

Will dangerous ‘east winds’ hit Oregon wildfires again this year? To Save Lake Tahoe, They Spared No Expense. The Fire Came Over the Ridge Anyway. Climate Change Is Making Extreme Weather Events More Common : NPR. ‘We thought it wouldn’t affect us’: heatwave forces climate reckoning in Pacific north-west. The record heatwave in the Pacific north-west is forcing a reckoning on the climate crisis, as many living in the typically mild region consider what rising temperatures mean for the future.

A “heat dome” without parallel trapped hot air over much of the states of Oregon and Washington in the United States, and southern British Columbia in Canada, in past days, shattering weather records in the usually temperate region. Temperatures in tiny Lytton, British Columbia, hit 49.6C (121.3F) and set a Canadian all-time record, days before a wildfire tore through the town. Yellowstone’s most famous geyser could shut down, with huge ramifications. When a band of geological surveyors and US army scouts mapped out what would become Yellowstone in 1870, the geysers and springs seemed endless – a land so unbound that Congress moved to name it the world’s first national park.

Nearly 150 years later, about 4 million people visit the park annually to see its most famous geyser: Old Faithful. It is a sight to behold, shooting tens of thousands of litres of boiling water hundreds of feet into the air about 17 times a day. While the geyser is highly predictable – it has erupted every 44 to 125 minutes since 2000 – a new climate assessment and a recent study have revealed that rising temperatures, reduced snowfall and increased rain threaten to shut Old Faithful off completely by the end of the century. If temperatures at Yellowstone rise 10F (5.6C) by the end of the century, as they are projected to, this vast ecosystem will be disrupted.
Drought is here to stay in the Western U.S. How will states adapt? Study blames climate change for 37% of global heat deaths. How to Kill a Zombie Fire - Atlas Obscura. This story originally appeared in Wired and is reproduced here as part of our Climate Desk collaboration.
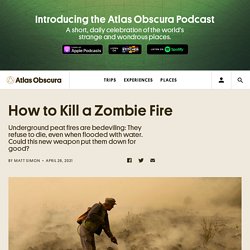
Humanity’s got a full-tilt zombie outbreak on its hands. As the world warms and certain regions—particularly the Arctic—dry, so does the super fuel known as peat. It’s basically concentrated carbon from dead plants, and it burns not at all like your typical Californian or Australian wildfire. Instead of sending towering flames upward, a peat fire burns in the opposite direction, smoldering deep in the soil. Firefighters often soak the ground with water and declare victory, only for the soil to reignite a surface fire months later. Peat fires can release 100 times the carbon that a wildfire does. Climate crisis hits 'worst case scenario' levels – Environment Agency head.
The climate emergency is already hitting “worst case scenario” levels that if left unchecked will lead to the collapse of ecosystems, with dire consequences for humanity, according to the chief executive of the Environment Agency.
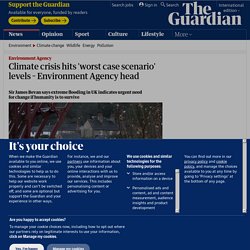
Warning that this is not “science fiction”, Sir James Bevan said on Tuesday that in recent years several of the “reasonable worst case scenarios” had happened in the UK, with more extreme weather and flooding. And he urged politicians to take action to reduce emissions and adapt to the “inevitable” impacts of the climate emergency. “Much higher sea levels will take out most of the world’s cities, displace millions, and make much of the rest of our land surface uninhabitable or unusable,” Bevan told the annual conference of the Association of British Insurers. “Much more extreme weather will kill more people through drought, flooding, wildfires and heatwaves than most wars have.
Where 2020's Record Heat Was Felt the Most. 2020 was effectively tied with 2016 for the hottest year on record, as global warming linked to greenhouse gas emissions showed no signs of letting up.
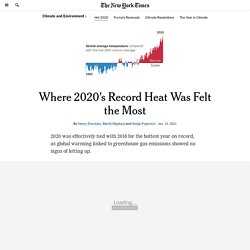
This analysis of global temperatures, by the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and released Thursday, found that 2020 was slightly warmer than 2016. ‘Moving a giraffe is a delicate process’: rising waters threaten Kenya's wildlife. Marooned giraffes, fleeing flamingoes and stranded impalas: in recent years the rising water levels in east Africa’s Rift Valley lakes have become the norm, displacing people, threatening wildlife and submerging schools and hotels.
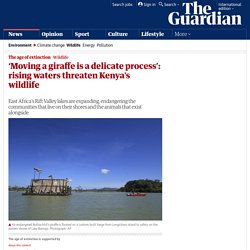
The gradual rise was first noticed 10 years ago but was accelerated by heavy rains in 2019, according to Kenya’s principal secretary in the ministry of environment and forestry, Chris Kiptoo. This year Lake Turkana, the northernmost lake in Kenya, was six metres deeper than usual by November. (2) Antarctica melting: Journey to the 'doomsday glacier' - BBC News. Amazon fires: Brazilian rainforest burning at record rate, space agency warns. Media playback is unsupported on your device Brazil's Amazon rainforest has seen a record number of fires this year, according to new data from the country's space research agency.
