

(2) Real World: What Is Soil Moisture? New Satellite Data Will Help Farmers Facing Drought. For several months, California has been in a state of “exceptional drought.”
The state’s usually verdant Central Valley produces one-sixth of the U.S.’s crops. Image Credit: White House via Wikimedia Commons About 60 percent of California is experiencing “exceptional drought,” the U.S. (4) Taking Control with Subsurface Drip Irrigation. (4) Irrigation Nation - 360° (4) Meet the Victims of Colombia’s Worst Drought in Decades. (4) Extreme Weather 101: Drought. National Geographic Society. #1 Water. Water is getting scarce – but what does this actually mean?
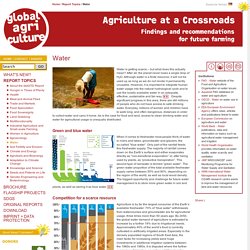
After all, the planet never loses a single drop of H2O. Although water is a finite resource, it will not be used up as long as we do not render it permanently unusable. However, it is important to integrate human water usage into the natural hydrological cycle and to use the locally available water in an adequate, effective, sustainable and fair way. "First, already more than a billion people live in river basins characterized by physical water scarcity.
In these areas water availability is a major constraint to agriculture. (...) Despite significant progress in this area, there are still millions of people who do not have access to safe drinking water. #2 How Does Drought Affect Our Lives? We often talk about drought's impacts as either “direct” or “indirect.” What does that mean? Well, to find out, let's think about dominoes. If you set up a long line of dominoes on the floor and knock the first domino in the line over, it will cause the second domino in the line to fall and hit the third, which will fall and hit the fourth, and so on. If those dominoes were drought impacts, the first domino you knock over might be farmers’ corn crops dying. The second domino might be that the farmers would not have money to buy a new tractor from the dealer in town. #3 Drought for Kids. #4 U.S. Drought Monitor. #5 Drought, Climate Change and Potential Agricultural Productivity. #6 Wet and wild 2018 is officially fourth-hottest year.
Overall, 2018 was the fourth-warmest year on record.
Only the three preceding years have been hotter. And these global records will likely be broken soon. Climate change trends suggest Earth’s fever will continue to climb, scientists reported on February 6. They spoke at a joint news conference by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA. The agencies collected data on global temperatures throughout 2018.
A warming trend started around the mid-1970s. In much of the Southern Hemisphere, 2018 scored record average highs for the second year in a row. Climate change also is leading to more erratic rains across much of the world. The United States experienced its wettest year since 1983. “The key message is that the planet is warming,” said Gavin Schmidt. “The long-term trends are extremely robust,” Schmidt added. #7 California Farmers Harvest Smaller Crops Due to Drought. TAGS: Marketing, Overseas December 18, 2014 With harvest time across California, many of the state's once-robust crops — from the grapes that make world-famous wines to popular almonds — are anticipated to be smaller than usual this year due to the state's historic drought.
The water shortage has also led to shrinking orange and pistachio crops as well, the Sacramento Bee reported Sunday. Farmers in rural California are expected to feel the effect as an estimated 420,000 acres (170,000 hectares) of farmland, or about 5 percent of the total, has gone unplanted this year, according to the newspaper. Also, economists at the University of California, Davis said that agriculture, once a $44 billion annual business in California, will suffer a financial hit of $2.2 billion due to revenue losses and higher water costs.
#8 Drought Tech: Innovative Solutions Help Farmers Manage Water. By Jodi Helmer | Photos By Jae C.
Hong Many areas in the Western U.S. and Canada—and beyond—have recently experienced historic droughts, and it’s no surprise that farmers have been hit hardest by the water shortages. “In research and in practice, we have shown that technology [is] very effective for helping farmers deal with drought,” notes Ximing Cai, endowed professor and water resources expert at the University of Illinois. To ease the impact of dry spells, several startups have created high-tech solutions to help farmers manage and conserve water.
Here are just a few. HydroBio uses satellite and weather data to issue irrigation prescriptions to farmers based on the specific needs of their fields. #9 How Farmers Conserve Water in a Drought - IFIC Foundation. #10 Prepare Your Farm or Ranch Before Drought Strikes. Having a good drought plan in place can help your operation weather even the most severe drought conditions.

Your plan should be part of a comprehensive conservation plan that considers the kinds and conditions of all of your resources, and consider how crops, forage, and other resources have reacted to drought in the past. Precipitation is the largest single determinant of drought. Temperature and other climate elements are also important. It is not uncommon for drought periods to be accompanied by higher summer temperatures. Drought planning involves preparing for not only average conditions, but also extremes. #11 The biggest Water Pollution guide on the Internet [Get updated on Causes] Assessing Drought in the United States. 607932main sheffield et al drought press conf. National Drought Mitigation Center. BASIN: Understanding Water Budgets and Balances. What is a water budget?

A water budget reflects the relationship between input and output of water through a region. The water balance graph shows precipitation and potential evapotranspiration both as line graphs. Thus we have a direct comparison of supply of water and the natural demand for water. It is possible to identify the periods when there is plenty of precipitation and when there is not enough. The following terms will be used in the questions that follow: Potential Evapotranspiration (PE): All the water that could enter the air from plants and evaporation if present.
Following is a data table of with monthly and total compares of Precipitation and Potential Evapotranspiration for Silver Lake, west and north of Nederland, and Boulder. Questions: National Geographic Society. A drought is a period of time when an area or region experiences below-normal precipitation.
The lack of adequate precipitation, either rain or snow, can cause reduced soil moisture or groundwater, diminished stream flow, crop damage, and a general water shortage. Droughts are the second-most costly weather events after hurricanes. Unlike with sudden weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms, it is often difficult to pinpoint when a drought has started or when it has ended.
The initial effects of a drought may be difficult to identify right away, so it may take weeks or months to determine that a drought has started. Drought: Identifying Impacts and Evaluating Solutions. The Impacts of a Megadrought on the Amazon Rainforest. Water pollution: An introduction to causes, effects, solutions. By Chris Woodford.
Last updated: March 24, 2019. Over two thirds of Earth's surface is covered by water; less than a third is taken up by land. As Earth's population continues to grow, people are putting ever-increasing pressure on the planet's water resources. In a sense, our oceans, rivers, and other inland waters are being "squeezed" by human activities—not so they take up less room, but so their quality is reduced. Poorer water quality means water pollution.
We know that pollution is a human problem because it is a relatively recent development in the planet's history: before the 19th century Industrial Revolution, people lived more in harmony with their immediate environment. How serious is the problem? #12 Dealing with drought.