

History Net: Where History Comes Alive – World & US History Online. Facts, information and articles about The Vietnam War U.S.

Marines in Operation Allen Brook (Vietnam War) 001. GCSE Bitesize: The US gets out of Vietnam. Opposition at home. Impact of war TRS. Vietnam profile - Timeline. A chronology of key events: 1858 - French colonial rule begins. 1930 - Ho Chi Minh founds the Indochinese Communist Party (ICP). 1941 - ICP organises a guerrilla force, Viet Minh, in response to invasion by Japan during World War II. 1945 - The Viet Minh seizes power.
Ho Chi Minh announces Vietnam's independence. BBC Bitesize - National 5 History - The Vietnam War - Revision 1. iWonder - The Longer View: Nuclear explosion. iWonder - Timeline: Britain’s hidden role in the space race. The Cuban Missile Crisis. President Kennedy and Secretary of Defense McNamara in an EXCOMM meeting.For 14 days in October 1962 the world stood on the brink of nuclear war.
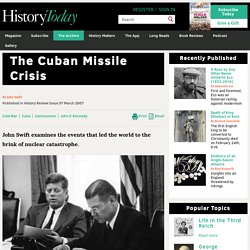
The Soviet Union had secretly stationed nuclear weapons on the island of Cuba, and when the government of the United States discovered them, and demanded their withdrawal, the most dangerous confrontation of the Cold War followed. A single miscalculation made either in the White House or the Kremlin could have precipitated catastrophe. How did this standoff arise? Clouds Over Cuba. Cwar 2. History Review Origins of the Cold War revision page. Cuban Missile Crisis. (A2) Andrei Gromyko, the Soviet Union's foreign secretary, book Through Russian Eyes: President Kennedy's 1036 Days was published in 1973.
In the book Gromyko wrote about the background to the Cuban Missile Crisis. The United States over several years had established offensive military bases around the socialist countries and, primarily, near the USSR borders... the placement of medium-range effective Soviet missiles in Cuba was undertaken only after the United States ruling circles continually rejected proposals to remove American military bases, including missile sites, on foreign territory. (A3) In 1984 Fidel Castro was interviewed by the American journalist, Tad Szulc. The journalist asked Castro why he was willing to allow Soviet missiles to be placed in Cuba. Nuclear Test Ban Treaty. On August 5, 1963, after more than eight years of difficult negotiations, the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union signed the Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty.
The destruction of Hiroshima and Nagasaki by atomic bombs marked the end of World War II and the beginning of the nuclear age. As tensions between East and West settled into a Cold War, scientists in the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union conducted tests and developed more powerful nuclear weapons. In 1959, radioactive deposits were found in wheat and milk in the northern United States. As scientists and the public gradually became aware of the dangers of radioactive fallout, they began to raise their voices against nuclear testing.
Leaders and diplomats of several countries sought to address the issue. Attempts to Negotiate a Treaty Conflict soon arose over inspections to verify underground testing. Kennedy Opposes Testing John F. Cuban Missile Crisis. For thirteen days in October 1962 the world waited—seemingly on the brink of nuclear war—and hoped for a peaceful resolution to the Cuban Missile Crisis.
In October 1962, an American U-2 spy plane secretly photographed nuclear missile sites being built by the Soviet Union on the island of Cuba. President Kennedy did not want the Soviet Union and Cuba to know that he had discovered the missiles. He met in secret with his advisors for several days to discuss the problem. After many long and difficult meetings, Kennedy decided to place a naval blockade, or a ring of ships, around Cuba. The aim of this "quarantine," as he called it, was to prevent the Soviets from bringing in more military supplies. No one was sure h ow Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev would respond to the naval blockade and U.S. demands. Cuban Missile Crisis Revision. Cuban Missiles Crisis 1962. 14 Oct: U2 spy-plane takes pictures of Missile bases in Cuba - experts tell Kennedy he has 10 days before they are operational. 16 Oct: Kennedy set up a Committee of the National Security Council to advise him. 22 Oct: Kennedy announced that he was mounting a naval blockade of Cuba.
B52 nuclear bombers were deployed, so that one-eighth of them were airborne all the time. That night, Oleg Penkovsky – a Western spy working in Russia – was arrested. His last message read; ‘Soviet attack imminent’. 23 Oct: Khrushchev explained that the missile sites were ‘solely to defend Cuba against the attack of an aggressor’. 20 Russian ships were heading for Cuba. 24 Oct:
Telephone Recordings: Dictation Belt 30.2. Cuban Missile Crisis Update. View parent collection and finding aid Download audio (mp3)

Four key summit meetings build up to Berlin. Khrushchev and 'Peaceful Co-existence' As a result, the period 1955–1963 was the time of GREATEST tension in the Cold War.

