

Interval training. High-intensity interval training. Exercise strategy High-intensity interval training (HIIT), also called high-intensity intermittent exercise (HIIE) or sprint interval training (SIT), is a form of interval training, a cardiovascular exercise strategy alternating short periods of intense anaerobic exercise with less intense recovery periods, until too exhausted to continue.
Though there is no universal HIIT session duration, these intense workouts typically last under 30 minutes, with times varying based on a participant's current fitness level.[1] The intensity of HIIT also depends on the duration of the session. Procedure[edit] HIIT exercise sessions generally consist of a warm up period followed by repetitions of high-intensity exercises separated by medium intensity exercises for active recovery, then a cool down period. The high-intensity exercise should be done at near maximum intensity. There is no specific formula to HIIT. Dietary supplement.
Product that provides additional source of nutrients As a softgel capsule used for fish oil or large amounts of vitamin E As a shake and bottled powder Production of cod liver oil, one of the first dietary supplement products manufactured in the 18th century[1] A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement the diet when taken by mouth as a pill, capsule, tablet, or liquid.[2] A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or synthetic, individually or in combination, in order to increase the quantity of their consumption.
The class of nutrient compounds includes vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids and amino acids. Creating an industry estimated to have a 2015 value of $37 billion,[4] there are more than 50,000 dietary supplement products marketed just in the United States,[5] where about 50% of the American adult population consumes dietary supplements. Exercise. Bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness Exercise is any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.[1] It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, preventing aging, developing muscles and the cardiovascular system, honing athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, improving health[2] and also for enjoyment.
Fitness culture. Fitness culture is a sociocultural phenomenon surrounding exercise and physical fitness.
It is usually associated with gym culture, as doing physical exercises in locations such as gyms, wellness centres and health clubs is a popular activity. An international survey found that more than 27% of world total adult population attends fitness centres, and that 61% of regular exercisers are currently doing "gym-type" activities.[1] Street workout. Street workout for Spartans Tarraco in Calafell, Spain Street workout is divided in two main branches, the first one being strength training and the second dynamics.
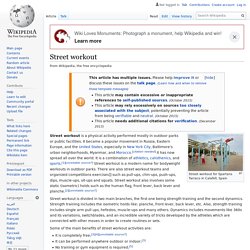
Strength training includes the isometric holds like: planche, front lever, back lever, etc. Also, strength training includes single arm pull ups, hefestos, muscle-ups and many others. Dynamics includes movements like 360s and its variations, switchblades, and an incredible variety of tricks developed by the athletes which are connected with other moves in order to create routines or sets. Some of the main benefits of street workout activities are: It is completely free;[3][4][unreliable source?] At the beginning of the 21st century, classic exercises were modified and combined with elements from other sports. Different groups developed their own style by combining classical calisthenics with exercises from gymnastics, break dance, hip hop and freerunning, or to develop new movements themselves.
Strength training. Strength training involves the performance of physical exercises which are designed to improve strength and endurance.
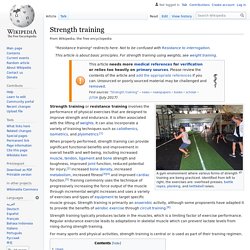
It is often associated with the use of weights but can take a variety of different forms.[1] Poor posture. Poor posture is the posture that results from certain muscles tightening up or shortening while others lengthen and become weak, which often occurs as a result of one's daily activities.
It may lead to pain, injury, or other health problems.[1][2] There are different factors which can have an impact on posture, including occupational activities and biomechanical factors such as force and repetition. Risk factors for poor posture also include psychosocial factors such as job stress and strain. Workers who have higher job stress are more likely to develop neck and shoulder symptoms.
Outline of exercise. Overview of and topical guide to exercise U.S.
Navy sailors exercising in the presence of their female instructor, 2010 Exercise – any bodily activity that enhances or log physical fitness and overall health and wellness. Fartlek. Fartlek, which means "speed play" in Swedish, is continuous training with interval training.[1] Fartlek runs are a very simple form of a long distance run.
Fartlek training “is simply defined as periods of fast running intermixed with periods of slower running. "[2] For some people, this could be a mix of jogging and sprinting, but for beginners it could be walking with jogging sections added in when possible. Ismakogie. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre.
Certaines informations figurant dans cet article ou cette section devraient être mieux reliées aux sources mentionnées dans les sections « Bibliographie », « Sources » ou « Liens externes »(août 2013). Améliorez sa vérifiabilité en les associant par des références à l'aide d'appels de notes. Long slow distance. Long slow distance (LSD) is a form of aerobic endurance training in running and cycling.[1][2] Physiological adaptations to LSD training include improved cardiovascular function, improved thermoregulatory function, improved mitochondrial energy production, increased oxidative capacity of skeletal muscle, and increased utilization of fat for fuel.[1] Ernst van Aaken, a German physician and coach, is generally recognized as the founder of the long slow distance method of endurance training.[3][4][5] History[edit] Joe Henderson[edit]
Méthode Feldenkrais. Un article de Wikipédia, l'encyclopédie libre. La Méthode Feldenkrais est une pédagogie où les élèves prennent conscience de leur mouvement dans l’espace et dans leur environnement, et des sensations kinesthésiques qui y sont reliées. Les apprentissages qu’elle permet de stimuler sont variés : la recherche d’une organisation plus aisée et efficace pour ses actions, tant dans la vie quotidienne que dans la pratique d’un sport ou d’un art,la recherche de souplesse des articulations, de coordination des mouvements, de mobilité de la cage thoracique et du bassin, de flexibilité de la colonne vertébrale,l’étude des tensions inutiles et de leur influence sur la respiration, la réflexion… Du fait de ce spectre assez large, la population pratiquant en France est elle aussi assez variée.
