

Is IBS an Autoimmune Disease? The pioneering work of gastroenterologist and researcher Mark Pimentel, MD, indicates that IBS—at least in the case of some patients—may be an autoimmune disease triggered by food poisoning that damages the nerves of the small intestine.
Read on to learn about our evolving understanding of IBS and how newly validated biomarkers and medications are paving the way for better diagnosis and treatment of this condition. If IBS is an autoimmune disease, what does that mean for treatment? Learn more about this new understanding of a long misunderstood disease.
#nutrition #chriskresser IBS: No Longer a Disease of Exclusion IBS has a reputation for being a “last-ditch” diagnosis, given to patients suffering from gut problems who do not fit the bill for any specific gastrointestinal disease. A New Understanding of SIBO and IBS, with Mark Pimentel. In this episode, we discuss: The link between food poisoning, SIBO, and IBSIBS and autoimmunityAvailable treatments for people with IBS-DGetting treatment for IBS-C and methane-predominant SIBOPimentel’s upcoming study on lovastatinSmall intestinal fungal overgrowth (SIFO)The low-fermentation diet (and problems with the low-FODMAP diet)New findings from Dr.
Pimentel Show notes: Chris Kresser. Fecal excretion of Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 and changes in fecal microbiota after eight weeks of oral supplementation with encapsulated probi... - PubMed - NCBI. What causes IBS. Disrupted Gut Clocks Linked with IBS, GERD, Obesity, and Other GI Concerns. Articles on IBS. Articles on IBS - Every article from A to Z about IBS under one page.
Use the search function below to find your topic of choice. * With each topic packaged into a ready-to-read format, you will be thrilled to read each article and start to absorb the materials * There are a countless number of topics related to Irritable Bowel Syndrome and it is not an easy task to shuffle through all the information to find what you are looking for. The articles on IBS list shown below will be a solid start to assisting you on the right path to understanding and reversing your IBS.
You can either use "ctrl + F" to find what you need to look for or you can always use the Google search box located below to find an article related to your topic of choice from this site. Ready to Search? Please note that your search results may include ads by Google, that could be of interest to you, displayed with the search results. Is Your IBS Really SIBO (Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth)? 5 Causes of IBS Your Doctor May Not Be Looking For. SIBO Gluten and IBS what is the connection? SIBO, Gluten and IBS: What Is The Connection?
When she came into my office complaining of bloating, Clare (name changed to protect her privacy) was convinced it was from something she was eating. In a way, she was right. Bloating can be caused by many things, some minor, some serious. I considered her case serious, as it was severely impacting her day-to-day life and her overall health. She was deficient in multiple nutrients. Prior to our visit, Clare had tested negative for celiac disease, but had started a gluten-free diet to help her rheumatoid arthritis and bloating. Endomicroscopy Offers Insight on Leaky Gut Syndrome.
Dysautonomia - Modern research. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common condition in the colon marked by constipation, diarrhoea, (often alternating with constipation, or sometimes noted by simply constipation), bloating and cramping abdominal pain from excessive spasms of the large intestine.
IBS has been called by many other names such as irritable colon, colitis, mucous colitis, spastic colon, spastic bowel, and functional bowel disease. Many doctors sometimes call it a “functional disorder” because there is no obvious sign of organic disease or physical changes when the colon is examined, and it is frequently worse during times of stress, or anxiety. This does not make the condition any less uncomfortable. IBS Treatment Options.
This is a post from the Gut Critters blog that ended November 18, 2016. Ray Medina gave permission for his material to be copied as long as it was attributed to him and not used for commercial purposes. – kiraonysko
10 Strategies to Eliminate IBS and Create Good Gut Health. About 60 million people — that’s 20 percent of Americans — have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
These people struggle with miserable, often disabling symptoms like bloating, cramps, diarrhea, constipation, and pain. Numerous culprits contribute to IBS. Your gut lining can break down from stress; too many antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin or Advil; steroids; intestinal infections; a low-fiber, high-sugar diet; alcohol and even C-sections (which we have seen a dramatic increase in recent years). What Are Beneficial Gut Bacteria. Chronic Stress, Cortisol Resistance, and Modern Disease (IBS in the middle) Microbiome differences between healthy people and those with IBS — The American Microbiome Institute. IBS affects somewhere around 11% of all humans.
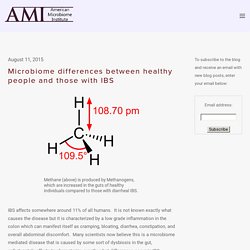
It is not known exactly what causes the disease but it is characterized by a low grade inflammation in the colon which can manifest itself as cramping, bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and overall abdominal discomfort. Many scientists now believe this is a microbiome mediated disease that is caused by some sort of dysbiosis in the gut, unfortunately efforts to characterize exactly what differences occur in IBS individuals have not been successful. A new article published last week in Nature Scientific Reports describes newly discovered differences in butyrate and methane producing bacteria in the guts of people with IBS.
The scientists sequenced the microbiomes of 66 healthy controls and 113 folks with IBS, at two time points 1 month apart. Toward a better understanding of the link between irritable bowel syndrome and anxiety and depression. Update on Irritable Bowel Syndrome – 2016 news. I thought it would be good to review some of the hundreds of studies published on PubMed in 2016 to see if anything especially interesting has been published.
