

Sticker Works Like an Anti-Mosquito Force Field. The Kite Patch is a little square sticker that emits a cloak of chemical compounds that block a mosquito's ability to sense humans.
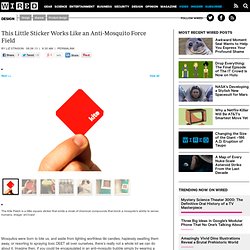
Image: ieCrowd The idea is to make humans "invisible" to mosquitos. Image: ieCrowd The sticker is small enough to be unobtrusive to the people who wear it. Image: ieCrowd Olfactor Laboratories developed non-toxic compounds that work against mosquitoes' long-range abilities to detect humans through CO2, as well as dampening the bug’s short-range ability to sense us from our basic human odors. Image: Olfactor Laboratories A scientist testing the chemical compounds. Image: Olfactor Laboratories Without the compounds.
Cool science, but is it news? The other day a news release with this headline landed in my email: "McMaster University researchers discover drug destroys human cancer stem cells but not healthy ones.
" "Can We Achieve Immortality?" U.S. Women Are Dying Younger Than Their Mothers, and No One Knows Why - Grace Wyler. While advancements in medicine and technology have prolonged life expectancy and decreased premature deaths overall, women in parts of the country have been left behind.
The Affordable Care Act took a major step toward implementation last Tuesday with the launch of the online insurance exchanges, limping across the finish line despite three years of Republican obstruction that culminated in this week’s 11th hour attempt to dismantle the law by shutting down the federal government. It’s easy to forget, amid the hyper-partisan controversy, that the main purpose behind President Obama’s signature health-care reform law is not to curtail individual freedom or send senior citizens to death panels, but to give more Americans access to health insurance.
Whether you think the Affordable Care Act is the right solution or a dangerous step toward tyranny, it’s hard to dispute that the U.S. health-care system is broken. Anti-aging drug breakthrough. Drugs that combat aging may be available within five years, following landmark work led by an Australian researcher.
The work, published in the March 8 issue of Science, finally proves that a single anti-aging enzyme in the body can be targeted, with the potential to prevent age-related diseases and extend lifespans. The paper shows all of the 117 drugs tested work on the single enzyme through a common mechanism. This means that a whole new class of anti-aging drugs is now viable, which could ultimately prevent cancer, Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes. "Ultimately, these drugs would treat one disease, but unlike drugs of today, they would prevent 20 others," says the lead author of the paper, Professor David Sinclair, from UNSW Medicine, who is based at Harvard University. Turning Off Pain Receptor In Mice Lengthens Their Lifespan by 10%
'Trust hormone' oxytocin helps old muscle work like new, study finds. Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have discovered that oxytocin -- a hormone associated with maternal nurturing, social attachments, childbirth and sex -- is indispensable for healthy muscle maintenance and repair, and that in mice, it declines with age.

The new study published in the journal Nature Communications, presents oxytocin as the latest treatment target for age-related muscle wasting, or sarcopenia. A few other biochemical factors in blood have been connected to aging and disease in recent years, but oxytocin is the first anti-aging molecule identified that is approved by the Food and Drug Administration for clinical use in humans, the researchers said. Mice That Feel Less Pain Live Longer. Scientists have found a way to beat back the hands of time and fight the ravages of old age, at least in mice.
A new study finds that mice bred without a specific pain sensor, or receptor, live longer and are less likely to develop diseases such as diabetes in old age. Young Blood Recharges Brains of Old Mice. Exposing older mice to young mouse blood has reversed some effects of aging on the brain, restoring some mental capabilities.
A new study suggests that factors circulating in young mouse blood could reverse impairments in age-related learning, memory, and neuron function. Previous studies have shown that blood-borne factors in old mice can impair cognitive function in young mice. A team led by Saul Villeda from University of California, San Francisco, and Tony Wyss-Coray of Stanford wanted to see if there are systemic factors in young blood that can reverse these age-related impairments.
News And Views 24. New York, March 29: Taking anti-aging pills or injections in a quest to remain youthful may undermine the body's natural defenses against the onslaught of old age, says a recent study of 184 men and women for up to 11 years.
