

Yes, broken hearts are real. But they're not what you think. The inventor of the newest baby accessory might just have one of the more interesting resumes around.
Meet Marcie Miller: engineer, new mom and former professional cheerleader for the Arizona Cardinals. Her creation, the Intel Smart Clip, is designed to warn parents if they've left their baby behind in a car — the latest effort to prevent hot car deaths among children. Courtesy of Marcie Miller Marcie Miller with her daughter, Brooklyn. Miller, who lives in Chandler, Arizona, where temperatures reached 111 degrees this summer, has heard the stories all too often. More than half of kids who die are simply left behind by a caregiver who has forgotten they are in the backseat. Miller's invention is designed to never let that happen. "Oh, 100 percent, yes," Miller, 34, told TODAY Parents. Marcie Miller straps her daughter Brooklyn into a car seat. Triiodothyronine. This article is about triiodothyronine as a hormone.
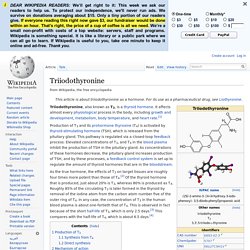
For its use as a pharmaceutical drug, see Liothyronine. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the pituitary gland. This pathway is regulated via a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated concentrations of T3, and T4 in the blood plasma inhibit the production of TSH in the pituitary gland. As concentrations of these hormones decrease, the pituitary gland increases production of TSH, and by these processes, a feedback control system is set up to regulate the amount of thyroid hormones that are in the bloodstream. As the true hormone, the effects of T3 on target tissues are roughly four times more potent than those of T4.[2] Of the thyroid hormone that is produced, just about 20% is T3, whereas 80% is produced as T4.
Production of T3[edit] Synthesis from T4[edit] T3 is the more metabolically active hormone produced from T4. Direct synthesis[edit] Uses[edit] I'm obsessed with my heart beat! (sleep, heartbeat, insurance, pounding) - Mental well-being and mental disorders. When I was a therapist I worked with lots of people with anxiety & panic, and even went through it myself.
First, make sure your doctor handling your heart issue checks you out and doesn't think medical intervention is needed. If he/she thinks you need to address it as anxiety, then therapy or self-help techniques can be helpful. Many people with MVP also experience problematic anxiety. It's not clear if one leads to the other, and it's different for different people. For some, the weird heart beat they feel leads to anxiety about their heart & health. Either way, it is very easy for some people to get too anxious and obsessive about their heart-related sensations. If you cannot afford therapy, try some cognitive-behavioral techniques that you can find in many self-help books. When I've had panicky symptoms that aggravate my irregular heartbeat, I found this breathing exercise to be the most helpful (saw Dr.
Take in a deep breath while counting to 4. Cortisol Levels Blood Test. Why do I need to register or sign in for WebMD to save?
We will provide you with a dropdown of all your saved articles when you are registered and signed in. How It Feels The blood sample is taken from a vein in your arm. An elastic band is wrapped around your upper arm. It may feel tight. Risks There is very little chance of a problem from having a blood sample taken from a vein. You may get a small bruise at the site. Results A cortisol test is done to measure the level of the hormone cortisol in the blood. The Adrenal Gland. (Excerpted from the book "From Fatigued to Fantastic!
") The adrenal glands, which sit on top of the kidneys, are actually two different glands in one. The center of the gland makes epinephrine (also known as adrenaline—for the adrenaline "junkies" out there) and is under the control of the autonomic nervous system. Symptoms of low cortisol. Cortisol. NOTE: This article is based on research that utilizes the sources cited here as well as the collective experience of the Lab Tests Online Editorial Review Board.
This article is periodically reviewed by the Editorial Board and may be updated as a result of the review. Any new sources cited will be added to the list and distinguished from the original sources used. Sources Used in Current Review. Dysautonomia. Dysautonomia (or autonomic dysfunction) is any disease or malfunction of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
The autonomic nervous system controls a number of functions in the body, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestive tract peristalsis, and sweating, amongst others. Dysfunction of the ANS can involve any of these functions. A number of conditions are forms of dysautonomia: postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST), vasovagal syncope, pure autonomic failure, neurocardiogenic syncope (NCS), neurally mediated hypotension (NMH), orthostatic hypotension, orthostatic hypertension, autonomic instability, paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity, and a number of lesser-known disorders such as cerebral salt-wasting syndrome.
Signs and symptoms[edit] The symptoms of dysautonomia are numerous and vary widely from person to person. The primary symptoms present in patients with dysautonomia are: Causes[edit] Management[edit] What Triggers Heart Palpitations? - Symptoms - Heart Disease. (7) What is happening physiologically when you feel your heart pounding. Heart beat feeling like it is pounding very hard...feeling and hearing each beat.