

Dynamic Earth . Plates & Boundaries. Volcanic Hazards of Yellowstone National Park. Yellowstone National Park is part of the largest active volcanic systems.

Many of the geologic features at Yellowstone are connected with the fact that the park lies on a 'hot spot’. The volcanic activity of Yellowstone's past was from caldera eruptions, which are giant explosions with violence, noise and enormous destruction. Hawaiian Volcanoes. Pacific Northwest Seismic Network. Plate tectonics describes the motions of the 15 to 20 large rigid and brittle tectonic plates into which the Earth's outermost layer (called the "lithosphere") is broken.
It does a good job at explaining the distribution of most of Earth's earthquakes, mountains and other geological features, and a particularly good job at explaining features on the ocean floor. However, it is challenged to explain the details of the older rocks on the continents, and the occurrence of deformation an earthquakes off of plate boundaries. Beyond merely describing current plate motions, Plate Tectonics provides an overarching framework that connects many elements of Earth science. Aleutian Trench. Hawaiian hotspot [This Dynamic Earth, USGS] Over the past 70 million years, the combined processes of magma formation, volcano eruption and growth, and continued movement of the Pacific Plate over the stationary Hawaiian "hot-spot" have left a long trail of volcanoes across the Pacific Ocean floor.
![Hawaiian hotspot [This Dynamic Earth, USGS]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/hawaiian-hotspot-dynamic-earth-97671384)
The Hawaiian Ridge-Emperor Seamounts chain extends some 6,000 km from the "Big Island" of Hawaii to the Aleutian Trench off Alaska. The Hawaiian Islands themselves are a very small part of the chain and are the youngest islands in the immense, mostly submarine mountain chain composed of more than 80 volcanoes. The length of the Hawaiian Ridge segment alone, from the Big Island northwest to Midway Island, is about equal to the distance from Washington, D.C. to Denver, Colorado (2,600 km).
The amount of lava erupted to form the Hawaiian-Emperor chain is calculated to be at least 750,000 cubic kilometers-more than enough to blanket the entire State of California with a layer of lava roughly 1.5 km thick. "Hotspots" Mountain Maker, Earth Shaker. Plate Tectonics: An Introduction. Divergent Plate Boundaries - Divergent Boundary - Geology.com. Earth Floor: Plate Tectonics. Divergent Boundaries Places where plates are coming apart are called divergent boundaries.

