

Introducing Curation Markets: Trade Popularity of Memes & Information (with code)! Curation Markets is a model that allows groups to more effectively coordinate & earn from value they co-create around shared goals.

Using Ethereum as a programmable, distributed, shared ledger, these groups can mint a token of value according to agreed upon rules without a centralized 3rd party being involved. In other words, a specific entity is not involved in the creation process of the tokens of value. It is a new type of organisational model & way for people to coordinate, unfettered, around shared goals. In essence, we allow the creation of global, joint-stock “memes”. Another phrase to describe this model is “meme markets”.
We will be able to mint tokens for things like sub-reddits, hashtags, people, memes and new organisations. Summary: The core, functional components of curation markets involve: For example: Assume that Truffle (an open source development framework for Ethereum) has an associated curation market. A simple, curation signal would be as follows: Shamir's Secret Sharing. Shamir's Secret Sharing is an algorithm in cryptography created by Adi Shamir.
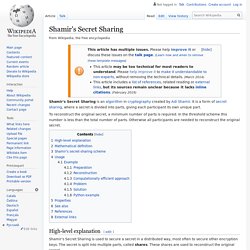
It is a form of secret sharing, where a secret is divided into parts, giving each participant its own unique part. To reconstruct the original secret, a minimum number of parts is required. In the threshold scheme this number is less than the total number of parts. Otherwise all participants are needed to reconstruct the original secret. High-level explanation[edit] Shamir's Secret Sharing is used to secure a secret in a distributed way, most often to secure other encryption keys.
To unlock the secret via Shamir's secret sharing, you need a minimum number of shares. Problem: Company XYZ needs to secure their vault's passcode. Arnaucube/flock-botnet: Twitter botnet with autonomous bots replying tweets with text generated based on probabilities in Markov chains. White paper waves smart contracts. A validating monotonic DHT "backed" by authoritative hashchains for data provenance (a Ceptr sub-project)
Party USA. An Error Has Occurred! Computer-supported cooperative work. The term computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW) was first coined by Irene Greif and Paul M.
Cashman in 1984, at a workshop attended by individuals interested in using technology to support people in their work.[1] At about this same time, in 1987 Dr. Charles Findley presented the concept of Collaborative Learning-Work.[2] According to Carstensen and Schmidt,[3] CSCW addresses "how collaborative activities and their coordination can be supported by means of computer systems". On the one hand, many authors consider that CSCW and groupware are synonyms. On the other hand, different authors claim that while groupware refers to real computer-based systems, CSCW focuses on the study of tools and techniques of groupware as well as their psychological, social, and organizational effects. The definition of Wilson (1991)[4] expresses the difference between these two concepts: Central concerns[edit] Matrix[edit] Same time/same place[edit] Face to face interaction.
CSCW Chasm paper. Organization: Alexa Crawls Starting in 1996, Alexa Internet has been donating their crawl data to the Internet Archive.

Flowing in every day, these data are added to the Wayback Machine after an embargo period. this data is currently not publicly accessible. March 17, 2006 47 "CSCW handbook" papers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Exploring the SEA: Service Execution Agreements - Ocean Protocol. This blogpost expands on the technical architecture of Ocean Protocol.

Specifically we’ll deep dive into Service Execution Agreements (SEAs). SEAs glue together services providers, consumers and verifiers in the Ocean Protocol Network. In our previous posts [1, 2], we referenced why it became clear that Service Level Agreements or SLAs pretty much hold together the world as we know it. Entire physical and digital service supply chains are being glued together by contractual bindings to mitigate counterparty risk, enforce availability, reliability and uptime. Building Responsible Cryptocurrencies – Holochain – Medium. Making Crypto Safe for the Mainstream I’ve been thinking a lot about how to make ICOs really solid, ethical, lasting sources of good.
However, at the heart of an ICO is the “C” — the cryptocurrency which is being offered. MIT/KIT Ceptr Webinar. FAQ · holochain/holochain-proto Wiki. How is Holochain different from blockchain?
Holochain and blockchain are built for fundamentally different use cases. Blockchain is relatively good for systems where it’s absolutely necessary to maintain global consensus. Holochain is much better than blockchain at anything that requires less than universal consensus (most things): It’s faster, more efficient, more scalable, adaptable, and extendable. Long before blockchains were hash chains and hash trees. These structures can be used to ensure tamper-proof data integrity as progressive versions or additions to data are made. Instead of trying to manage global consensus for every change to a huge blockchain ledger, every participant has their own signed hash chain (countersigned for transactions involving others).
The initial Bitcoin white paper introduced a blockchain as an architecture for decentralized production of a chain of digital currency transactions. Freedomlayer/offst: Offst payment engine.