

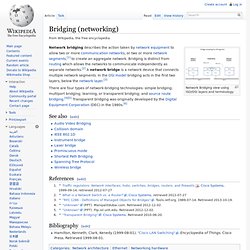
Windows 8 Client Nic Teaming?? Bridging (networking) Network Bridging view using ISO/OSI layers and terminology There are four types of network-bridging technologies: simple bridging; multiport bridging; learning, or transparent bridging; and source route bridging.[4][5] Transparent bridging was originally developed by the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in the 1980s.[6]
Any REAL Benefits of NIC Teaming for Gaming? - LAN - Networking. Your question husky mctarflash January 29, 2009 3:59:34 PM I am considering a new MoBo, and one of my choices has dual Ethernet connections for NIC teaming.
I play BF2 and other online games where lag and ping are crucial. Considering I have a 6 Mb/s cable internet connection (or whatever the correct designation is), is there any benefit to teaming? See full content. Network bridge vs. NIC teaming ? Quote: That isn't quite right.
Bridging is usually used when you wish to combine two network connections, but not necessarily have them doing the same task (an example is if you want a VM to appear as a real machine on your network). You can bridge the VM's software NIC (if it has one) with a physical card giving it direct access to then LAN (rather than doing NAT) It does make the computer see them as 1, but they'll only have one connection to the LAN/Internet.
Now on to teaming. Teaming is quite different than bridging in the fact that the two network cards will be performing the same task. Here's what teaming does not do, it will not increase the speeds of your downloads. Edit: I just realize you're the same guy from the other thread. OSI model. Model with 7 layers to describe communications systems The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model) is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology.
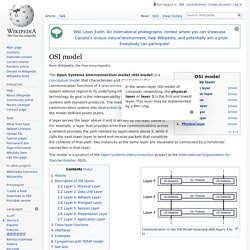
Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard protocols. The model partitions a communication system into abstraction layers. The original version of the model defined seven layers. A layer serves the layer above it and is served by the layer below it. The model is a product of the Open Systems Interconnection project at the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Communication in the OSI-Model (example with layers 3 to 5) History[edit] In the late 1970s, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) conducted a program to develop general standards and methods of networking. Description of OSI layers[edit] Layer 1: Physical Layer[edit]
Link aggregation. Link Aggregation between a switch and a server Further umbrella terms used to describe the method include port trunking,[1]link bundling,[2] Ethernet/network/NIC bonding,[1] or NIC teaming.
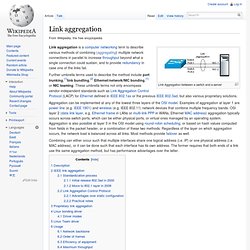
These umbrella terms not only encompass vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet defined in IEEE 802.1ax or the previous IEEE 802.3ad, but also various proprietary solutions. Aggregation can be implemented at any of the lowest three layers of the OSI model. Examples of aggregation at layer 1 are power line (e.g. IEEE 1901) and wireless (e.g. Combining can either occur such that multiple interfaces share one logical address (i.e. Description[edit] Link aggregation addresses two problems with Ethernet connections: bandwidth limitations and lack of resilience. With regard to the first issue: bandwidth requirements do not scale linearly. The second problem involves the three single points of failure in a typical port-cable-port connection. Driver modes[edit] Nic Teaming! beat a dead horse please! Quote: That is a combined speed of multiple sessions.
No one single connection can get beyond the speed of one of the NICS, the advantage of aggregation is that multiple sessions are not limited to the speed of one NIC, they are spread across NICs. A higher aggregate speed. Take a look at the LACP page on Wikipedia, that probably will help. TCP/IP creates a virtual circuit between you and the entity you are talking to, imagine a TFTP session, or a SSH login, you are assigned a NIC by LACP when the circuit is created, for the duration of that circuit you can't exceed the speed of the NIC that handles that circuit - packets are not split between NICs.
What this means in the real application world, when streaming HD video, you will not get faster than what one NIC will support for that video, but if you are moving a file at the same time as you are watching your movie, the HD video most likely won't suffer, because the move will most likely get assigned to the other NIC. Nic Teaming! beat a dead horse please! Any REAL Benefits of NIC Teaming for Gaming? - LAN - Networking. Windows 8 client nic teaming. Janssen Jones - Blog - Hyper-V Tips and Tricks - NIC teaming - Easier in Windows 8! For the remaining days of our 12 Days of Hyper-V Tips and Tricks, I'll be focusing on new features that are coming in Windows 8.
I've been using Hyper-V since it first shipped, and with each release, more and more of the "must haves" and "nice to haves" have been filling in, to the point that with Windows 8, I'm not looking for much more in my Virtualization solution. Virtualization FAQ 1 (Hyper-V NIC Teaming, CSV, Snapshots, DCs):Concurrency, Inc. Blog. Hello, I just had the opportunity to participate in the presentation of VIR471-INT at Tech Ed 2011!
I really enjoy the opportunity to get to know people using Hyper-V and to share my experiences with the platform. I thought I would take a second to note some key questions we discussed in the session and to address them with more detail here: “How should I structure my CSVs?” In addressing this question, we focused on the idea that CSV volumes are dependent on SMB and you need to be very careful with CSVs in relationship to patching domain controllers. NIC Teaming in Windows 8 & Hyper-V. One of the many new features in Windows 8 is native NIC Teaming or Load Balancing and Fail Over (LBFO).
This is, amongst many others, a most welcome and long awaited improvement. Now that Microsoft has published a great whitepaper (see the link at the end) on this it’s time to publish this post that has been simmering in my drafts for too long. Most of us dealing with NIC teaming in Windows have a lot of stories to tell about incompatible modes depending on the type of teaming, vendors and what other advanced networking features you use.
Combined with the fact that this is a moving target due to a constant trickle of driver & firmware updates to rid of us bugs or add support for features. This means that what works and what doesn’t changes over time. When it works it rocks and provides great benefits (if not it would have been dead). Windows 8 Client Nic Teaming?? NIC Teaming includes several parts: The core teaming engineThe PowerShell management cmdlets ("NetLbfo")The NIC Teaming GUI The core teaming engine is a server feature.
It is not licensed for or included in Windows 8 or Windows RT; there is no way to enable it on these operating systems. The PowerShell cmdlets ("NetLbfo") are built into Windows Server 2012, Windows 8, and Windows RT. However these cmdlets are only useful when targeting a Windows Server 2012 machine. Networking - How to enable Integrated Load Balancing in Windows 8. NIC Teaming in Windows 8 & Hyper-V. NIC Teaming in Windows 8 & Hyper-V. Networking - How to enable Integrated Load Balancing in Windows 8.