

Norse Mythology - World History Encyclopedia. Norse mythology refers to the Scandinavian mythological framework that was upheld during and around the time of the Viking Age (c. 790- c. 1100 CE).
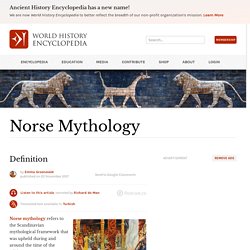
Complete with a creation myth that has the first gods slaying a giant and turning his body parts into the world, various realms spread out beneath the World Tree Yggdrasil, and the eventual destruction of the known world in the Ragnarök, the Nordic mythological world is both complex and comprehensive. Its polytheistic pantheon, headed by the one-eyed Odin, contains a great number of different gods and goddesses who were venerated in customs integrated into the ancient Scandinavians' daily lives.
Main sources Peeling back the layers of history in order to form a properly detailed and accurate picture of the myths, beliefs, and customs as they actually were in the Viking Age is no mean feat, especially for an overwhelmingly oral society, as Scandinavia mostly was at the time. Nordic Model Definition. What Is the Nordic Model?
The Nordic model is the combination of social welfare and economic systems adopted by Nordic countries. It combines features of capitalism, such as a market economy and economic efficiency, with social benefits, such as state pensions and income distribution. Nordic countries. Nordic countries. The old Nordic religion today. Old Norse language, alphabet and pronunciation. Old Norse was a North Germanic language once spoken in Scandinavia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and in parts of Russia, France and the British Isles and Ireland.

It was the language of the Vikings or Norsemen. The modern language most closely related to Old Norse is Icelandic, the written form of which has changed little over the years, while the spoken form has undergone significant changes. The earliest known inscriptions in Scandinavia date from the the 2nd century AD and were written in Runes mainly on stone, or on personal artifacts such as brooches and swords. The majority of these inscription have been found in Denmark and Sweden, and they are written in a language much more archaic than Old Norse. The Weather and Climate in Scandinavia. Scandinavian countries can be either a winter wonderland or balmy summer destination.
The climate varies from north to south and from west to east, so each locale has a unique temperature signature. Depending on the month you travel to Scandinavia, travelers can expect to pack shorts, bundle up with a parka, or dress in layers to accommodate the fluctuations in weather. The areas that are included as part of Scandinavia can be debated, but typically Scandinavia is considered to be comprised of Denmark, Finland, Greenland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden. Differences in Climate Scandinavia's regions have different climates, and temperatures vary widely between the regions. Somali mythology. Somali mythology covers the beliefs, the myths, the legends and folk tales circulating in Somali society that were passed down to new generations in a timeline spanning several millennia.
Many of the things that constitute Somali mythology today are traditions whose accuracy have faded away with time or have transformed considerably with the coming of Islam to the Somali Peninsula. The culture of venerating saints and the survival of several religious offices in modern Somalia show that old traditions of ancient Somalia had a significant impact on Somali Islam and Somali literature in later centuries.
Similarly practitioners of traditional Somali medicine and astronomy also adhere to remnants of an old cultural belief system that once flourished in Somalia and the wider Horn of Africa. Somalia - The World Factbook. Somalia Population Growth Rate 1950-2021. Somali Culture - Religion — Cultural Atlas. History, Geography, Culture, & Facts. Somalia, easternmost country of Africa, on the Horn of Africa.
It extends from just south of the Equator northward to the Gulf of Aden and occupies an important geopolitical position between sub-Saharan Africa and the countries of Arabia and southwestern Asia. The capital, Mogadishu, is located just north of the Equator on the Indian Ocean. Britannica Quiz Geography of Africa Quiz. 11 Egyptian Gods and Goddesses. Egyptian Gods - The Complete List - World History Encyclopedia. The gods and goddesses of Ancient Egypt were an integral part of the people's everyday lives. It is not surprising then that there were over 2,000 deities in the Egyptian pantheon. Some of these deities' names are well known: Isis, Osiris, Horus, Amun, Ra, Hathor, Bastet, Thoth, Anubis, and Ptah while many others less so. The more famous gods became state deities while others were associated with a specific region or, in some cases, a ritual or role. The goddess Qebhet, for example, is a little known deity who offered cool water to the souls of the dead as they awaited judgment in the afterlife, and Seshat was the goddess of written words and specific measurements overshadowed by Thoth, the better known god of writing and patron of scribes.
Ancient Egyptian religion - The Gods. Egyptian religion was polytheistic.
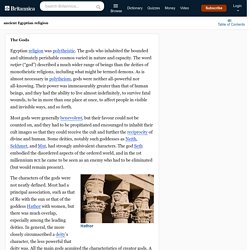
The gods who inhabited the bounded and ultimately perishable cosmos varied in nature and capacity. The word netjer (“god”) described a much wider range of beings than the deities of monotheistic religions, including what might be termed demons. As is almost necessary in polytheism, gods were neither all-powerful nor all-knowing. Everything About the Weather in Egypt 2021 - Egypt Climate 2021. The weather in Egypt has an arid Sahara climate which is generally sunny, but as being a part of the northern hemisphere, seasons in Egypt follow much of the same patterns as in Europe and USA as winter is between November and January with an average temperature of 10° C (50° F) while the summer is between June & August with an average temperature of 40° C (104° F).

It is clear now that the best time to be in Egypt is during the northern hemisphere fall, winter or Early Spring from October till April which you will have a variety of options to explore the allure and wonders of the mesmerizing country like a Nile cruise, camel ride, water-spots like diving & snorkeling and many more. Weather in Egypt January. Egypt Population 1950-2021. Legal Research Guide: Egypt.
Back to Foreign and International Law Introduction Historic Background The Egyptian legal system was founded on the Napoleonic Codes, Roman law, and Islamic Shari’a.
In 1874, Egypt gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in matters of legal and administrative regulation. In the following year, a national legal system was established. Egypt Religions - Demographics. Religions: Muslim (predominantly Sunni) 90%, Christian (majority Coptic Orthodox, other Christians include Armenian Apostolic, Catholic, Maronite, Orthodox, and Anglican) 10% (2015 est.)
Definition: This entry is an ordered listing of religions by adherents starting with the largest group and sometimes includes the percent of total population. Egypt Geography & Maps. With a population of approximately 90,000,000 people, Egypt is located in the northeast corner of the African continent on the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered to the northeast by Palestine and Israel, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south and Libya to the west. The geography of Egypt can be divided into four different regions: the Nile Valley and Delta, the Western Desert, the Eastern Desert and the Sinai Peninsula. Despite covering only about 5.5% of the total area of Egypt, the Nile Valley and Delta are the most important regions in the country.
The majority of Egypt’s population lives there as it is the only region with cultivatable land. The Nile is the world’s largest river at 6,690 km (4,160 mi) long. Languages Spoken In Egypt - WorldAtlas. Modern Standard Arabic is the official language of the African country of Egypt and is used in most written documents and taught in schools across the country.
Arabic was introduced to Egypt under the Arab occupation. Arabic easily became integrated with other Semitic languages such as Syriac, Berber, and Assyrian to form other variants of Arabic spoken in the country today.