

Så anlägger du ett surjordsparti - Gröna rader. Grönsaker bäst i jord med lågt pH - Gröna rader. Kalka inte jorden om du inte vet att den har väldigt lågt pH.
Forskning har visat att grönsaker och de flesta andra växter trivs bäst i en lätt sur jord med ett pH-värde mellan 5,5 och 6,5. Text: Margareta Magnusson, Hortonom och agronomie doktor, SLU Umeå Här upptäckte jag först att broccoli stortrivs på en lätt jord med pH kring 5,0. Gödslingen bestod av kogödsel och grönmassa. Som nybliven hortonom i början av 1980-talet jobbade jag som trädgårdsrådgivare för yrkesodlare i norra Sverige, med grönsaksodling och växtnäring som främsta intresse. Växtnäringsstudier i norr När jag så efter några år började jobba vid Sveriges lantbruksuniversitet (SLU) vid trädgårdsavdelningen på Röbäcksdalen i Umeå fick jag äntligen möjlighet att specialstudera växtnäringsbehovet för grönsaker.
Försök med olika typer avgödsel Vi provade och kombinerade olika typer av gödselmedel, både mineralgödsel och organiska gödselmedel, främst kogödsel. Övre bilden: Vitlök på våren i min egen KRAV-certifierade odling. How to Prepare Garden Soil for Planting. Healthy soil is the basis of healthy plants and a healthy environment. When garden soil is in good shape there is less need for fertilizers or pesticides. As author and respected gardener Frank Tozer writes, “When building soil you not only improve your plants health, but you can also improve your own.” How to Identify the Soil Type in Your Garden - Earthly Mission. Groups. Testimini tokes be lushte shtepije me... - Hikmete Boshnjaku. How Plants Use Nitrogen - Organic Gardening - Heirloom Gardener.
Farmers, gardeners, and students of science all know that plants need an environmental supply of nitrogen to survive, much less thrive.
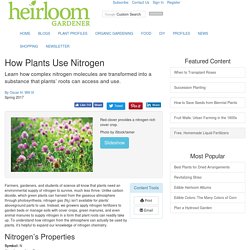
Unlike carbon dioxide, which green plants can harvest from the gaseous atmosphere through photosynthesis, nitrogen gas (N2) isn’t available for plants’ aboveground parts to use. Instead, we growers apply nitrogen fertilizers to garden beds or manage soils with cover crops, green manures, and even animal manures to supply nitrogen in a form that plant roots can readily take up. To understand how nitrogen from the atmosphere can actually be used by plants, it’s helpful to expand our knowledge of nitrogen chemistry. Nitrogen’s Properties Symbol: NAtomic number: 7Atomic mass: 14.0067 u ± 0.0001 uElectron configuration: 1s22s22p3Electrons per shell: 2,5Melting point: -346 degrees FahrenheitBoiling point: -320.4 degrees Fahrenheit How Nitrogen Works in the Soil Fixing Nitrogen with Legumes Oscar H.
Soil Nutrient Deficiencies and How to Fix Them - The Free Range Life. The secret to richer, carbon-capturing soil? Treat your microbes well. Imagine if someone invented machines to suck carbon out of the atmosphere — machines that were absurdly cheap, autonomous, and solar powered, too.
Wouldn’t that be great? But we already have these gadgets! They’re called plants. The problem is, plants die. So there’s one hurdle remaining: We have to figure out how to lock away the carbon in dead plants so that it doesn’t just return to the atmosphere. Soil. Soil is the mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids and a myriad of micro- and macro- organisms that can support plant life.
It is a natural body that exists as part of the pedosphere and it performs four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means of water storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of the atmosphere; and it is a habitat for organisms that take part in decomposition and creation of a habitat for other organisms.
Soil is considered the "skin of the earth" with interfaces between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere.[1] Soil consists of a solid phase (minerals & organic matter) as well as a porous phase that holds gases and water.[2][3][4] Accordingly, soils are often treated as a three-state system.[5] Overview[edit] Soil is a major component of the Earth's ecosystem. Soil. An important factor influencing the productivity of our planet's various ecosystems is the nature of their soils.