“During life, the numbers of bifidobacteria decrease from up to 90% of the total colon microbiota in vaginally delivered breast-fed infants to <5% in the colon of adults and they decrease even more in that of elderly as well as in patients with certain disorders such as antibiotic-associated diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, obesity, allergies, and regressive autism.” [2016] ” Butyrate is an essential metabolite in the human colon, as it is the preferred energy source for the colon epithelial cells, contributes to the maintenance of the gut barrier functions, and has immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties. Researchers identify intestinal microbiota profile related to severity of IBS symptoms - Gut Microbiota for Health.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is the most prevalent functional gastrointestinal disorder in western societies and recent research has proposed gut microbiota as one of the potential main factors involved.

However, little is known regarding the relationship between the composition and function of the gut microbiota and clinical symptoms of IBS. Paired mucosal and faecal microbiota sample analysis in the exploratory set of patients revealed that faecal and mucosal microbiota were structurally distinct but highly correlated. Although there were no differences in faecal microbiota composition between patients with IBS when compared to healthy subjects, a computational statistical procedure identified a microbial signature for severe IBS within the IBS group, consisting of 90 bacterial operational taxonomic units (OTUs), which are the most commonly used microbial diversity units clustered on the basis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequence identity alone.
Who are the most active Irritable Bowel Syndrome Researchers? Gut Bacteria causing Irritable Bowel Syndrome / CFS. While researching my last post I came across an article describing the differences of bacteria seen with IBS.
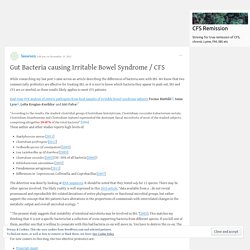
We know that two commercially probiotics are effective for treating IBS, so it is nice to know which bacteria they appear to push out. IBS and CFS are co-morbid, so these results likely applies to most CFS patients. Real-time PCR analysis of enteric pathogens from fecal samples of irritable bowel syndrome subjects Teemu Rinttilä12, Anna Lyra13, Lotta Krogius-Kurikka1 and Airi Palva1* “According to the results, the studied clostridial groups (Clostridium histolyticum, Clostridium coccoides-Eubacterium rectale, Clostridium lituseburense and Clostridium leptum) represented the dominant faecal microbiota of most of the studied subjects, comprising altogether 29-87% of the total bacteria” [2006] These author and other studies reports high levels of: The detection was done by looking at RNA sequences.
For new comers to this blog, the two effective probiotics are: Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Gluten. Fibromyalgia IBS and Endotoxemia. IBS Probiotics. The following are a list of probiotics effective (i.e. improve, not necessarily cure) Irritable Bowel Syndrome according to studies on PubMed.com. IBS is co-morbid with CFS and thus they become recommended probiotics for CFS. For this I raised the criteria to studies on humans and not on mice.
In general mixtures were eliminated with the exception of “unique mixtures” – Prescript Assist and VSL#3 NOTE: Probiotics do produce natural antibiotics. It is strongly recommended that the probiotics below be rotated and not taken continuously. “Overall, more than 50% of trials presented negative outcomes. Prescript Assist – multiple species Symbioflor 2 – E.Coli Probiotic Mutaflor — E.Coli Nissle 1917. International guide to help physicians use probiotics. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed or administered in adequate amounts, have beneficial effects on the body. Probiotics are also usually used for the prevention and management of digestive symptoms that may be related to changes or an imbalance in the bacterial community living in our gut, the gut microbiota, such as bloating or discomfort, among others.
In spite of increasing evidence and knowledge about probiotics, so far, it has not been an easy task for doctors to choose the most appropriate probiotic for each case. This is due to the fact that “probiotics” is an umbrella term that covers a huge range of bacterial strains and other microorganisms. We are glad to hear about the publication of this new guide as a tool to increase knowledge on the use of probiotics for the management of lower gastrointestinal symptoms in primary care. Diet and probiotics emerge as promising treatments “First of all, I think it’s a ‘real’ condition, one that we can recognize fairly readily, [even] given that there are tremendous variations in presentation and natural history,” he tells GMFH editors.
Dr. The Role of Bacteria, Probiotics and Diet in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Effectiveness of probiotics in those with IBS - Gut Microbiota for Health. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most common functional gastrointestinal disorders, affecting more than 10% of the population, with the highest impact in women. Although its origin is still unknown, reduced gut microbial diversity could be involved in its development. Clinical trial for probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome fails to show efficacy — The American Microbiome Institute. Irritable bowel syndrome is the most common functional gastrointestinal disorder, affecting about 10-15% of people in the United States alone, according to the International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders website. Are diets the answers to colon ills? Food, irritable bowel s... : Current Opinion in Gastroenterology. Sensitivity to wheat, gluten and FODMAPs in IBS: facts or fiction? Abstract. Low FODMAP Diet Offers Road to Relief for IBS.
The Overlapping Area of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) and Wheat-Sensitive Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): An Update. Diet for IBS – FODMAP. A diet low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) A diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome.Halmos EP, Power VA, Shepherd SJ, Gibson PR, Muir JG. [2014]Low FODMAP diet information“Diets differing in FODMAP content have marked effects on gut microbiota composition.
Minty Fresh & Symptom-Free. Can Vitamin D Treat IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)?