

Multiple Intelligences. The theory of multiple intelligences was developed in 1983 by Dr.

Howard Gardner, professor of education at Harvard University. It suggests that the traditional notion of intelligence, based on I.Q. testing, is far too limited. Instead, Dr. Gardner proposes eight different intelligences to account for a broader range of human potential in children and adults. These intelligences are: Linguistic intelligence (“word smart”)Logical-mathematical intelligence (“number/reasoning smart”)Spatial intelligence (“picture smart”)Bodily-Kinesthetic intelligence (“body smart”)Musical intelligence (“music smart”)Interpersonal intelligence (“people smart”)Intrapersonal intelligence (“self smart”)Naturalist intelligence (“nature smart”) Dr.
The theory of multiple intelligences proposes a major transformation in the way our schools are run. The theory of multiple intelligences also has strong implications for adult learning and development. How to Teach or Learn Anything 8 Different Ways . . . EdtechInfluencers Crowdsourced Ebook r21.
Flipping the Elementary Classroom. How to do an "in-class" flip with young learners As a first grade teacher at a “Lighthouse” school in Baltimore County, I work with young students who each have their own digital learning device.

My colleagues and I are also working to create models of digital, personalized, and blended learning for students using these new tools. As I continue to research and study 21st century learning both at school and in my graduate program at Loyola University, I keep hearing about the popular “flipped learning” classroom model. Flipped learning happens when the teacher delivers a lesson to students via a screencast or video assigned as homework, allowing in-class time to be spent reinforcing or applying the skill that was learned. Can you flip an elementary classroom? As I started searching for ideas, I found it very difficult to find flipped lesson examples for elementary students. My main concern with attempting this type of lesson is the fact that my students are only six years old. Reflection. The Flipped Classroom Model: A Full Picture.
Due to Khan Academy’s popularity, the idea of the flipped classroom has gained press and credibility within education circles. Briefly, the Flipped Classroom as described by Jonathan Martin is: Flip your instruction so that students watch and listen to your lectures… for homework, and then use your precious class-time for what previously, often, was done in homework: tackling difficult problems, working in groups, researching, collaborating, crafting and creating. Classrooms become laboratories or studios, and yet content delivery is preserved. Flip your instruction so that students watch and listen to your lectures… for homework, and then use your precious class-time for what previously, often, was done in homework: tackling difficult problems, working in groups, researching, collaborating, crafting and creating.
What are the 4Cs? 4Cs Poster 21st Century Skills. An Educators Guide to the Four Cs. P21 Framework Brief. Measures of Effective Teaching (MET) Project - K-12 Education. Two-thirds of American teachers feel that traditional evaluations don’t accurately capture the full picture of what they do in the classroom.
They want information that they can trust from measures that are fair and reliable. The Measures of Effective Teaching (MET) project was designed to find out how evaluation methods could best be used to tell teachers more about the skills that make them most effective and to help districts identify and develop great teaching. When it came to identifying what great teaching looks like, we knew that it was imperative to go straight to the source: teachers. Through the MET project, we sought to answer the following critical questions: Is it possible to identify and measure effective teaching?
The outstanding work of our partners has proven the answer is “yes.” Based on lessons learned through the MET project, our partners identified nine guiding principles to inform the design and implementation of high-quality teacher support and evaluation systems.
Bias/Equality. Professional Development / Depth of Knowledge (DOK) The DOK has 4 levels.
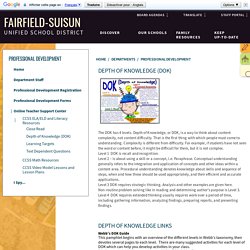
Depth of Knowledge, or DOK, is a way to think about content complexity, not content difficulty. That is the first thing with which people must come to understanding. Complexity is different from difficulty. For example, if students have not seen the word or content before, it might be difficult for them, but it is not complex. Level 1 DOK is recall and recognition. Level 2 – is about using a skill or a concept, i.e. Level 3 DOK requires strategic thinking. Universal Design for Learning principles and checkpoints. Unnamed. Backward Design. Differentiation. Exploratory Pedagogical Models. A note before we start: Everyone is learning the "Webquest" model, simply by interacting with this Webquest.
As such you will not be allowed to choose a "Webquest" for your teaching presentation/exploration. After brief exploration of the various exploratory models, choose the model you intend to use to teach the mini lesson. Click on the model below and navigate through all the links connected to that model. Keep in mind that you will need to create a 5-10 minute mini-lesson using your model, in order to teach your model, so explore all resources thoroughly. Inquiry Based Methods: El sdaie strategies. Accommodations and Modifications for Students with Disabilities. BLOOMS Taxonomy Activity.