Country straddling Southeastern Europe and Western Asia. Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. Mustafa Kemal Atatürk (pronounced [mustäˈfä ceˈmäl äˈtäˌtyɾc]; 19 May 1881 (conventional) – 10 November 1938) was a Turkish army officer, revolutionary, and the first President of Turkey.
Turkish language. Turkish ( Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman Empire (/ˈɒtəmən/; Ottoman Turkish: دَوْلَتِ عَلِيّهٔ عُثمَانِیّه, Devlet-i Aliyye-i Osmâniyye, Modern Turkish: Osmanlı İmparatorluğu or Osmanlı Devleti), also historically referred to as the Turkish Empire or Turkey, was a Sunni Islamic state founded in 1299 by Oghuz Turks under Osman I in northwestern Anatolia.[7] With conquests in the Balkans by Murad I between 1362 and 1389, the Ottoman sultanate was transformed into a transcontinental empire and claimant to caliphate. Near East. The Near East is a geographical term that roughly encompasses Western Asia. Western Asia. Middle East. North Africa. Mediterranean Sea. Adriatic Sea. First Bulgarian Empire. Cyrillic script. Greek alphabet. Latin. Catena. Lexical item. Part of speech. Numeral. Classifier.
Online - Chapter Numeral Classifiers. Pragmatics. Silk Road - HISTORY. Syncretism. Great Wall of China. Great Wall of China. Zhang Qian. Han dynasty. Western Asia. East Africa. Kra–Dai languages. Shan language. Tai languages. Kra–Dai languages. Austro-Tai languages. Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages. Hmong–Mien languages. Sino-Tibetan languages. Learn Japanese. Learn Japanese — Start speaking Japanese with Mango Languages. Learn Japanese – Tae Kim's Guide to Learning Japanese. Learn Japanese in just 5 minutes a day. For free. Japanese language. Southern Europe. Southeast Asia. Silk Road. Roots of the Arabic Language - Hebrew, Amharic, Aramaic & Maltese. A Sociolinguistic Comparison of Two Modern Semitic Languages: Hebrew and Amharic on JSTOR.
Amharic. Similarities between Hebrew and Amharic (this post is frequently updated) Why is Amharic so different to other Semitic languages like Arabic, Hebrew, Tigrinya, and Ge'ez? Bet. Bet. Afro Asiatic Language Family. Afro Asiatic Language Family. Biogeographic realm. Assyrian people. Assyrian people. Mesopotamia. Akkadian Empire. Babylonia.
East Semitic languages. 30th century BC. Eastern Aramaic languages. Akkadian language. Sahel. Chadic languages. Hausa language. Afro Asiatic Language Family. Metropolitan Borough of Greenwich. Royal Borough of Greenwich. Greenwich. Greenwich Mean Time. Royal Observatory, Greenwich. Prime meridian. Eastern Hemisphere. Europe. Eastern Europe. Georgia. Kutaisi.