Deux groupes sont fortement représentés : les danseurs et danseuses, et les personnes du troisième âge. Reiki. Traditions[edit] Today many branches of Reiki exist, though there exist two major traditions, respectively called Traditional Japanese Reiki and Western Reiki. Traditional Japanese Reiki[edit] The term Traditional Japanese Reiki is normally used to describe the specific system that formed from Usui's original teachings[41] and the teachings that did not leave Japan. During the 1990s, Western teachers travelled to Japan in order to find this particular tradition of Reiki, though found nothing.
They therefore started to establish Reiki schools, and started to teach Reiki levels 1 and 2 to the Japanese. Usui Reiki Ryōhō Gakkai (臼井靈氣療法學會 in Traditional Chinese Characters, meaning "Usui Reiki Healing Method Learning Society")[43] is the name of the society of Reiki masters founded by Mikao Usui. Alexander Technique. Postural awareness technique The Alexander Technique, named after its creator Frederick Matthias Alexander, is an educational process that was created to retrain habitual patterns of movement and posture.
Alexander believed that poor habits in posture and movement damaged spatial self-awareness as well as health, and that movement efficiency could support overall physical well-being. He saw the technique as a mental training technique as well.[1]:221 Alexander began developing his technique's principles in the 1890s[2] in an attempt to address voice loss during public speaking.[1]:34–35 He credited his method with allowing him to pursue his passion for reciting in Shakespearean theater.[3] Category:Physical exercise. Category:Postural awareness techniques. Power training. A box jump being performed in a gym. Plyometrics are a basic and effective power training exercise which require little or no equipment. Jumping with the addition of weights, such as dumbbells or a trap bar, can lead to an even greater ability to perform powerfully.
Power training typically involves exercises which apply the maximum amount of force as fast as possible; on the basis that strength + speed = power.[1] Jumping with weights or throwing weights are two examples of power training exercises. Regular weight training exercises such as the clean and jerk and power clean may also be considered as being power training exercises due to the explosive speed required to complete the lifts.
Activity tracker. The Fitbit Surge, showing a clock display as an added feature. Samsung Galaxy Fit activity trackers An activity tracker, also known as a fitness tracker, is a device or application for monitoring and tracking fitness-related metrics such as distance walked or run, calorie consumption, and in some cases heartbeat. It is a type of wearable computer. The term is now primarily used for smartwatches that are synced, in many cases wirelessly, to a computer or smartphone for long-term data tracking. There are also independent mobile and Facebook apps.[1] Some evidence has found that the use of these type of devices results in less weight loss rather than more.[2] Sleep tracker devices have a tendency to underdetect wakefulness.[3] History[edit] The term "activity trackers" now primarily refers to wearable devices that monitor and record a person's fitness activity.
List of sports. Outline of sports. Bodybuilding. Control and development of musculature Bodybuilding is the use of progressive resistance exercise to control and develop one's musculature for aesthetic purposes.[1] An individual who engages in this activity is referred to as a bodybuilder. Anaerobic exercise. Physical exercise intense enough to cause lactate formation. CrossFit. CrossFit is a branded fitness regimen created by Greg Glassman.[1] It is a registered trademark of CrossFit, Inc.,[2] which was founded by Glassman and Lauren Jenai in 2000.[3][4][5] CrossFit has been criticized for allegedly causing people to suffer from unnecessary injuries[11] and exertional rhabdomyolysis, a possible life-threatening breakdown of muscle from extreme exertion.[12][13][14] Outline of sports.
Outline of sports. Brazilian jiu-jitsu. Brazilian jiu-jitsu (/dʒuːˈdʒɪtsuː/; Portuguese: [ˈʒiw ˈʒitsu], [ˈʒu ˈʒitsu], [dʒiˈu dʒiˈtsu]) (BJJ; Portuguese: jiu-jitsu brasileiro) is a martial art, combat sport, and a self defense system that focuses on grappling and especially ground fighting. Brazilian jiu-jitsu was formed from Kodokan Judo ground fighting (newaza) fundamentals that were taught by a number of individuals including Takeo Yano, Mitsuyo Maeda and Soshihiro Satake. Arnis. Right of self-defense. Pencak-Silat. Wuxia. Self-defense. Yoga. Course d'orientation. Course d'orientation.