

Taking Emotions to the Workplace. HOW ARE YOU FEELING TODAY? Understanding Stress: Symptoms, Signs, Causes, and Effects. What is stress?

The Body’s Stress Response When you perceive a threat, your nervous system responds by releasing a flood of stress hormones, including adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones rouse the body for emergency action. Your heart pounds faster, muscles tighten, blood pressure rises, breath quickens, and your senses become sharper. These physical changes increase your strength and stamina, speed your reaction time, and enhance your focus—preparing you to either fight or flee from the danger at hand. Stress is a normal physical response to events that make you feel threatened or upset your balance in some way. The stress response is the body’s way of protecting you. The stress response also helps you rise to meet challenges. But beyond a certain point, stress stops being helpful and starts causing major damage to your health, your mood, your productivity, your relationships, and your quality of life.
How do you respond to stress? Stress doesn’t always look stressful. Contrasting and categorization of emotions. The contrasting and categorisation of emotions describes how emotions are thought to relate to each other.
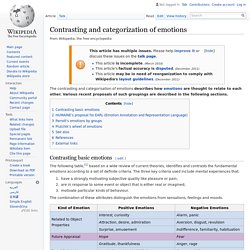
Various recent proposals of such groupings are described in the following sections. Contrasting basic emotions[edit] The following table,[1] based on a wide review of current theories, identifies and contrasts the fundamental emotions according to a set of definite criteria. The three key criteria used include mental experiences that: have a strongly motivating subjective quality like pleasure or pain;are in response to some event or object that is either real or imagined;motivate particular kinds of behaviour.
The combination of these attributes distinguish the emotions from sensations, feelings and moods. HUMAINE's proposal for EARL (Emotion Annotation and Representation Language)[edit] The emotion annotation and representation language (EARL) proposed by the Human-Machine Interaction Network on Emotion (HUMAINE) classifies 48 emotions.[2] List of Feeling Words. Human Emotions Chart - Free, Comprehensive Chart Of Emotions. List of Emotions - Human Emotional Chart. This list of human emotions plots the descending spiral of life from full vitality of the energy of life and high consciousness through half-vitality and half-consciousness down to death.

This list of emotions chart also enables to both predict and understand human behavior in all manifestations, making possible to predict the behavior of a potential spouse, a business partner, employee or friend - before you commit to a relationship. Numbers assigned to this list of emotions chart are arbitrary to show a relative degree or intensity of perceived emotion of happiness in accordance to available creative power or life's energy to the individual. Happiness encompasses a whole range of emotions from certain energy frequency level (4.0 enthusiasm level in our chart below) and up. - What we call the Happiness Domain. Neuroscientist Richard J. Davidson, Ph.D., described it well when he said: happiness “is a kind of a placeholder for a constellation of positive emotional states. " Recognize these emotions. The Passion and Reason 15 The book Passion and Reason provides clear definitions and descriptions of 15 separate emotions.
These are: Anger — Conspecific threat, trespass, loss attributed to an agent, unjust insult, thwarted goals, plea for justice Envy — Desiring other's stature objects Jealousy — Threat to sexual access. Fright — Concern for a future specific unpleasant event. Anxiety — Concern for an unidentified unpleasant event. The Rationalized 22 The book The Cognitive Structure of Emotions describes these 22 distinct emotions in an organized structure: The Search for Basic Emotions. Table of Contents Before reading this you might want to explore your own emotions.

One way to help a person do this is to study this web page: Understand, Identify Release Your Emotions. It was written by Mary Kurus. When you return to this page you can explore how you might want to classify your emotions. In a very simple way the left brain is very logical and linear and is always trying to figure out how the right brain sees the big picture and has more insight into emotions. Later in this web page, I describe seven basic emotions that seem to cover all the many presented on this web page. Language Confusing Before we start, a word of warning. Basic Emotions. List of Emotions. Emotion classification. Emotion classification, the means by which one emotion is distinguished from another, is a contested issue in emotion research and affective science.
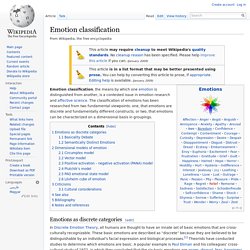
The classification of emotions has been researched from two fundamental viewpoints: one, that emotions are discrete and fundamentally different constructs; or two, that emotions can be characterized on a dimensional basis in groupings. Emotions as discrete categories[edit] Basicality Debate[edit] Humans' subjective experience is that emotions are clearly recognizable in ourselves and others.
This apparent ease of recognition has led to the identification of a number of emotions that are said to be basic, and universal among all people. On "basic emotion" accounts, activation of an emotion, such as anger, sadness, or fear, is "triggered" by the brain's appraisal of a stimulus or event with respect to the perceiver's goals or survival.