

v04_id131_con_axialmu.jpg. Tolomatic Linear Actuator Blog: "Back and Forth" Linear actuator. Conceptual design of a basic traveling-nut linear actuator.
Note that in this example the lead screw (gray) rotates while the lead nut (yellow) and tube (red) do not. Floppy disc drive with leadscrew and stepper motor. Hydraulic pump. Gearpump with external teeth, note the rotational direction of the gears.
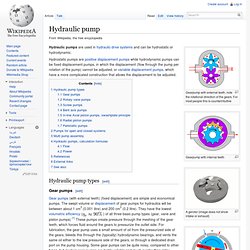
For most people this is counterintuitive Gearpump with internal teeth A gerotor (image does not show intake or exhaust) Fixed displacement vane pump Principle of screw pump (Saugseite = intake, Druckseite = outflow) Axial piston pump, swashplate principle Radial piston pump Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic. Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement (flow through the pump per rotation of the pump) cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pumps, which have a more complicated construction that allows the displacement to be adjusted. Essex robotic fish robot Jindong Liu homepage. The website dedicated to robotic fish. PPF-04, Koichi Hirata, NMRI, Japan The NMRI (National Maritime Research Institute) developed many projects of robotic fish (series PF and series PPF) with a view to apply, in the future, the capacities of fish to our boats and submarines.
The PPF-04 is one (all) small robotic fish of 19 cm and 400 g, remote controlled. Its size makes it possible to test it in a small tank (like a bath-tub). The study carried, inter alia, on the relation between the speed and the amplitude of the oscillations of the caudal fin. Robotic fish homepage of NMRI : Do not hesitate to visit the most possible pages: they contain photographs, diagrams, videos. Meet “Smoky,” the Robot Fish. German scientists are looking at how fish move through water to see if technology can be adapted to make shipping more friendly to underwater habitats.
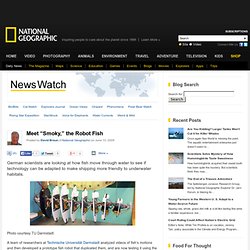
Photo courtesy TU Darmstadt A team of researchers at Technische Universität Darmstadt analyzed videos of fish’s motions and then developed a prototype fish robot that duplicated them, and are now testing it using the locomotional patterns of various species of fish in order to refine it and improve its efficiency, the university said in a statement today. “Their fish robot, dubbed ‘Smoky,’ consists of a ‘skeleton’ composed of ten segments enshrouded in an elastic skin that are free to move relative to one another and made to undergo snaking motions similar to those of fish by waterproof actuators.
Including its tail fin, the fish robot, which is a 5:1 scale model of a gilt-head sea bream, is 1.50 meters [about 5 feet] long.” Fish Robot As An Alternative Marine Propulsion System Of The Future. The team of Darmstadt researchers analyzed videos of fish’s motions and then developed a prototype fish robot that duplicated them, and are now testing it using the locomotional patterns of various species of fish in order to refine it and improve its efficiency.
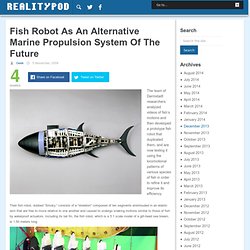
Their fish robot, dubbed “Smoky,” consists of a “skeleton” composed of ten segments enshrouded in an elastic skin that are free to move relative to one another and caused to undergo snaking motions similar to those of fish by waterproof actuators. Including its tail fin, the fish robot, which is a 5:1 scale model of a gilt-head sea bream, is 1.50 meters long. The researchers hope that use of their fish robot for ship propulsion will help prevent shoreline erosion and the underminings of submarine installations caused by ships’ screws. The fish robot’s “soft” drive action should also prevent the churning up of seabeds and riverbeds and its effects on marine plants and aquatic-animal populations. Popular on the Web. Pneumatic motor. A pneumatic motor or compressed air engine is a type of motor which does mechanical work by expanding compressed air.
Pneumatic motors generally convert the compressed air energy to mechanical work through either linear or rotary motion. Linear motion can come from either a diaphragm or piston actuator, while rotary motion is supplied by either a vane type air motor or piston air motor. Pneumatic motors have existed in many forms over the past two centuries, ranging in size from hand-held turbines to engines of up to several hundred horsepower. Some types rely on pistons and cylinders; others use turbines. Many compressed air engines improve their performance by heating the incoming air or the engine itself.
Classification[edit] Linear[edit] In order to achieve linear motion from compressed air, a system of pistons is most commonly used. Piston motors are the most commonly used in hydraulic systems. Rotary[edit] Application[edit] Robot Fish. The Earth Life Web, Fish Muscles. Gram for gram fish have more muscle than any other vertebrate, a male salmon or tuna can be nearly 70% muscle, which is one reason why fish are so good to eat.

The muscles of fish are layered rather than bundled as in the other vertebrates. Each segment, or sheet, of muscles is called a myomere or myotome and is separated from its neighbor by a sheet of connective tissue. Fish Swimming. So, all the fish has to do to remain in position in a vortex street, is to gently ride the vortices, gently swaying from one side to the other curling round to catch each of the vortices and have them run down the side of their bodies and push them upstream as in the diagrams.

Simple, elegant and very efficient. When it wants to dart away, it chooses upstream because it’s easier to form a strong vortex against the current. A sharp twist in the water and it spins itself away upstream to either create another vortex itself or hop a free ride from others it can sense in the water... The pinball effect. It has taken a couple of years but finally I understand Viktor Schauberger’s comment that has stuck in my mind ever since I read it: “fish don’t’ swim, they’re swum” Zero Friction?
The lessons we can learn from fish don’t stop here. Conclusion.