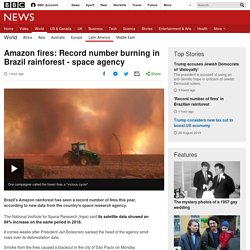
The National Institute for Space Research (Inpe) said its satellite data showed an 84% increase on the same period in 2018. It comes weeks after President Jair Bolsonaro sacked the head of the agency amid rows over its deforestation data. Earth's future is being written in fast-melting Greenland. HELHEIM GLACIER, Greenland (AP) — This is where Earth’s refrigerator door is left open, where glaciers dwindle and seas begin to rise.
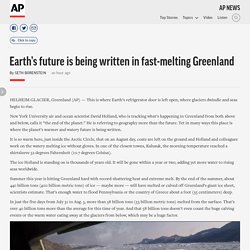
New York University air and ocean scientist David Holland, who is tracking what’s happening in Greenland from both above and below, calls it “the end of the planet.” He is referring to geography more than the future. Climate change: Arctic permafrost now melting at levels not expected until 2090. Permafrost hs begun thawing in the Canadian Arctic more than 70 years early because of climate change, according to new research. A "series of anomalously warm summers” has dramatically accelerated melting rates at three sites despite average annual ground temperatures remaining low. Ponds and hillocks have formed as a result. India heatwave temperatures pass 50 Celsius. Date created : 01/06/2019 - 22:45 New Delhi (AFP) Temperatures passed 50 degrees Celsius (122 Fahrenheit) in northern India as an unrelenting heatwave triggered warnings of water shortages and heatstroke.
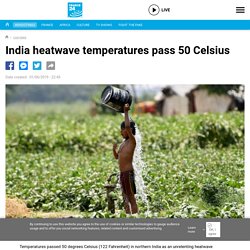
The thermometer hit 50.6 degrees Celsius (123 Fahrenheit) in the Rajasthan desert city of Churu on Saturday, the weather department said. All of Rajasthan suffered in severe heat with several cities hitting maximum temperatures above 47 Celsius. Climate change has contributed to droughts since 1900, and is likely to get worse, says tree-ring study. Using studies of tree rings going back centuries, scientists have unearthed clear evidence that the rise of human-generated greenhouse gases was having an effect on global drought conditions as early as 1900.
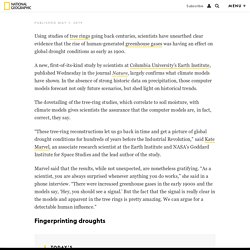
A new, first-of-its-kind study by scientists at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, published Wednesday in the journal Nature, largely confirms what climate models have shown. African heatwaves could increase ‘five-fold’ with 3C of global warming. The number of heatwaves affecting the African continent every year could be five times higher by 2050 as a result of climate change, a new study finds. Global warming of 3C above pre-industrial levels could also alter rainfall patterns across the continent, the research says, which could bring droughts to some countries and an increase in flood risk to others. However, limiting warming to 1.5C – the aspirational goal of the Paris Agreement – could greatly reduce the risk of heatwaves and other climate extremes in Africa, the lead author tells Carbon Brief. Continental countdown The new study, published in Earth’s Future, focuses on how global warming could impact a range of climate variables that tend to have a large effect on human life, including heatwaves, “hot nights” and rainfall intensity.
Non-survivable humid heatwaves for over 500 million people – Climate Guide. Researchers at MIT warn that if climate change remains unchecked (Business As Usual-scenario = RCP 8.5) over half a billion people will, from 2070 onwards, experience humid heat waves that will kill even healthy people in the shade within 6 hours. The Wet Bulb Temperature (WBT) would exceed 35°C (95°F), at which the body – of any mammal – cannot cool itself, overheats and shuts down. Three regions were studied: China (2018), South Asia (2017) and the Persian Gulf (2015).
The researchers predict (at RCP 8.5) WBT exceeding 35°C about once every decade for the Northern Plains in China (400+ million people), at locations in the Chota Nagpur plateau, northeastern India, and Bangladesh in South Asia (70+ million people). Persian Gulf regions that would be affected include cities such as Doha, Qatar, Abu Dhabi, Dubai (UAE) and Bandar Abbas (Iran). The Uninhabitable Earth: David Wallace-Wells on the horrors of climate change. “It is, I promise, worse than you think.” That was was the first line of David Wallace-Wells’s horrifying 2017 essay in New York magazine about climate change. It was an attempt to paint a very real picture of our not-too-distant future, a future filled with famines, political chaos, economic collapse, fierce resource competition, and a sun that “cooks us.”
