

Non-defining vs defining relative clauses. English Grammar, Relative Pronouns. Writing - Relative Clauses overview. №37 English: Which or That or Who? Relative clauses, complex sentences - Grammar, Syntax, Vocabulary. Relative clauses exercises (intermediate -) Rephrasing Exercises - Relative clauses 1. Relative Clause Quiz. This relative clause quiz focuses on the use of the relative pronouns 'who', 'that', 'which', 'whose', or 'whom'.
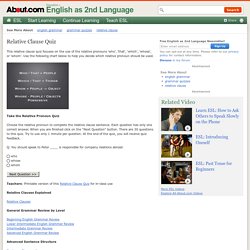
Use the following chart below to help you decide which relative pronoun should be used. ESL - English relative clauses quiz 5 - Mixed relative pronouns. Relative Clause Exercises. Relative Clause Exercises Here's a list of all the relative clause exercises on the site.

Would you like more Perfect English Grammar? 1: Sign up for my free email newsletter and get my free ebook '10 Really, Really Useful Phrasal Verbs'. 2: Buy my book! ↓ HomeWhat's New? Search my site: That and Which Clauses. Add modifying clauses for inanimate nouns Adjective vs.
Modifying Clause (Relative Clause) antique (Adj) – old, especially items wanted by collectors economical (Adj) – having the quality of saving money hybrid – powered by more than one source (e.g., gas and battery) vehicle (N) – a means of transportation. Relative Clauses. Relative Clauses. Content.
English Grammar Explanations - Relative clauses. Relative clauses are clauses starting with the relative pronouns who*, that, which, whose, where, when.

They are most often used to define or identify the noun that precedes them. Here are some examples: Do you know the girl who started in grade 7 last week? Can I have the pencil that I gave you this morning? A notebook is a computer which can be carried around. Relative clauses. Relative Clauses. (See a list of all the exercises about relative clauses here).

We can use relative clauses to join two English sentences, or to give more information about something. I bought a new car. It is very fast.→ I bought a new car that is very fast. She lives in New York. She likes living in New York.→ She lives in New York, which she likes. Defining and Non-defining. AdjClausesTest. Adjective Clauses (#5), by Dennis Oliver - Free English Grammar Lessons. Study: Hotel rooms have unseen guests. SAN FRANCISCO (AP) — Hotel guests leave behind more than just socks and old paperbacks: A new study found viruses on TV remotes, light switches and even hotel pens after cold sufferers checked out.

The germ testing was done before the rooms were cleaned, so it likely overstates the risks that most travelers would face. Nevertheless, it shows the potential hazards if a hotel's turnaround amounts to little more than changing the sheets and wiping out the tub. "You sure hope the cleaning people were good," said Dr. Owen Hendley, the University of Virginia pediatrician who presented results of the study Friday at a meeting of the American Society for Microbiology. Besides hotel hazards, the findings point out things that people may not think to clean in their homes when someone has a cold. "We know that viruses can survive on surfaces for a long time — more than four days," said Dr. Its aim was to test the survival of rhinoviruses, which cause about half of all colds, especially in children. Interactive Learning Tool. Az Review: Adjective Clauses. That and Which Clauses. Add modifying clauses for inanimate nouns Adjective vs.
Modifying Clause (Relative Clause) antique (adj.) – old, especially items wanted by collectors economical (adj.) – having the quality of saving money hybrid – powered by more than one source (e.g., gas and battery) vehicle (n.) – a means of transportation Replacing the Subject or Object Noun That / Which Add commas if the clause adds extra information that is not essential to identifying who the person is. Adjective Clauses and Relative Pronouns. Combine the two sentences.
Change the underlined pronoun in the second sentence to a relative pronoun such as "that", "who", or "whose". Make sure your adjective clause immediately follows the noun it modifies, even if you have to break the main clause. After writing the sentences, listen to each correct sentence and repeat it after the speaker. 1. I like people. Quick Quiz. Adjective Clauses (Relative Clauses) Adjective clauses (or relative clauses) are a type of subordinate clause that act as adjectives.
The whole clause does the job of an adjective. Which woman? The happy woman. Now, look at this sentence. The woman who looks happy danced across the street. This time, a whole clause is modifying the noun woman! Exercise #5 adjective clauses. Directions: Combine two sentences together to make one sentence. Put the adjective clause after the noun that it describes. You can use "who" or "that" to put the clauses together. Example: The student is a very nice person. / She comes from Japan. The student who comes from Japan is a very nice person. Adjective Clauses (#4), by Dennis Oliver - Free English Grammar Lessons.