Source E Although Khrushchev has been careful to pay lip service to the coexistence theme, this has apparently meant for him little more than an absence of armed conflict. In a speech in Prague in June 1954, he stressed Soviet possession of the atom and hydrogen bombs, as well as the necessity for maintaining and increasing Soviet armed strength. Several times he referred to the West as ‘the enemy’ and spoke of capitalist encirclement… On 10 August … he indicated that there could be trade and increased diplomatic intercourse, but no change in ideology, thereby implying no respite from political warfare.
Analysis of Khrushchev's views in a top secret CIA briefing paper (September 1955) Source G Norman Lowe, Mastering Modern World History (1982) Written as a GCSE revision book by a History teacher. Freedom's Fury 1 - A documentary on the 1956 Olympic ... Middle East [1956] Alternative title: October War Suez Crisis, Suez CrisisStock footage courtesy The WPA Film Library(1956), international crisis in the Middle East, precipitated on July 26, 1956, when the Egyptian president, Gamal Abdel Nasser, nationalized the Suez Canal.
![Middle East [1956]](http://cdn.pearltrees.com/s/pic/th/suez-crisis-middle-east-1956-117339780)
HisRev 9 2 Korean War map 2. The Berlin Blockade factsheet. The Warsaw Security Pact: May 14, 1955. The Warsaw Security Pact: May 14, 1955 Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance Between the People's Republic of Albania, the People's Republic of Bulgaria, the Hungarian People's Republic, the German Democratic Republic, the Polish People's Republic, the Rumanian People's Republic, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and the Czechoslovak Republic, May 14, 1955 (1) who, having presented their full powers, found in good and due form, have agreed as follows: Article 1.
Untitled. The North Atlantic Treaty, signed Washington D.C. 4 April 1949 The Parties to this Treaty reaffirm their faith in the purposes and principles of the Charter of the United Nations and their desire to live in peace with all peoples and all governments. They are determined to safeguard the freedom, common heritage and civilisation of their peoples, founded on the principles of democracy, individual liberty and the rule of law. They seek to promote stability and well-being in the North Atlantic area.
Origins of the Cold War 1945-49. FOUR causes of the Cold War [BARE]. NINE events which caused the Cold War. FOUR decisions made at the Yalta Conference. TWO decisions and three disagreements at the Potsdam conference. The ‘salami tactics’ that brought Communists to power in Eastern Europe FIVE causes [CABAN] and FOUR results [CENA] of the Berlin crisis, 1948–9. Berlin Blockade. A move to test our ability and our will to resist. President Truman, speaking in 1949. The Berlin Blockade and Airlift. AirBrige to Berlin Home. Truman Library: The Berlin Airlift Online Research File. JonesPullingOut. 49Vittles.
PICTURE source analysis. Homework - due Monday 5th October. Sources Soviet Expansion. Source Helpdesk SEEU sources. Cold War. Cold War Museum.
What was the Cold War (overview) 10 Amazing Cold War Propaganda Posters. The Cold War lasted from the end of World War II right up to the early 1990s, although the Soviet Union and the USA never actually engaged in direct battle. Instead, the Cold War was expressed through weapons development (the nuclear arms race), technological development (the space race), espionage and propaganda. Western democratic states churned out huge amounts of propaganda material throughout the First and Second World Wars, but practically decommissioned their propaganda machines post 1945. The History of Media Use for Propaganda Purposes. Published in 1947 by the Catechetical Guild Educational Society of St. Paul, Minnesota “A nation that knows how to popularize cornflakes and luxury automobiles ought to be able to tell the world the simple truth about what it is doing and why it is doing it.” – Lyndon B.
The Cold War. Causes of the Cold War Summary & Analysis. 5: GCSE History - Communist takeover of Eastern Europe 1945-48. History of the Atomic Age. GCSE Bitesize: Causes of the Cold War Activity. GCSE Bitesize: Differences between Yalta and Potsdam. Differences between Capitalism & Communism and why did it start in Russia? Please note that this information was part of our old 'history classroom content' written in 2003, we have updated is slightly to meet the needs of the new curriculum but further updates will be made in 2010. Classtools.net Arcade Game Generator. Arcade Game Generator Input one set of questions and answers, and create a whole batch of interactive, arcade-style games [view examples] Save them for use in the class, embed them in your blog/website/wiki! IPad versions of "Wordshoot" and "Flashcards" already available - more to follow!
STEP 1: QUIZ TITLE a. The Political Compass.