

CIS Center for Internet Security. GCA Founding Organizations - Global Cyber Alliance. Quantum Entanglement Offers Unprecedented Precision for GPS, Imaging and Beyond. Picture a supervisor and an employee working together on a project.
Because it takes time for the employee to share information with his supervisor through methods like emails and meetings, the efficiency of their partnership is limited. But if the two could entangle their brains together, the employee and the supervisor would automatically have the same information -- saving time and allowing them to jointly tackle a common problem more efficiently.
Quantum metrology has been used to improve sensor precision in places like the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, or LIGO, which has opened up a new window for astronomers. However, almost all prior quantum metrology demonstrations, including LIGO, only involve a single sensor. However, RF waves are usually received by a network of sensors, each of which processes information individually -- more like a group of independent employees working with their supervisors.
MuckRock. Structural Reforms to Improve the Security of Classified Networks and the Responsible Sharing and Safeguarding of Classified Information. By the authority vested in me as President by the Constitution and the laws of the United States of America and in order to ensure the responsible sharing and safeguarding of classified national security information (classified information) on computer networks, it is hereby ordered as follows: Section 1.

Policy. Surveillance Compounded: Real-Time Crime Centers in the U.S. - Atlas of Surveillance. Source: Chino Chief of Police Over the last two decades, law enforcement agencies across the United States have been obtaining more and more sophisticated surveillance technologies to collect data.
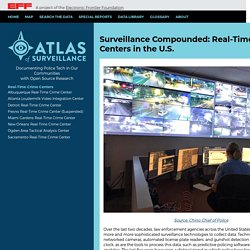
Technologies such as networked cameras, automated license plate readers, and gunshot detection are deployed around the clock, as are the tools to process this data, such as predictive policing software and AI-enhanced video analytics. Many Police Departments Have Software That Can Identify People In Crowds. As protesters demand an end to police brutality and the coronavirus pandemic sweeps the nation, police departments around the country are using software that can track and identify people in crowds from surveillance footage — often with little to no public oversight or knowledge.
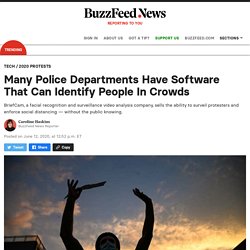
Dozens of cities around the country are using BriefCam, which sells software that allows police to comb through surveillance footage to monitor protests and enforce social distancing, and almost all of these cities have hosted protests against police brutality in the weeks since George Floyd was killed in police custody, BuzzFeed News has found. Some cities said they were not using BriefCam in conjunction with the protests or the pandemic. The St.
Paul Police Department told BuzzFeed News that it has not used BriefCam “to detect social distancing or face masks” or “for crowd detection/monitoring protests.” The department representative did not respond when asked if there is department policy that prevents it. How Secret Partners Expand NSA’s Surveillance Dragnet. Huge volumes of private emails, phone calls, and internet chats are being intercepted by the National Security Agency with the secret cooperation of more foreign governments than previously known, according to newly disclosed documents from whistleblower Edward Snowden.
The classified files, revealed today by the Danish newspaper Dagbladet Information in a reporting collaboration with The Intercept, shed light on how the NSA’s surveillance of global communications has expanded under a clandestine program, known as RAMPART-A, that depends on the participation of a growing network of intelligence agencies. It has already been widely reported that the NSA works closely with eavesdropping agencies in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and Australia as part of the so-called Five Eyes surveillance alliance.
The NSA documents state that under RAMPART-A, foreign partners “provide access to cables and host U.S. equipment.” Source documents for this article can be found here. Pelosi and Democrats Help Pass Renewal of NSA Spy Powers. With bipartisan backing, the House of Representatives passed a bill Thursday that would renew one of the government’s most sweeping surveillance authorities for six years with minimal changes.
The measure, which passed 256-164, reauthorized Section 702 of the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act, which was set to expire later this month. The law was first passed in 2008 to legalize President George W. Bush’s warrantless wiretapping program. It allows the National Security Agency to collect Americans’ communications with people overseas, as long as the NSA is “targeting” the foreigners involved. More than 5,000 Commenters Weigh in on DHS’ Proposal to Collect More Biometrics from Immigrants. The Homeland Security Department received more than 5,000 comments on a proposed rule that would expand the scope of its biometric information collection activities related to immigration enforcement.
The rule would allow U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services to collect more types of biometric information—such as face and iris scans—from more people, including children. Atlas of Surveillance. Video Analytics User Manuals Are a Guide to Dystopia. A few years ago, when you saw a security camera, you may have thought that the video feed went to a VCR somewhere in a back office that could only be accessed when a crime occurs.
Or maybe you imagined a sleepy guard who only paid half-attention, and only when they discovered a crime in progress. In the age of internet-connectivity, now it’s easy to imagine footage sitting on a server somewhere, with any image inaccessible except to someone willing to fast forward through hundreds of hours of footage. Fixing surveillance. Biometrics. IFLA Statement on the Right to be Forgotten (2016) The "right to be forgotten" refers to an individual’s ability to request that a search engine (or other data provider) remove links to information about himself or herself from search results.

This has also been referred to as the "right to delist," the "right to obscurity," the "right to erasure" or the "right to oblivion. " In the media, the terms may be used interchangeably or be differentiated based on legal scope. In this document, the "right to be forgotten" (RTBF) is used as a general term for these concepts and their application.
The purpose of RTBF court rulings and legislation is to allow individuals to make information about themselves that is already on the Internet much more difficult to discover. Artificially Intelligent. Expectations Online. SOLD! Questionable. US.Gov. Digital Ownership. Video Media.