As shown in the drawing above, when Earth's brittle surface layer (the lithosphere) is pulled apart, it typically breaks along parallel faults that tilt slightly outward from each other. Discovering Plate Boundaries Home. Caldera Demonstration Model. Dina: Hi.
I’m Dr. Dina. I work with the U.S. Geological Survey in Menlo Park, California with the Volcano Hazards Program. When most people think about volcanoes, they think of a triangle shape and that’s what many volcanoes look like, but there are other shapes too, and one of those is called a caldera. Episode 1: Yellowstone's Restless Giant - Yellowstone National Park. Glossary Earthquake – The abrupt shaking of the ground caused by a shift of rock along a fracture in the Earth.
Geyser – Hot springs that periodically erupt, shooting scalding water and steam into the air. Though hot springs can be common, the special requirements needed for a geyser to erupt make them rare. In addition to hot water, a unique conduit system or natural “plumbing” system is needed for pressure to build and yet withstand the force of eruptions. A narrow constriction above a larger reservoir chamber allows water to become superheated above the boiling point without boiling. Tracking the Hot Spot - Yellowstone National Park. Plateboundary.rice.edu/TGpart2_notes.pdf. High School Earth Science/Theory of Plate Tectonics. Wegener's continental drift hypothesis had a great deal of evidence in its favor but it was largely abandoned because his theory on how the continents moved was disproved.
In the meantime, scientists developed explanations to explain the locations of fossils on widely different continents (land bridges) and the similarity of rock sequences across oceans (geosynclines), which were becoming more and more cumbersome. When seafloor spreading came along, scientists recognized that the mechanism to explain drifting continents had been found. Like the scientists did before us, we are now ready to merge the ideas of continental drift and seafloor spreading into a new all-encompassing idea: the theory of plate tectonics. Lesson Objectives Earth's Tectonic Plates Now you know that seafloor and continents move around on Earth's surface.
Earthquakes are not spread evenly around the planet, but are found mostly in certain regions. Figure 6.14: The lithospheric plates and their names. How Plates Move. Earthquakes suggest new tectonic plate is forming. Two magnitude-8 earthquakes took place within two hours in unstable plate region Keith Koper (CBS News) A new study suggests that two recent earthquakes may indicate a literal seismic shift in our understanding of tectonic plate movements.
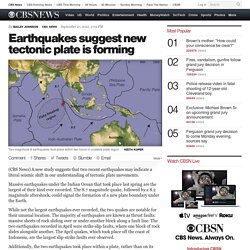
Tectonic Plates. The edges of these plates, where they move against each other, are sites of intense geologic activity, such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.
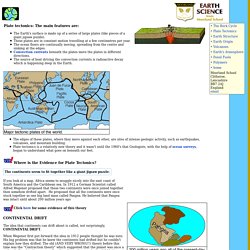
Plate tectonics is a relatively new theory and it wasn't until the 1960's that Geologists, with the help of ocean surveys, began to understand what goes on beneath our feet. Where is the Evidence for Plate Tectonics? It is hard to imagine that these great big solid slabs of rock could wander around the globe. Scientists needed a clue as to how the continents drifted. Granite - Yosemite National Park.
A large amalgamation of plutons is called a batholith.
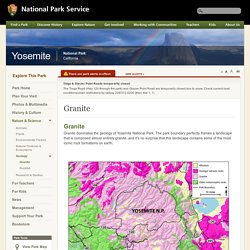
Yosemite is situated within the 70-mile-wide, 300-mile-long Sierra Nevada Batholith. High School Earth Science/Theory of Plate Tectonics. Geology in the Parks. In a contest between a dense oceanic plate and a less dense, buoyant continental plate, guess which one will sink? The dense, leading edge of the oceanic plate actually pulls the rest of the plate into the flowing asthenosphere and a subduction zone is born! Where the two plates intersect, a deep trench forms.
Geologists aren't sure how deep the oceanic plate sinks before it completely melts, but we do know that it remains solid far beyond depths of 100 km beneath the Earth's surface. Www.geology.sdsu.edu/visualgeology/geology101/Geology100Exams/Tectonics.pdf. Why is the seafloor so recent and the continental crust so old? How Tall Can Mountains Be? Continental crust. The thickness of the Earth's crust (km). Importance[edit] Because the surface of continental crust mainly lies above sea level, its existence allowed land life to evolve from marine life. Its existence also provides broad expanses of shallow water known as epeiric seas and continental shelves where complex metazoan life could become established during early Paleozoic time, in what is now called the Cambrian explosion.[3] Origin[edit] Forces at work[edit] Plate Tectonics : Earthview. The Geological Society. The Himalayan mountain range and Tibetan plateau have formed as a result of the collision between the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate which began 50 million years ago and continues today.
Northward migration of India 225 million years ago (Ma) India was a large island situated off the Australian coast and separated from Asia by the Tethys Ocean. The supercontinent Pangea began to break up 200 Ma and India started a northward drift towards Asia. 80 Ma India was 6,400 km south of the Asian continent but moving towards it at a rate of between 9 and 16 cm per year. At this time Tethys Ocean floor would have been subducting northwards beneath Asia and the plate margin would have been a Convergent oceanic-continental one just like the Andes today. Earth Floor: Plate Tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics has done for geology what Charles Darwin's theory of evolution did for biology. It provides geology with a comprehensive theory that explains "how the Earth works. " The theory was formulated in the 1960s and 1970s as new information was obtained about the nature of the ocean floor, Earth's ancient magnetism, the distribution of volcanoes and earthquakes, the flow of heat from Earth's interior, and the worldwide distribution of plant and animal fossils.
The theory states that Earth's outermost layer, the lithosphere, is broken into 7 large, rigid pieces called plates: the African, North American, South American, Eurasian, Australian, Antarctic, and Pacific plates. Several minor plates also exist, including the Arabian, Nazca, and Philippines plates. The plates are all moving in different directions and at different speeds (from 2 cm to 10 cm per year--about the speed at which your fingernails grow) in relationship to each other. Plate Tectonics in a Nutshell. The theory of plate tectonics is a relatively new scientific concept. While its forerunner—the theory of continental drift—had its inception as early as the late 16th century, plate tectonics only emerged and matured as a widely accepted theory since the 1960s (see This Dynamic Earth booklet). In a nutshell, this theory states that the Earth’s outermost layer is fragmented into a dozen or more large and small solid slabs, called lithospheric plates or tectonic plates, that are moving relative to one another as they ride atop hotter, more mobile mantle material (called the asthenosphere).
The average rates of motion of these restless plates—in the past as well as the present—range from less than 1 to more than 15 centimeters per year. With some notable exceptions, nearly all the world’s earthquake and volcanic activity occur along or near boundaries between plates. New Ocean - The New Southern Ocean. Updated August 20, 2009. Index of /eoc/teachers/t_tectonics. Plate Tectonics. In much the same way that geographic borders have separated, collided, and been redrawn throughout human history, tectonic plate boundaries have diverged, converged, and reshaped the Earth throughout its geologic history.
Chapter -12 HW. Chapter -12 HW. Flipbook.pdf. Tri fold note books (evidence, boundaries, causes) - Mrs. Lafrate's Class. CHAPTER 10 PLATE TECTONICS.pdf. Plate Tectonic Animation - Earthguide Online Classroom - Plate Tectonics Animations.