

Capitalism. Democratic Party (United States) Since the 1930s, the party has promoted a social liberal platform.[2][11][12] Until the late 20th century the party had a powerful conservative and populist wing based in the rural South, which over time has greatly diminished.
Today its Congressional caucus is composed mostly of progressives and centrists.[13] History The Democratic Party evolved from the Jeffersonian Republican or Democratic-Republican Party organized by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in opposition to the Federalist party of Alexander Hamilton and John Adams. The party favored republicanism, a weak federal government, states' rights, agrarian interests (especially Southern planters) and strict adherence to the Constitution; it opposed a national bank, close ties to Great Britain, and business and banking interests. Conservatism. Truth. Truth is most often used to mean being in accord with fact or reality,[1] or fidelity to an original or to a standard or ideal.[1]
Magic (paranormal) Magic or sorcery is an attempt to understand, experience and influence the world using rituals, symbols, actions, gestures and language.[1][2][3][4] Modern Western magicians generally state magic's primary purpose to be personal spiritual growth.[5] Modern theories of magic may see it as the result of a universal sympathy where some act can produce a result somewhere else, or as a collaboration with spirits who cause the effect.[6] The belief in and the practice of magic has been present since the earliest human cultures and continues to have an important religious and medicinal role in many cultures today.[7][8] Magic is often viewed with suspicion by the wider community, and is sometimes practiced in isolation and secrecy.[4]
Calm. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia CALM may refer to: Organisations Science/medicine terms.
Cold. Cold refers to the condition or subjective perception of having low temperature, the opposite of hot.
[note 1] A lower bound to temperature is the absolute zero, defined as 0 K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to −273.15 °C on the Celsius scale, −459.67 °F on the Fahrenheit scale, and 0 °R on the Rankine scale. Boy. A boy is a young male human, usually child or adolescent.
When he becomes an adult he's described as a man. The most apparent thing that differentiates a boy from a girl is that a boy typically has a penis while girls have a vagina. However, some intersex children with ambiguous genitals, and genetically female transgender children, may also be classified or self-identify as a boy. The term "boy" is primarily used to indicate biological sex distinctions, cultural gender role distinctions or both. The latter most commonly applies to adult men, either considered in some way immature or inferior, in a position associated with aspects of boyhood, or even without such boyish connotation as age-indiscriminate synonym.
Etymology The word "boy" comes from Middle English boi, boye ("boy, servant"), related to other Germanic words for boy, namely East Frisian boi ("boy, young man") and West Frisian boai ("boy"). Characteristics of boys Uses of the term "boy" and related terms. Royal family. A royal family is the immediate family of a king or queen regnant, and sometimes his or her extended family.

The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, while the terms ducal family, grand ducal family or princely family are more appropriate to describe the relatives of a reigning duke, grand duke, or prince. However, in common parlance members of any family which reigns by hereditary right are often referred to as royalty or "royals". Police. A police force is a constituted body of persons empowered by the state to enforce the law, protect property, and limit civil disorder.[1] Their powers include the legitimized use of force.
The term is most commonly associated with police services of a state that are authorized to exercise the police power of that state within a defined legal or territorial area of responsibility. Police forces are often defined as being separate from military or other organizations involved in the defense of the state against foreign aggressors; however, gendarmerie are military units charged with civil policing. As police are often interacting with individuals, slang terms are numerous. Many slang terms for police officers are decades or centuries old with lost etymology. Etymology History Ancient policing In Ancient Greece, publicly owned slaves were used by magistrates as police. Winter. Winter (/ˈwɪntər/) is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring.
It is caused by the axis of the Earth in the respective hemisphere being oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather, but when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter is associated with snow and freezing temperatures. Sadness. A detail of the 1672 sculpture Entombment of Christ, showing Mary Magdalene crying.
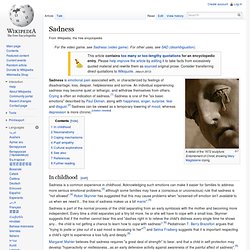
In childhood[edit] Sadness is a common experience in childhood. Acknowledging such emotions can make it easier for families to address more serious emotional problems,[3] although some families may have a (conscious or unconscious) rule that sadness is "not allowed".[4] Robin Skynner has suggested that this may cause problems when "screened-off emotion isn't available to us when we need it... the loss of sadness makes us a bit manic".[5] Sadness is part of the normal process of the child separating from an early symbiosis with the mother and becoming more independent. Every time a child separates just a tiny bit more, he or she will have to cope with a small loss. Neuroanatomy[edit] Coping mechanisms[edit] A sad adolescent When some individuals feel sad, they may exclude themselves, in doing so they take time to recover from this feeling.
Pupil empathy[edit] Pupil size may be an indicator of sadness. Sky. Water. Water in three states: liquid, solid (ice), and gas (invisible water vapor in the air). Clouds are accumulations of water droplets, condensed from vapor-saturated air. Video demonstrating states of water present in domestic life. Water is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H 2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms that are connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at standard ambient temperature and pressure, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state, steam (water vapor). Safe drinking water is essential to humans and other lifeforms even though it provides no calories or organic nutrients.
Chemical and physical properties Impact from a water drop causes an upward "rebound" jet surrounded by circular capillary waves. Water is the chemical substance with chemical formula H 2O: one molecule of water has two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom. The major chemical and physical properties of water are: Ice. A glacier is made from ice, itself resulting from snow accumulation.
Frozen water in the form of an ordinary (household) ice cube. The white zone in the center is due to tiny air bubbles. Ice is water frozen into a solid state. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities such as soil particles or air inclusions.