

This is a guide for parents on the different methods of reinforcements and punishments suitable for influencing their teenager's behaviours and keeping them on the right track.
This guide is meant to be as interactive as possible with explanations on punishments and reinforcements.
Operant conditioning: Positive-and-negative reinforcement and punishment. Reinforcement and Punishment (Positive and Negative) - Examples and Explanation.
Learning: Negative Reinforcement vs. Punishment. Positive and Negative Punishment. Difference Between Positive and Negative Punishment. Positive vs Negative Punishment - Psychestudy. Punishment is a fundamental concept of Operant Conditioning, whose major objective is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior from occurring again.
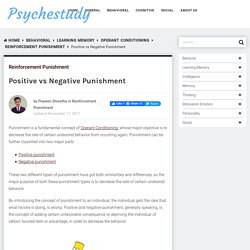
Punishment can be further classified into two major parts These two different types of punishment have got both similarities and differences, as the major purpose of both these punishment types is to decrease the rate of certain undesired behavior. Schedules of Reinforcement: When to use positive and negative reinforcement – Parenting With Psychology. I’m back at my keyboard after a few weeks’ hiatus during which I spent all my free time landscaping.

I completely understand how the stereotypical scene of the stay at home mom working out in the garden developed. You can use your hands in a productive manner, making progress rather than just cleaning up and fixing things. There are small, well-defined projects that can be accomplished and checked off your list rather than the ongoing and endless refinement of child rearing. And perhaps the most appealing feature of gardening is that your plants cannot talk, whine, yell, etc. Back to the topic at hand, we’ve already had an introduction to operant conditioning (see Understanding Reinforcement vs. Rewarding behavior is key to parenting teens, study suggests. Parenting is hard, and parenting teens brings about an entirely new set of challenges, from keeping their rooms clean to getting them home before curfew.
But, a new study suggests parents who want their teenagers to keep their grades up could have better success if they focus more on rewarding good behavior and less on threatening to punish the bad. According to the report, published in PLOS Computational Biology, British researchers have found that adolescents focus well on positive incentives, but have difficulty staying motivated to avoid penalties. The study shows that teens and adults learn in different ways, according to the study’s lead author Stefano Palminteri, a researcher with the Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience at University College London.
It suggests that “in some cases positive feedback may have more of an effect than negative feedback on learning” in adolescents. “Rewards give them something they want to think about,” Allen said. Examples of Positive and Negative Reinforcement. Positive Reinforcement Example. Positive Reinforcement: Definition. Difference Between Positive and Negative Reinforcement. Variable ratio schedule of reinforcement. Fixed Ratio Schedules of Reinforcement. Schedules Reinforcement 3: Interval Schedules. Operant Conditioning (B.F. Skinner)
How Reinforcement and Punishment Modify Behavior Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning normally attributed to B.F. Skinner, where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Parenting Children with Positive Reinforcement (Examples + Charts) Children don’t come with instructions and discipline is often experienced by parents and children alike as an arena where our will and wits are tested.
Positive reinforcement is only one of many forms of discipline, but from the perspective of positive psychology, it may as well be the most important one as it focuses on amplifying what is already good in our children and in ourselves as their caretakers. Positive reinforcement as a form of positive discipline allows us to tap into our children’s individual strengths, draw attention to their personality traits and interests, and as a result give us an opportunity to connect, communicate effectively, and ultimately empower them to be more of themselves. Before you read on, we thought you might like to download our 3 Positive Psychology Exercises for free. You can download the free PDF here. 12 Examples of Positive Punishment & Negative Reinforcement. You might be thinking that “positive punishment” sounds like an oxymoron, after all, how can punishment be positive?
Not many people “like” punishment, right? The disconnect in understanding this concept comes from the usage of the word “positive;” here at PositivePsychology.com, we generally use the term “positive” to refer to things that are inherently good, things that are life-giving, and things that promote thriving and flourishing. The concept of positive punishment comes from a very different era and a very different perspective on psychology; namely, the 1930s and behaviorism.