The primary hormones administered are human growth hormone (HGH) which prompts the body to make another hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), a precursor of estrogen and testosterone. The chance of living through the length of the study depended mostly on the participants' blood levels of IGF-1. Every 1-nanogram per milliliter decrease in IGF-1 translated into about one more week of life. The lower IGF-1 levels were particularly beneficial for cancer survivors. Feeling "In Control" Helps Some Live a Longer Life - News Room. February 03, 2014 The less education you have, the more your attitude counts when it comes to staying alive and well.
That’s the finding of a new study conducted by personality researchers from the University of Rochester and Brandeis University. They found that adults without college degrees live longer if they feel like they’re in control of their lives. Those who feel little control are three times as likely to die. “Being uneducated and poor doesn’t mean you’re doomed, despite all of the studies showing people with less education are more likely to experience disease, disability, and premature death,” says lead author Nicholas Turiano, Ph.D., a postdoctoral-fellow in Psychiatry at the U of R. Aging Successfully Reversed in Mice; Human Trials to Begin Next.
Scientists have successfully reversed the aging process in mice according to a new study just released.
Human trials are to begin next, possibly before the year is over. The study was published in the peer reviewed science journal Cell after researchers from both the U.S and Australia made the breakthrough discovery. Lead researcher David Sinclair of the University of New South Wales says he is hopeful that the outcome can be reproduced in human trials. A successful result in people would mean not just a slowing down of aging but a measurable reversal. The study showed that after administering a certain compound to the mice, muscle degeneration and diseases caused by aging were reversed. Altering Community of Gut Bacteria Promotes Health and Increases Lifespan. Study provides first systemic understanding of aging gut January 9, 2014/Novato, California: Scientists at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging have promoted health and increased lifespan in Drosophila by altering the symbiotic, or commensal, relationship between bacteria and the absorptive cells lining the intestine.
The research, appearing in the January 16, 2014 edition of Cell, provides a model for studying many of the dysfunctions that are characteristic of the aging gut and gives credence to the growing supposition that having the right balance of gut bacteria may be key to enjoying a long healthy life. Jasper says the bacterial load in fly intestines increases dramatically with age, resulting in an inflammatory condition. Biological Clock. It may not be the eternal spring that Ponce de León searched for, but thanks to Steve Horvath PhD, a professor of human genetics and biostatistics at the University of California, Los Angeles, the Fountain of Youth is not as elusive as it once was. Our Real Biological Clock Horvath has developed a biological clock that makes it possible to measure the age of humans via tissue samples.
"Many people associate the term 'biological clock' with issues surrounding fertility. Others think of it as a measure of longevity. I simply define a biological clock as a device that measures the passage of time in organs, tissues, and cells, based on biological data," Horvath explains.
Resveratrol Anti-Aging Drug. Calorie Restriction. Cell Rejuvenation. Telomerase. Synergy - Combined Effect. Exercise 10 min a day to live longer. Even as little as 75 minutes a week of physical activity can extend your life by nearly two years, according to U.S. researchers who found some benefits regardless of body weight. The study by Steven Moore of the U.S. National Cancer Institute and his co-authors also suggests that regular activity would boost life expectancy even more. The researchers pooled data on 650,000 men and women aged 40 and older in Sweden and the U.S. who reported their activity levels.
Long Lived Animals. Long Lived People. Head Transplant. Herbs, Drugs & Chemicals. Repair DNA and Cells using Nanotech. Home > Press > Nanobotmodels Company offer vision of future DNA and cell-repair techniques Abstract: Five decades of research and practical application of computers in biomedicine has given rise to the discipline of medical informatics, which has made many advances in genomic and translational medicine possible. Ukraine | Posted on March 15th, 2010 Developments in nanotechnology and nanorobotics are opening up the prospects for nanomedicine and regenerative medicine where informatics and DNA computing can become the catalysts enabling health care applications at sub-molecular or atomic scales. While nanomedicine promises a new exciting frontier for clinical practice and biomedical research, issues involving cost-effectiveness studies, clinical trials and toxicity assays, drug delivery methods, and the implementation of new personalized therapies still remain challenging.
DNA repair nanorobotics will utilize the same tasks that living systems already prove possible. The Toxins That Affected Your Great-Grandparents Could Be In Your Genes.