

Emotional Regulation Skills to Help Manage Difficult Emotions. Isn’t it great when life’s highs can trigger a fantastic feeling of dancing hand-in-hand with euphoria?

But it’s not too brilliant when life’s lows cause a spiral into an emotional meltdown. Getting to grips with our positive and negative emotions can help us to navigate all kinds of situations in a balanced way. Understanding how our emotions impact us, those around us, and how we interact with our social world requires the skill of Emotional Regulation (ER). The problem is, our emotional triggers are a complex web of feelings, perspective, contexts, past experiences, and physiological reactions.
Managing reactions to situations that rock our emotional status quo is challenging. For those who struggle to navigate their way around how they emotionally react to their own emotions and those of other people, it can be devastating. 5 Ways to Express and Identify Emotions Before we get started, you might want to try this exercise on Expressing emotions wisely. Our Favorite Activities for Toddlers. What is Emotion Regulation? + 6 Emotional Skills and Strategies. Emotional self-regulation. Emotional self-regulation or emotion regulation is the ability to respond to the ongoing demands of experience with the range of emotions in a manner that is socially tolerable and sufficiently flexible to permit spontaneous reactions as well as the ability to delay spontaneous reactions as needed.[1] It can also be defined as extrinsic and intrinsic processes responsible for monitoring, evaluating, and modifying emotional reactions.[2] Emotional self-regulation belongs to the broader set of emotion-regulation processes, which includes both the regulation of one's own feelings and the regulation of other people's feelings.[3][4] Theory[edit] Process model[edit] The process model of emotion regulation is based upon the modal model of emotion.
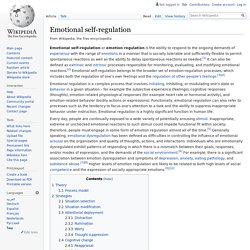
The modal model of emotion suggests that the emotion generation process occurs in a particular sequence over time. This sequence occurs as follows: Situation selectionSituation modificationAttentional deploymentCognitive changeResponse modulation. THE PARADOX: The Big Secret of Emotion Regulation. The mind-body system for regulating emotions is a paradox!
You know how it goes. Whether you are just starting a diet, or trying not to think about ‘that guy!’ The more important you make it to not think about something, the more you think about it! In the last two blogs the mind-body-vehicle and passengers metaphors helped explain why despite our best intentions, we can get off track, stuck at an impasse, or simply lost on the road of life. Our natural and auto-pilot instinct is to reduce our discomfort and move towards what feels good.
The big secret, that nobody ever teaches you, is that over time, what once ‘worked’ to make you feel better short-term, can make you feel worse long-term. Emotional Regulation Is Nonsense. Every time I hear the term “emotional regulation” (or “emotion regulation”) I throw a tiny fit inside my head.
And since it crops up often in my field, I’m throwing little fits all the time. (If you ask me what time it is, and I stare blankly at you, it’s because I’m having one of these fits. Give me a moment and then try again.) I don’t mind telling you I hate that phrase. I spit on it. Neuroscience & Emotional Intelligence in Change Management.
Regulation Strategies. Emotional Agility. Mind-Body Therapy. Mindful Emotion Regulation. 22 Emotion Regulation Worksheets & Strategies: Improve Your DBT Skills. Using the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (ERQ) Used to describe a person’s ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences, emotion regulation is a concept receiving ever-growing interest in mental health and psychotherapy research.

Regardless of the source, unchecked emotions have the potential to spin out of control and escalate to regrettable and sometimes distressing situations and actions. While most of us apply a range of strategies to adapt and cope with stressful situations, some of these approaches are more beneficial than others. The ability to identify, understand, and modify the intensity of one’s emotions is essential in the development of adaptive responses, particularly towards those emotions regarded as negative.
The following article will examine just some of the methods by which emotion regulation strategies can be measured and assessed, adapted versions for use with children and adolescents, and guidance on how to score and interpret the results. What is the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire? Hofmann, S. Regulation Strategies. Endogenous Opioid System. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Conflict Management. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Placebo.