The twelve signs
> Blurfin
> Places
> Galaxy
> Constellations
Pisces (constellation)
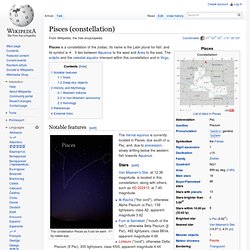
The constellation Pisces as it can be seen by naked eye.
Van Maanen's Star, at 12.36 magnitude, is located in this constellation, along with others, such as HD 222410, at 7.45 magnitude. CL 0024+1654 is a massive galaxy cluster that lenses the galaxy behind it, creating arc-shaped images of the background galaxy. The cluster is primarily made up of yellow elliptical and spiral galaxies, at a distance of 3.6 billion light-years from Earth (redshift 0.4), half as far away as the background galaxy, which is at a distance of 5.7 billion light-years (redshift 1.67).[1] 3C 31 is an active galaxy and radio source in Perseus located at a distance of 237 million light-years from Earth (redshift 0.0173). Its jets, caused by the supermassive black hole at its center, extend several million light-years in both directions, making them some of the largest objects in the universe.[1]
Aquarius (constellation)
(Unicode ♒), a representation of water.
In the Greek tradition, the constellation became represented as simply a single vase from which a stream poured down to Piscis Austrinus. The name in the Hindu zodiac is likewise kumbha "water-pitcher", showing that the zodiac reached India via Greek intermediaries. In the first century CE, Ptolemy's Almagest established the common Western depiction of Aquarius. His water jar, an asterism itself, consists of Gamma, Pi, Eta, and Zeta Aquarii; it pours water in a stream of more than 20 stars terminating with Fomalhaut, now assigned solely to Piscis Austrinus. The water bearer's head is represented by 5th magnitude 25 Aquarii while his left shoulder is Beta Aquarii; his right shoulder and forearm are represented by Alpha and Gamma Aquarii respectively.
Capricornus. (Unicode ♑).
Notable features[edit]
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac.
It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is (Unicode U+2650 ♐), a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus to the east.
Scorpius. Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac.
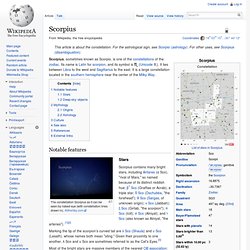
Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is Notable features The constellation Scorpius as it can be seen by naked eye (with constellation lines drawn in). AlltheSky.com Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco (Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco (Sargas, of unknown origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco (Girtab, "the scorpion"); π Sco (Iclil); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (also known as Alniyat, "the arteries"). [1][2]
Libra (constellation)
Libra /ˈliːbrə/ is a constellation of the zodiac.
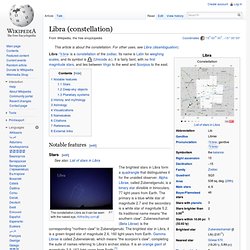
Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is The constellation Libra as it can be seen with the naked eye. AlltheSky.com The brightest stars in Libra form a quadrangle that distinguishes it for the unaided observer. Alpha Librae, called Zubenelgenubi, is a binary star divisible in binoculars, 77 light-years from Earth. Libra is home to several other binary and double stars. Σ Librae was formerly known as γ Scorpii despite being well inside the boundaries of Libra. Libra is home to one bright globular cluster, NGC 5897. Libra is home to the star Gliese 581, which has a planetary system consisting of at least 6 planets. The family of candidate habitable planets was extended in late September 2010 to include exoplanets around red dwarf stars because of Gliese 581 g, which is a tidally locked planet in the middle of the habitable zone.
Libra as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c.1825 H.
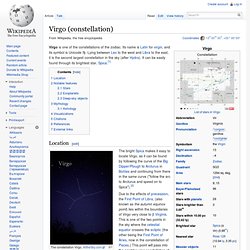
Virgo (constellation)
The bright Spica makes it easy to locate Virgo, as it can be found by following the curve of the Big Dipper/Plough to Arcturus in Boötes and continuing from there in the same curve ("follow the arc to Arcturus and speed on to Spica").[2] Besides Spica, other bright stars in Virgo include β Virginis (Zavijava), γ Vir (Porrima), δ Virginis (Auva) and ε Virginis (Vindemiatrix).
Other fainter stars that were also given names are ζ Virginis (Heze), η Virginis (Zaniah), ι Virginis (Syrma) and μ Virginis (Rijl al Awwa). The star 70 Virginis has one of the first known extrasolar planetary systems with one confirmed planet 7.5 times the mass of Jupiter. The star Chi Virginis has one of the most massive planets ever detected, at a mass of 11.1 times that of Jupiter. The sun-like star 61 Virginis has three planets: one is a super-Earth and two are Neptune-mass planets. SS Virginis is a variable star with a noticeable red color. Virgo possesses several galaxy clusters, one of which is HCG 62. H.A.
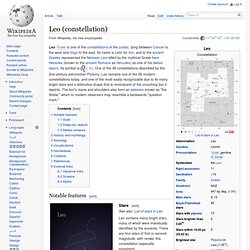
Leo (constellation)
The constellation Leo as it can be seen by the naked eye (the bright object in the centre of the picture is the planet Jupiter).
AlltheSky.com Leo contains many bright stars, many of which were individually identified by the ancients. There are four stars of first or second magnitude, with render this constellation especially prominent: There are several other bright double and binary stars in Leo. Zeta Leonis, called Adhafera, is an optical triple star. The other named stars in Leo are Mu Leonis, Rasalas (an abbreviation of "Al Ras al Asad al Shamaliyy," meaning "The Lion's Head Toward the South"); and Theta Leonis, Chertan or Coxa ("hip"). [2] Leo is also home to one bright variable star, the red giant R Leonis.
Cancer (constellation)
Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac.
Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as one. Its astrological symbol is (Unicode ♋). Cancer is a medium-size constellation with an area of 506 square degrees and its stars are rather faint, its brightest star Beta Cancri having an apparent magnitude of 3.5. It contains two stars with known planets, including 55 Cancri, which has five: one super-earth and four gas giants, one of which is in the habitable zone and as of such has expected temperatures similar to Earth.
Gemini (constellation)
Taurus (constellation)
Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac, which means it is crossed by the plane of the ecliptic.
Its name is a Latin word meaning "bull", and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:
Aries (constellation)
(Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere). Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand.