You're Not Allowed to Die Here. 'We've never seen this': massive Canadian glaciers shrinking rapidly. Scientists in Canada have warned that massive glaciers in the Yukon territory are shrinking even faster than would be expected from a warming climate – and bringing dramatic changes to the region. After a string of recent reports chronicling the demise of the ice fields, researchers hope that greater awareness will help the public better understand the rapid pace of climate change. The rate of warming in the north is double that of the average global temperature increase, concluded the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in its annual Arctic Report Card, which called the warming “unprecedented”.
“The region is one of the hotspots for warming, which is something we’ve come to realize over the last 15 years,” said David Hik of Simon Fraser University. “The magnitude of the changes is dramatic.” Previous research found that between 1957 and 2007, the range lost 22% of its ice cover, enough to raise global seal levels by 1.1 millimetres. Stunning Look at the Damage - Florida click 2x on pic & wait a few seconds. Which cities will sink into the sea first? Maybe not the ones you expect. Better scientific understanding of global warming makes the discussion about its geopolitical consequences increasingly urgent.
As New Mexico Reservoirs Hit Bottom, Worries Grow Over the Future — Water Deeply. Europe's heatwave is forcing nuclear power plants to shut down click 2x. Drought 2018. Temperatures in south-west Europe could break 48C record this weekend. Large parts of southern and western Europe are expected to experience high temperatures this weekend with forecasters warning that thermometers could reach up to 48C in Spain. Good boy knows just how to beat the heat. 'We have different ways of coping': the global heatwave from Beijing to Bukhara. Media reaction: The 2018 summer heatwaves and climate change. Canada heatwave: more than 30 deaths reported as extreme weather continues. A heatwave rolling through central and eastern Canada has caused the deaths of more than 30 people, with officials warning that the extreme weather conditions are expected to continue for at least another day.
In Del Mar, a 'Planned Retreat' May Be Only Option as Seas Rise. Hundreds of coastal homes in the Southern California city of Del Mar could be threatened by rising seas, officials say.One possible solution is to have a "planned retreat" and remove the most vulnerable homes.But residents of these million-dollar homes say even rumors of such a plan could cause home values to plummet. There aren't many easy answers in the Southern California town of Del Mar, where city leaders and residents are trying to figure out a way to combat rising seas in an area where million-dollar homes line the coast.
One idea being floated in low-lying areas of the town is a "planned retreat," which would eventually tear down structures most threatened by rising sea levels, according to the Los Angeles Times. Dozens of wild horses found dead amid Southwest drought. How climate change may be driving extreme weather. March 27, 2017 —Whether a specific extreme weather event can be linked to climate change rarely gets a straightforward answer from climate scientists or meteorologists. Rising Seas Could Submerge the Oldest English Settlement in the Americas. Erratic Weather Threatens Livelihood Of Rice Farmers In Madagascar : Parallels. Sea Level Bombshell. Climate Change Is Complex. Answers to Questions. click 2x.
Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers will determine sea level rise. PINE Island. Irma Fla sewage overflow click 2x. Irma brought out the truth about the Florida Keys - CNN. Scientists Saw A Nearly Unheard Of Antarctic Meltdown. Highest Recorded Temperatures In Antarctica Announced click 2x. Migratory birds bumped off schedule as climate change shifts spring. Global Warming’s Terrifying New Chemistry click 2x. 1.5 C vs 2 C global warming: New study shows why half a degree matters. How climate change may drive extreme weather. Michigan's Tart Cherry Orchards Struggle To Cope With Climate Change. Global Warming Might Be Speeding Up - Bloomberg.
Retreating Yukon glacier caused a river to disappear. Antarctica: Return of the Weddell polynya supports Kiel climate model. Explorers See Greenland's Glaciers Like Never Before. Barrier reef suffers huge coral loss. Combatting Climate Change Is "A Matter Of Survival" Says Fijian Minister. 6 Devastating Heat Waves Hitting the Planet.
Antarctica greeningclick 2x. Temperature anomaly by year -Gyphycat. 'Impossible To Save': Scientists Are Watching China's Glaciers Disappear : Parallels. Arctic temperatures soar 45 degrees above normal, flooded by extremely mild air on all sides. It’s Not Your Imagination. Summers Are Getting Hotter. click 2x. Can We Come Back from Climate Change's Brink? Drought’s over; climate change isn't. 7 Things That Might Surprise Your About California's Drought. Could climate change transform Earth into Venus? [Infographic] More-severe climate model predictions could be the most accurate: study. Global Warming Scenarios. Are We Making Forest Fires Stronger? 'hole' larger than Maryland reappears in Antarctica after 42 years click 2x.
The Year Climate Change Began to Spin Out of Control. Artificial Snow Could have Devastating Effects on Climate. Melting Permafrost. Three Reasons Scientists Are Freaked out by Crazy-High Arctic Temperatures. Hotter, Drier, Hungrier: How Global Warming Punishes the World’s Poorest.