

Dwarf Star Acts As Cosmic Magnifying Glass, Confirming Prediction Made Decades Ago. Astronomers have observed a white dwarf acting as a magnifying glass for another, Sun-like star that it is orbiting.
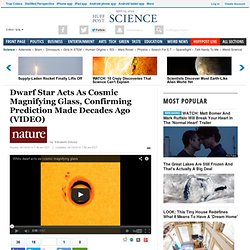
The binary star system, 808 parsecs (2,600 light years) away from Earth in the constellation Lyra, was previously classified as a possible exoplanet system. Using data from NASA’s Kepler spacecraft, physicists Ethan Kruse and Eric Agol of the University of Washington in Seattle observed an increase of just 0.1% in the larger star's brightness every 88 days, lasting for 5 hours. They say that the effect is the result of an orbiting white dwarf — a dense, compact, burnt-out star whose gravitational effects act as a magnifying glass every time it crosses the line of sight between its companion star and Earth. Kruse and Agol publish their findings in Science today. Massive bodies are known to distort space-time and bend the path of light travelling past them.
This story originally appeared in Nature News. Mysterious Ribbon Of Energy At The Edge Of The Solar System 'Still Mysterious' Report Scientists.
Triple star system 'can reveal secrets of gravity' Astronomers have discovered a unique triple star system which could reveal the true nature of gravity.
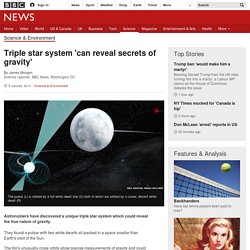
They found a pulsar with two white dwarfs all packed in a space smaller than Earth's orbit of the Sun. The trio's unusually close orbits allow precise measurements of gravity and could resolve difficulties with Einstein's theories. The results appear in Nature journal and will be presented at the 223rd American Astronomical Society meeting. "This triple system gives us a natural cosmic laboratory far better than anything found before for learning exactly how such three-body systems work and potentially for detecting problems with general relativity that physicists expect to see under extreme conditions," said Scott Ransom of the US National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Charlottesville, VA.
"This is a fascinating system in many ways, including what must have been a completely crazy formation history, and we have much work to do to fully understand it. " Gaia 'billion-star surveyor' lifts off. 19 December 2013Last updated at 10:57 GMT By Jonathan Amos Science correspondent, BBC News Launch of the Gaia satellite from Sinnamary in French Guiana Europe has launched the Gaia satellite - one of the most ambitious space missions in history.
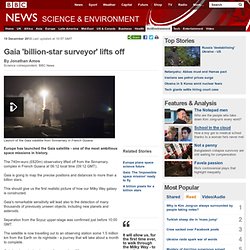
The 740m-euro (£620m) observatory lifted off from the Sinnamary complex in French Guiana at 06:12 local time (09:12 GMT). Gaia is going to map the precise positions and distances to more than a billion stars. This should give us the first realistic picture of how our Milky Way galaxy is constructed. Gaia's remarkable sensitivity will lead also to the detection of many thousands of previously unseen objects, including new planets and asteroids. Continue reading the main story “Start Quote It will allow us, for the first time ever, to walk through the Milky Way - to say where everything is, to say what everything is” End QuoteProf Gerry GilmoreCambridge University Separation from the Soyuz upper-stage was confirmed just before 10:00 GMT. Astronomers Find Impossible Planet 11 Times Bigger Than Jupiter. Astronomers have found a planet which shouldn't exist.
The planet, HD 106906b, is far larger than anything in our solar system at about 11 times the mass of Jupiter. But the truly weird thing about the planet is not its mass, but its distance from its star. HF 106906b orbits its host star at about 650 times the distance of the Earth to our Sun. And that's a problem, because current theories of planet formation can't really explain how it managed to get there. Above: artist's impression of a similar exoplanet "This system is especially fascinating because no model of either planet or star formation fully explains what we see," said Vanessa Bailey, from the University of Arizona, who led the team, according to Phys.org.
Usually, it is thought, planets either form close to their stars around small rocks similar to asteroids, or from a fast collapse of a distant disc of material further from the star itself. Smic Dawn: Three Galaxies Combine Into One In Dramatic Nasa Picture Of The Birth Of The Universe.