

Automatic transmission. Syncromesh gearbox. Baulk ring. Drive shaft phasing. Straight gear.
All Gear Types. Helical Gear: Helical gear is a cylindrical shaped gear with helicoid teeth.
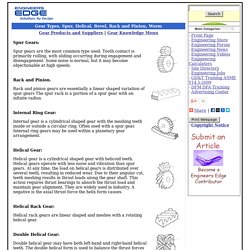
Helical gears operate with less noise and vibration than spur gears. At any time, the load on helical gears is distributed over several teeth, resulting in reduced wear. Due to their angular cut, teeth meshing results in thrust loads along the gear shaft. This action requires thrust bearings to absorb the thrust load and maintain gear alignment. Helical Gear: Helical gear is a cylindrical shaped gear with helicoid teeth. The Final Drive.
Hypoid gears. Double Helical gears. Phasing. Spur Gear. Universal joint. Multi coil clucth. Diaphram-clutch. Cone clutch. Universal joint. GCSE Bitesize: Gears: 1. Internal cone clutch. Plate clutch. Three shafts of a gearbox. Propshaft with center bearing. What is a Differential?" The differential is a device that splits the engine torque two ways, allowing each output to spin at a different speed.
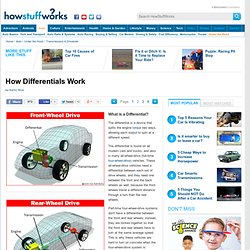
The differential is found on all modern cars and trucks, and also in many all-wheel-drive (full-time four-wheel-drive) vehicles. These all-wheel-drive vehicles need a differential between each set of drive wheels, and they need one between the front and the back wheels as well, because the front wheels travel a different distance through a turn than the rear wheels. Part-time four-wheel-drive systems don't have a differential between the front and rear wheels; instead, they are locked together so that the front and rear wheels have to turn at the same average speed.
This is why these vehicles are hard to turn on concrete when the four-wheel-drive system is engaged. All Gears. Four wheel drive. Spiral bevel gear. Rear wheel drive. Final Drive.