

History: Vikings. Vikings - DK Find Out. Viking longship Viking longship The Vikings built long, narrow ships that could travel incredible distances across rough seas.

Viking longship › Explorers Explorers Thanks to their sturdy ships, the Vikings travelled widely across the Northern Hemisphere. Viking explorers › Vikingburials Vikingburials Wealthy Vikings were sometimes buried along with their ships. Viking burial › Viking crafts Viking crafts The Vikings were skilled craftsmen, creating high-quality cloth, delicate jewellery, and strong weapons and armour. Viking crafts › Viking gods Viking gods At the front of a Viking warship was a figurehead, perhaps representing a warrior spirit. Viking gods › Viking warriors Viking warriors This wall of shields protected the rowers from attack. Viking warriors › Vikingtraders Vikingtraders The deck of a longship covered a storage space where goods could be kept for trade.
Viking traders › Who werethe Vikings? The Vikings. Primary History - Vikings. How the Vikings Worked - HowStuffWorks. It is late morning at a monastery on the coast of Ireland.
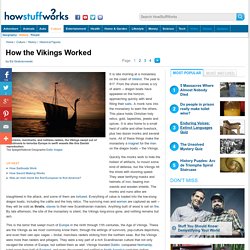
The year is 817. From the shore comes a cry of alarm -- dragon boats have appeared on the horizon, approaching quickly with wind filling their sails. A monk runs into the monastery to warn the others. This place holds Christian holy relics, gold, tapestries, jewels and spices. It is also home to a small herd of cattle and other livestock, plus two dozen monks and several nuns.
Vikings - Exploration. The mid-10th-century reign of Harald Bluetooth as king of a newly unified, powerful and Christianized Denmark marked the beginning of a second Viking age.
Large-scale raids, often organized by royal leaders, hit the coasts of Europe and especially England, where the line of kings descended from Alfred the Great was faltering. Harald’s rebellious son, Sven Forkbeard, led Viking raids on England beginning in 991 and conquered the entire kingdom in 1013, sending King Ethelred into exile. Sven died the following year, leaving his son Knut (or Canute) to rule a Scandinavian empire (comprising England, Denmark, and Norway) on the North Sea. After Knut’s death, his two sons succeeded him, but both were dead by 1042 and Edward the Confessor, son of the previous (non-Danish) king, returned from exile and regained the English throne from the Danes.
Upon his death (without heirs) in 1066, Harold Godwinesson, the son of Edward’s most powerful noble, laid claim to the throne. Vikings Daily Life. Upper class Vikings were called Jarls (from which we derive our word Earl).

Below them were a class of farmers and craftsmen called Karls. At the bottom of the heap were a class of slaves called thralls. Slavery was common in the world at that time. It was accepted as an inevitable part of life. The Vikings captured women and children on their raids and made them slaves. However Viking women had a good deal of freedom. Viking merchants imported glass and silk from the Byzantine Empire. Viking craftsmen included blacksmiths, bronzesmiths, coopers, leather tanners, saddlers, shoemakers and other men who made leather goods like purses and belts. Vikings for children. The Vikings wanted new land because the places where they came from in Scandinavia – Norway, Sweden and Denmark – weren’t very easy to live on.

It was hard to grow crops, which meant there wasn’t a lot of food as the population got bigger. Britain and Europe had plenty of good farmland, so the Vikings tried to claim some of that land for themselves. Even though the Anglo-Saxons were pretty well established in England, the Vikings would turn up every now and then to raid towns and take a bit of land. Sometimes, instead of fighting the Vikings, the Anglo-Saxons decided it was better to pay them money so they’d stay away. This payment was called Danegeld.
Middle Ages for Kids: Vikings. Back to Middle Ages for kids The Vikings were people who lived in Northern Europe during the Middle Ages.
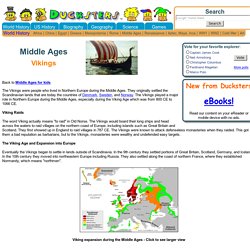
They originally settled the Scandinavian lands that are today the countries of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway. The Vikings played a major role in Northern Europe during the Middle Ages, especially during the Viking Age which was from 800 CE to 1066 CE. Viking Raids The word Viking actually means "to raid" in Old Norse. Vikings for Kids - Primary History. Snaith Vikings.