

Pathway to the Global Brain (part 1/5): Introduction to Cybernetics. What is the nature of intelligence?
If you share this, please use the hashtags #GlobalBrain and/or #LongReads The Global Brain is a concept representing the hypothesized emergence of a higher-level distributed intelligence caused by human-machine communication networks on the Internet. Leading research and model-building on this phenomenon is occurring at the Global Brain Institute in Belgium. The following blog series is in preparation for my Ph.D. work on the Global Brain. I would like to create a new perspective on our evolutionary history which combines evolutionary anthropology and cybernetics. I hope you enjoy the groundwork for this work (below). Biological intelligence is a fleeting phase in the evolution of the universe. – Paul Davies The human story is a story about reaching towards the Sun. – Me Imagine it is the year 3,000 C.E.
If you are like me, this would be quite a strange future. 1) “The Wheel of Time” scenario – humanity experiences series of endless cycles. Alien Timescapes. Monkey’s Thoughts Control Robot Halfway Across the World. The New York Times today reports on an awesome experiment in which thoughts were extracted from a monkey in the US and used to control a walking robot in Japan.
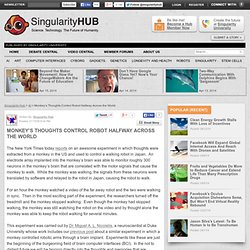
An electrode array implanted into the monkey’s brain was able to monitor roughly 300 neurons in the monkey’s brain that are correlated with the motor signals that cause the monkey to walk. While the monkey was walking, the signals from these neurons were translated by software and relayed to the robot in Japan, causing the robot to walk. For an hour the monkey watched a video of the far away robot and the two were walking in sync. Blog Archive » First Human Infected w.
Cybernetics. Cybernetics is a transdisciplinary[1] approach for exploring regulatory systems, their structures, constraints, and possibilities.

Cybernetics is relevant to the study of systems, such as mechanical, physical, biological, cognitive, and social systems. Cybernetics is applicable when a system being analyzed incorporates a closed signaling loop; that is, where action by the system generates some change in its environment and that change is reflected in that system in some manner (feedback) that triggers a system change, originally referred to as a "circular causal" relationship. Some say this is necessary to a cybernetic perspective. System dynamics, a related field, originated with applications of electrical engineering control theory to other kinds of simulation models (especially business systems) by Jay Forrester at MIT in the 1950s.
Norbert Wiener defined cybernetics in 1948 as "the scientific study of control and communication in the animal and the machine Definitions[edit] W. A Turing Machine Overview. Robots with a mind of their own. Self-Replicating Repairing Robots ( Data. Robot Uses Air Powered Muscles To Run Like A Human (video. High-Speed Robot Hand. Robot Hand Copies Your Movements, Mimics Your Gestures (video. Robot see, robot do. 2010 may go down in history as the year of gesture recognition.
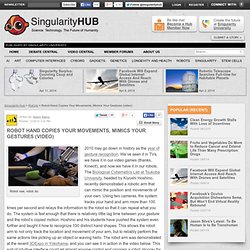
We’ve seen it in TVs, we have it in our video games (thanks, Kinect!) , and now we have it in our robots. The Biological Cybernetics Lab at Tsukuba University, headed by Kiyoshi Hoshino, recently demonstrated a robotic arm that can mimic the position and movements of your own. Using two cameras, the system tracks your hand and arm more than 100 times per second and relays the information to the robot so that it can repeat what you do. The Hoshino Lab should be commended for its cool approach to robotic controls, but I’m not sure how impressed we should be with their camera setup. Also, while I’m totally in favor of gesture controlled robots, the video above demonstrates that there are some serious limitations to the technology. Even with these limitations, I think that the Hoshino Lab shows us that non-traditional controls for robotics could arrive much sooner than we think. Only better. ABB Robotics - Fanta Can Challenge- Level II - Superior Motion C.
Designing woman and women in science. MIT's Nexi MDS Robot: First Test of Expression. Medical Robots and technological therapy. Born in Belgrade, in what was then Yugoslavia, Maja Matarić originally wanted to study languages and art.

After she and her mother moved to the United States, in 1981, her uncle, who had immigrated some years earlier, pressed her to concentrate on computers. As a graduate student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Matarić wrote software that helped robots to independently navigate around obstacles placed randomly in a room. For her doctoral dissertation, she developed a robotic shepherd capable of corralling a herd of twenty robots. At the end of her graduate training, Matarić, influenced by her knowledge of cognitive science, became interested in how people could benefit from interacting with robots. “We wanted to do something entirely different,” Matarić told me.
In 2003, Matarić initiated a pilot trial for stroke patients with Carolee Winstein, a professor of biokinesiology and physical therapy at U.S.C. She turned and looked squarely at the robot. ASIMOs new artificial intelligence. (ASIMO is learning!) Asimo learns to sing and dance, but has yet to learn how to love. Dancing Sony Robots. Asimo Running at 2007 CES.