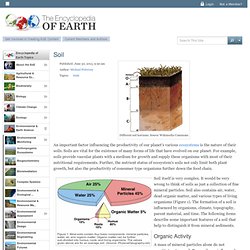
Soils are vital for the existence of many forms of life that have evolved on our planet. For example, soils provide vascular plants with a medium for growth and supply these organisms with most of their nutritional requirements. Soil Structure & Composition. Sunday, 06 June 2010 07:35 The Plant Lady Living Matter Mostly in the top 4" of the soil.
Good guys & bad guys...but large volume & diversity control the trouble makers by making it a competive environment for resources. Soil and Health Library. Soilcomposition. How to Assess Soil Composition. The health of garden plants depends on the soil's composition — the proper balance of mineral pieces, organic matter, air, and water.
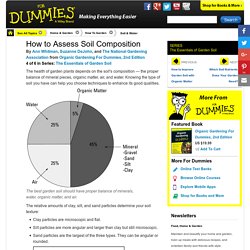
Knowing the type of soil you have can help you choose techniques to enhance its good qualities. The best garden soil should have proper balance of minerals, water, organic matter, and air. The relative amounts of clay, silt, and sand particles determine your soil texture: Clay particles are microscopic and flat. Silt particles are more angular and larger than clay but still microscopic. Determine the type of soil you have. For most plants, the ideal mixture is approximately 40 percent sand, 40 percent silt, and 20 percent clay. Clay soils are naturally fertile, but the individual particles are so small that they pack tightly, leaving little room for water and air. 8 Steps for Making Better Garden Soil. Starting to build a new garden isn’t difficult.
Most people begin by going out into their yards with a shovel or garden tiller, digging up the dirt and putting in a few plants. Following the organic and natural methods, add a little mulch or compost, and you’re well on your way to make good soil for your homegrown vegetables. But in the long run, the success of your garden depends on making healthy garden soil. Testing Your Soil pH Without a Kit. I’m always looking for quick tips to make my gardening chores easier.
I ran across a couple of gardening hacks about testing your soil pH without a kit and I thought I would try them out and see what I need to do with my garden. Let’s do a little kitchen chemistry! But first… Build Million Dollar Garden Soil - Life Is Just Ducky. It’s not pretty to look at, tasty to eat, or a juicy tidbit to tell our friends, but without it you can kiss the hopes of a great garden goodbye.
What is it? So how do you get it? Building Fertile Soil - Organic Gardening. I Love My 4X4 But... Cam finds getting around in the country, especially in the winter, so much easier with his 4X4 truck... Composting Humanure. Soil Amendment, When and What to Add to your Organic Vegetable Garden Q&A workwithnature. Soil Structure & Composition. "Weeds" as Soil Indicators. What Should I Do? By Phil Williams Wednesday, May 7, 2014, 9:19 AM The types of “weeds” that grow seemingly spontaneously in your garden are telling you valuable information about your soil and microclimate if you care to listen. There are certain “weeds” that appear when the soil has been degraded to rehabilitate the soil back to life, or simply as a protectant cover when we leave the soil bare, and open to the elements.
These unappreciated plants do all the hard work to make their home eventually no longer suitable for themselves. Plantain If you have hard compacted soil, expect “weeds” with strong taproots to show up to bust up the compaction. If you have a wet area that is not draining well, expect plants that like those conditions like sedges and goldenrod. The Importance of Carbon in the Soil. Tolerate drought better. Organic matter acts like a sponge, soaking up extra water and releasing it when needed. Grow larger and more vigorously. Understanding the Soil. Quotes from Understanding the Soil Processes Most of us will agree that the soil is the major natural resource available to mankind. Yet it is and has been abused by us to the point of self destruction. Many past civilizations have perished due to their abuse of the soil (like Mesopotamia and the Mayan civilization).
Why didn't anyone stop the destruction? Types of humus in soils. Humus occurs in soils in many types, differentates in regard to morphology and fractional composition. A type of humus is it a morphological form of naturals accumulation of humic substances in profile or on the surface of soil, conditioned by general direction of soil-forming process and humification of organic matter. Your Garden’s Soil pH Matters - Organic Gardening. Właściwości gleby - jak zbadać glebę w ogrodzie.