

Unearthing the Antibacterial Mechanism of Medicinal Clay: A Geochemical Approach to Combating Antibiotic Resistance. Inner Workings: Combating antibiotic resistance from the ground up. GetSharedSiteSession?rc=1&redirect= To view the full text, please login as a subscribed user or purchase a subscription.
Click here to view the full text on ScienceDirect. Fig 1 Total antibiotic consumption in selected countries, 2000 and 2010. GetSharedSiteSession?rc=1&redirect= Infographic. Antibiotic use in agriculture varies greatly between country. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011 Marshall 718 33. Antibiotic use in animals - Antibiotic Resistance - Uppsala University. Antibiotics are often used in modern animal production and it has been estimated that the consumption in the food animal sector will increase by two-thirds between 2010 and 2030.
Similar to the situation in humans, antibiotic consumption has been shown to increase the risk for carriage or infections with resistant bacteria in the animal population. In most cases, antibiotics are administered to healthy animals for growth promotion or prevention of disease rather than for therapeutic purposes. There are great variations in antibiotic use in animals between countries, which cannot be explained only by differences in animal species and production systems. Antibiotics are sometimes used to compensate for poor farming practices and are expected to improve production. The Ethical Significance of Antimicrobial Resistance.
The Rise of Antiobiotic Resistant Infections. ReAct facts burden of antibiotic resistance May 2012. Scientists reveal the frightening speed at which bacteria can develop antibiotic resistance. Maryn McKenna: What do we do when antibiotics don’t work any more? Could ants be the solution to antibiotic crisis?
Scientists have pinpointed a promising new source of antibiotics: ants.
They have found that some species – including leaf-cutter ants from the Amazon – use bacteria to defend their nests against invading fungi and microbes. Chemicals excreted by the bacteria as part of this fight have been shown to have particularly powerful antibiotic effects and researchers are now preparing to test them in animals to determine their potential as medicines for humans. Doctors say new antibiotics are urgently needed as superbug resistance to standard antimicrobial agents spreads. More than 700,000 people globally now die of drug-resistant infections each year, it is estimated – and some health officials say this figure could be even higher.
Last week, UN secretary general Ban Ki-moon, speaking at the first general assembly meeting on drug-resistant bacteria, said antimicrobial resistance was now a fundamental threat to global health. “Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem,” he said last week. Researchers Nanoengineer Kryptonite For Antibiotic Resistant Superbugs. Credit: BBC/YouTube A research team at the University of Melbourne led by graduate student Shu Lam has nanoengineered a peptide polymer that attacks and kills a deadly class of drug-resistant bacteria.
The polymer selectively targets bacteria and is not harmful to healthy human tissue. A superbug that is resistant to a last-line-of-defense antibiotic failed to develop resistance to the polymer after many generations of exposure. The discovery of antibiotics is often described as revolutionizing 20th century medicine. Lam’s team may have taken the first steps toward doing the same for the 21st century.
Antimicrobial Resistance. England’s chief medical officer warns of ‘antibiotic apocalypse’ The “antibiotic apocalypse” may already be upon us.

According to Dame Sally Davies, chief medical officer for England, 50,000 people are dying every year in Europe and the US from infections that antibiotics have lost the power to treat. Davies has been at the forefront of the UK’s efforts against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and taken on a global leadership role. She has described the threatened loss of antibiotics to the world as on a par with terrorism and climate change. As the final report of Jim O’Neill, the economist charged by the prime minister with finding solutions to the crisis, was published, Davies warned that the death toll was already high and our life spans, which once seemed to be forever lengthening, may fall.
Combating Antimicrobial Resistance: Policy Recommendations to Save Lives. , Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA)* Correspondence: Robert J.

Guidos, 1300 Wilson Boulevard, Suite 300, Arlington, VA 22209 (rguidos@idsociety.org). Antimicrobial resistance is recognized as one of the greatest threats to human health worldwide [1]. Drug-resistant infections take a staggering toll in the United States (US) and across the globe. Publications. Superbugs will 'kill every three seconds' Image copyright Science Photo Library A global revolution in the use of antimicrobials is needed, according to a government backed report.

Lord Jim O'Neill, who led the Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, said a campaign was needed to stop people treating antibiotics like sweets. It is the first recommendation in the global plan for preventing medicine "being cast back into the dark ages". Antibiotic basics - Antibiotic Resistance - Uppsala University. Antibiotics are drugs used to treat bacterial infections in humans and animals.
The word comes from the Greek words ‘anti’, meaning ‘against’, and ‘biotikos’, meaning ‘concerning life’. Antibiotics function by interfering with essential processes or structures in the bacterial cell. This either kills the bacterium or slows down bacterial growth. Importantly, antibiotics are not active against viruses. Therefore, they should not be used for viral infections, such as common cold, most upper respiratory infections, the flu, viral gastroenteritis or measles. Microbial Friends Location. Bacteria basics - Antibiotic Resistance - Uppsala University. Bacteria are found all around us; in the air we breathe, in the soil and water, even inside and on our bodies.
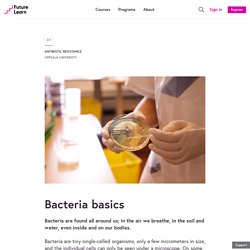
Bacteria are tiny single-celled organisms, only a few micrometers in size, and the individual cells can only be seen under a microscope. On some surfaces, for example when grown on agar plates in the laboratory, bacteria can form colonies that can be made up of several hundred thousands of cells and thus are visible to the eye.
Colonies of Salmonella typhimurium growing on an agar plate. Courtesy of Dr. M. Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and common pathogens Bacteria can be broadly categorized into two groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Microbial Friends Function. Factsheet Important milestones. Antibiotic pyramid. Factsheet Risks for the individual. A doctor's reality - Antibiotic Resistance - Uppsala University. 0:07Skip to 0 minutes and 7 secondsAs an infectious disease physician, I prescribe antibiotics on a daily basis.
And although there are antibiotic guidelines at a hospital that antibiotics should be used for certain indications, the choice of therapy is often difficult. First, you have to determine the likelihood of the patient being infected at all. Then you have to distinguish bacterial infection from viral and other infections that shouldn't be treated with antibiotics at all. In most cases, this can be assessed based on the history of symptoms and clinical examinations. Blood samples, x-rays, CT scans, and other investigations are, at this stage, helpful to diagnose the infection site and probable pathogen.
Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescriptions Among US Ambulatory Care Visits, 2010-2011.