

Alpine Biome. Alpine Biome at Animal Corner. Terrestrial Biome - Alpine During the summertime, temperatures in Alpine biomes reach around 40 to 60 degrees fahrenheit, however, come winter, temperatures are well below freezing and as the altitude increases, it can get much colder.
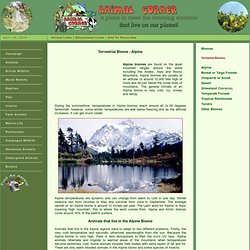
Alpine temperatures are dynamic and can change from warm to cold in one day. Winter seasons last from October to May and summer from June to September. The average rainfall on an Alpine biome is around 12 inches per year. The Latin word for 'Alpine' is 'Alps' meaning 'high mountain', this is where the word comes from. Animals that live in the Alpine Biome Animals that live in the Alpine regions have to adapt to two different problems. Alpine animals are naturally aided to adapt to Alpine climates by having shorter limbs such as legs, ears and tails. Despite the challenging landscape and harsh climate, here is a list of animals and birds that live in the Alpine Biome.
The Alpine Biome. The Alpine Biome Alpine biomes by their nature do not fit into a simple climatic scheme.

In general, as one ascends a mountain, temperature drops by about 10 C for every 1000 meters in altitude gained (a suspiciously round number!). This means that if you start at sea level at 30 C and go up 1,000 meters the temperature will be 20 C; at the top of a 3,000 meter mountain the temperature will be 0 C. This the only thing you can say about the climate in alpine regions is that it is colder than one would expect at sea level at the same latitude. Rainfall also varies considerably; as the rising air cools it loses the ability to retain moisture and clouds form, with the result of increasing precipitation on the side of a mountain exposed to winds. In these web pages the alpine "biome" will be considered to be the upper altitudes of mountains, where cooler climates give rise to communities which resemble (but do not duplicate) the taiga, tundra and ice biomes.
Alpine Biome. Did you know that the Arctic Tundra is the world's youngest biome?

It was formed 10,000 years ago. Located at latitudes 55° to 70° North, the tundra is a vast and treeless land which covers about 20% of the Earth's surface, circumnavigating the North pole. It is usually very cold, and the land is pretty stark. Almost all tundras are located in the Northern Hemisphere. Small tundra-like areas do exist in Antarctica in the Southern Hemisphere, but because it is much colder than the Arctic, the ground is always covered with snow and ice. Tundra comes from the Finnish word "tunturia", which means a barren land. The main seasons are winter and summer. The Arctic tundra is also a windy place and winds can blow between 30 to 60 miles (48 to 97 kilometers) per hour.
The tundra is basically like a desert when it comes to precipitation. There is barely any vegetation in the tundra, only about 1,700 different species, which isn't very much. Surprisingly there are animals in the tundra. Tundra. Tundras are among Earth's coldest, harshest biomes.
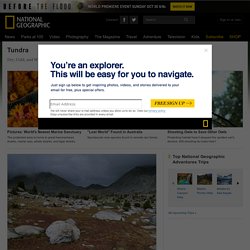
Tundra ecosystems are treeless regions found in the Arctic and on the tops of mountains, where the climate is cold and windy and rainfall is scant. Tundra lands are snow-covered for much of the year, until summer brings a burst of wildflowers. Mountain goats, sheep, marmots, and birds live in mountain, or alpine, tundra and feed on the low-lying plants and insects. Hardy flora like cushion plants survive on these mountain plains by growing in rock depressions where it is warmer and they are sheltered from the wind. Alpine. Tundra.