

Skin and scales, feathers and fur - Digital book. Photosynthesis for Kids. What is Photosynthesis?
The word photosynthesis can be separated to make two smaller words: “photo” which means light “synthesis” which means putting together. Fun Photosynthesis Facts for Kids. All living things need energy to live, and energy comes from food.
But, have you ever seen plants munching on pizza or eating a bowl of cereal? Nope. Predator and Prey in an Ecosystem. Animal Partnerships. —By Arden Dore Imagine life without your best friend.
Who would you hang out with and talk to about your problems? Life would be so lonely! You rely on your friends for companionship, fun, and support. Animals rely on each other, too. GCSE Bitesize: Predators and prey. What are some examples of predator-prey relationships? Ants helping stick insects?: ABC online education. What are some examples of mutualism between animals?
In the mutualistic relationship between oxpeckers and zebras, the bird lives on the zebra, where it feeds on the bugs and parasites on the skin.
The oxpecker benefits by getting food, and the zebra gains from pest removal. In case of danger, the oxpeckers fly upward while screaming a warning of the looming danger. The bacteria found in humans' digestive tracts help in food digestion. The “good” bacteria feed on the foods that cannot be completely digested by humans. By feeding on this food, the bacteria stay alive. Who's for dinner? (food chain/ food web) - game. What are Food Chains and Food Webs. Herbivore - an animal that eats plants.

(See photos) Carnivore - an animal that eats other animals. (See photos) Omnivore - an animal that eats both plants and animals eg bears and humans. (See photos) Producer - usually a green plant that produces its own food by photosynthesis Primary Consumer - Animals that consume only plant matter. They are herbivores - eg rabbits, caterpillars, cows, sheep, and deer. BBC Bitesize - KS3 Biology - Food chains and food webs - Revision 1. What is the difference between food chains and food webs?
THE SUN provides food for GRASSThe GRASS is eaten by a GRASSHOPPERThe GRASSHOPPER is eaten by a FROGThe FROG is eaten by a SNAKEThe SNAKE is eaten by a HAWK.

TREES produce ACORNS which act as food for many MICE and INSECTS.Because there are many MICE, WEASELS and SNAKES have food.The insects and the acorns also attract BIRDS, SKUNKS, and OPOSSUMS.With the SKUNKS, OPPOSUMS, WEASELS and MICE around, HAWKS, FOXES, and OWLS can find food.They are all connected! Like a spiders web, if one part is removed, it can affect the whole web. KS2 Bitesize Science - Food chains : Read. KS2 Science - Food chains. Finding out how you move and grow.

Can you label the human skeleton? When you've finished move onto the animal skeletons. Do you know which groups living things belong to? Look at the plants and animals as they go past. Can you drag them into the correct groups? Fabulous Food Chains: Crash Course Kids #7.1. Living Things Change: Crash Course Kids #41.1. When it rains in the desert: ABC online education. A haven in the harsh desert heat: ABC online education. How do mangrove trees live in mud and sea water?: ABC online education. 00:00:05:11NARRATOR:This mangrove area is a very special place for Jacobi, Tyson, their dad and granddad.00:00:16:24BIRD:It's a special place for me too.00:00:21:10NARRATOR:You'll soon see lots of reasons why mangroves are special.

Listen to that squishy sound. The ground is very wet. That's because twice a day seawater comes in and floods this whole area. This is what this mangrove area looked like about six hours ago at high tide. The water reached the branches on some of the trees. How fire affects NSW plants and animals. Fire heats the soil, cracking seed coats and triggering germination; it triggers woody seed pods held in the canopy to open, releasing seed onto a fresh and fertile ash bed; it clears thick understorey reducing competition for seedlings; it encourages new growth that is food for many animals; and, it creates hollows in logs and trees that are used by animals for nesting and shelter.
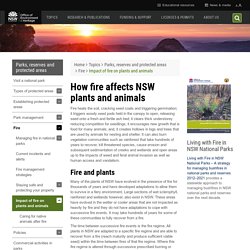
It can also burn vegetation communities such as rainforest that take hundreds of years to recover, kill threatened species, cause erosion and subsequent sedimentation of creeks and wetlands and open areas up to the impacts of weed and feral animal invasion as well as human access and vandalism. Fire and plants Many of the plants of NSW have evolved in the presence of fire for thousands of years and have developed adaptations to allow them to survive in a fiery environment.
Large sections of wet sclerophyll, rainforest and wetlands however, also exist in NSW. Australian Government - Australian Emergency Management Institute. 5 unexpected ways that wildfires affect wildlife, ecosystems of forests. By By Heather Janssen, AccuWeather.com Staff Writer June 10, 2016, 4:27:12 AM EDT Wildfires have scorched more than 9 million acres in the United States so far this year, destroying buildings and homes in their paths.
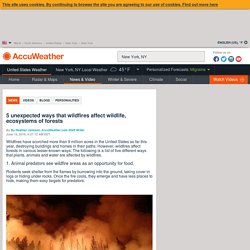
However, wildfires affect forests in various lesser-known ways. The following is a list of five different ways that plants, animals and water are affected by wildfires. 1. Rodents seek shelter from the flames by burrowing into the ground, taking cover in logs or hiding under rocks. Australia’s ecosystems: Drought – Science – Skwirk Interactive Schooling Year 8, NSW. Drought is part of the Australian environment and affects more ecosystems than fire or flood.
Australia is the driest inhabited continent and the climate is highly variable across the continent generally, as well as from year to year. Droughts can have a devastating effect on large areas of land and can destroy both agricultural and natural ecosystems. Drought can also degrade the land and affect the way land is used in the future. What is drought? There is no universal definition of drought - it depends on the climate of the area.