

Treasures in Full. Medieval Clothing and Fabrics. What People Wore in the Middle Ages By Melissa Snell, About.com Guide In medieval times, as today, both fashion and necessity dictated what people wore.
Medieval Clothing. Facts and interesting information about clothing, costume, dresses and fashionideal for research into period costumes.

Medieval 1100-1450. Someone suggested to me that for one of my posts I should examine the historical accuracy of costumes from movies set in the medieval era.
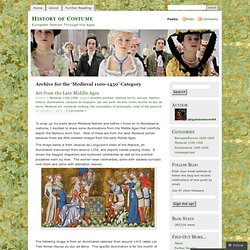
So, as something fun, that is what I shall do. However, I do not think it is completely fair to critique a film’s costumes on historical accuracy alone, for many designers choose to make costumes UN-historically correct for the purpose of the film. Therefore, I shall examine and give two ratings per movie: accuracy (based on clothing actually worn during the era portrayed) and relevancy (based on how well the costumes enhance the purpose and style of the movie).
Ivanhoe (1952): This movie is based on Sir Walter Scott’s fictional novel. It is set in the 1190s during the reign of Richard I, more commonly known as Richard the Lionheart, and includes the character of Robin Hood. Accuracy: 4 stars. Relevancy: 5 stars. The Court Jester (1956): This is a very fun comedy set generically in medieval times. Accuracy: 3.5 stars. Relevancy: 5 stars. 10 of the best medieval walled cities. For history buffs, photographers and anyone who’s ever said “Wow!”
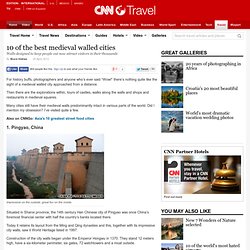
There’s nothing quite like the sight of a medieval walled city approached from a distance. Then there are the explorations within, tours of castles, walks along the walls and shops and restaurants in medieval squares. Many cities still have their medieval walls predominantly intact in various parts of the world. Did I mention my obsession? I’ve visited quite a few. Also on CNNGo: Asia's 10 greatest street food cities 1.
Pinterest. St Mark's Basilica. For its opulent design, gold ground mosaics, and its status as a symbol of Venetian wealth and power, from the 11th century on the building has been known by the nickname Chiesa d'Oro (Church of gold).[2] History[edit] Earliest construction[edit] The first St Mark's was a building next to the Doge's Palace, ordered by the doge in 828, when Venetian merchants stole the supposed relics of Mark the Evangelist from Alexandria, and completed by 832; from the same century dates the first St Mark's Campanile (bell tower).
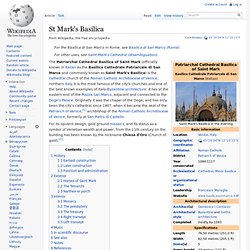
The church was burned in a rebellion in 976, when the populace locked Pietro IV Candiano inside to kill him, and restored or rebuilt in 978. Nothing certain is known of the form of these early churches. Detail of the gable showing Venice's patron apostle St. Later construction[edit] Byzantium (ca. 330–1453) In 330 A.D., the first Christian ruler of the Roman empire, Constantine the Great (r. 306–337) (26.229), transferred the ancient imperial capital from Rome to the city of Byzantion located on the easternmost territory of the European continent, at a major intersection of east-west trade.
The emperor renamed this ancient port city Constantinople ("the city of Constantine") in his own honor (detail, 17.190.1673–1712); it was also called the "New Rome," owing to the city's new status as political capital of the Roman empire. Mosaics - Hagia Sophia. Hagia Sophia was beautifully decorated with mosaics within the centuries during Byzantine period.
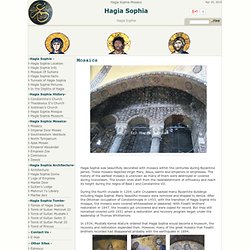
These mosaics depicted Virgin Mary, Jesus, saints and emperors or empresses. Celtic mythology. Vikings. The Viking period began in AD 793 with a raid on the monastery of Lindisfarne by pirates from Scandinavia.
In the following centuries their swift sailing ships enabled them to attack the undefended coastal and river ports, towns and monasteries of western Europe and beyond in the search for wealth, slaves, and new lands to settle. The name Viking is generally applied to the Scandinavian peoples from the late eighth century until around AD 1100. They lived in a number of small kingdoms, but as their rulers sought to increase their wealth and power, the smaller kingdoms were absorbed by more powerful neighbours, creating the modern kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden.
Raiding was only one aspect of the Viking age and excavation of their settlements and cemeteries has shown that they were mainly farmers, fishers and hunters, and also skilled craftsmen. The literature of their sagas reveals a hierarchical society with a complex culture. Norse Mythology. Room 40: Medieval Europe. Medieval_Becket_slideshow_KS34c. History - British History in depth: The Bayeux Tapestry: Unpicking the Past. Medieval tapestries. Medieval architecture. Explore the Paintings. Thematic Essays. Style Guide: Medieval Revivals. The Gallery at Strawberry Hill watercolour, Thomas Sandby, 1781, Museum no. D.1837-1904 The Medieval Revivals style was inspired by architecture and decorative arts from 1000-1600. The interest in Norman, Gothic and Jacobean styles reflected a romantic nostalgia for Britain's past. This was coupled with an increasingly serious study of actual Medieval buildings and furnishings.
Login. Medieval. Medieval astrology.