Bugatti – The World Fastest And Expensive Car – 5
Dynamics in numbers. The new Bugatti Veyron 16.4 Grand Sport Vitesse boasts a remarkable maximum torque of 1,500 Nm (at 3,000–5,000 rpm) from the 7.9-liter capacity of its W16 engine. The maximum output (1,200 hp) is reached at 6,400 rpm. For More Photos of Bugatti >> Spread your love!
Southern Europe
Southern region of Europe Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe.[1] It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria,[note 1] Croatia, Cyprus,[note 2] Gibraltar,[note 3] Greece,[note 4] southern Italy,[note 5] Malta,[note 6] Monaco,[note 7] Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France,[note 8] Spain, Turkey (East Thrace),[note 9] and Vatican City.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11] Different methods can be used to define southern Europe, including its political, economic, historical, and cultural attributes. Geographically, southern Europe is the southern portion of the European continent. The major islands in southern Europe generally include the Balearic Islands, Corsica, Crete, Cyprus,[note 2] Sardinia, and Sicily, as well as the island country of Malta. [edit]
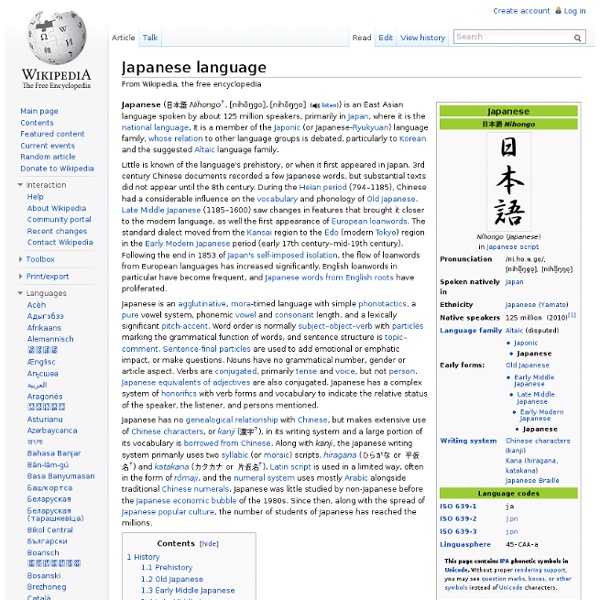
Kana
Japanese syllabic writing systems Katakana, with a few additions, are also used to write Ainu. A number of systems exist to write the Ryūkyūan languages, in particular Okinawan, in hiragana. Taiwanese kana were used in Taiwanese Hokkien as glosses (ruby text or furigana) for Chinese characters in Taiwan when it was under Japanese rule. Due to the limited number of phonemes in Japanese, as well as the relatively rigid syllable structure, the kana system is a very accurate representation of spoken Japanese. Etymology[edit] 'Kana' is a compound of kari (仮, 'borrowed; assumed; false') and na (名, 'name'), which eventually collapsed into kanna and ultimately 'kana'.[2] As the name suggests, 'kana' were "false" kanji due to their purely phonetic nature, as opposed to mana (真名) which were "true" kanji used for their meanings. Terms[edit] Although the term 'kana' is now commonly understood as hiragana and katakana, it actually has broader application as listed below:[2] Hiragana and katakana[edit]
Linguistics
In the early 20th century Ferdinand de Saussure distinguished between the notions of langue and parole in his formulation of structural linguistics. According to him, parole is the specific utterance of speech, whereas langue refers to an abstract phenomenon that theoretically defines the principles and system of rules that govern a language.[9] This distinction resembles the one made by Noam Chomsky between competence and performance, where competence is individual's ideal knowledge of a language, while performance is the specific way in which it is used.[10] In classical Indian philosophy of language, the Sanskrit philosophers like Patanjali and Katyayana had distinguished between sphota (light) and dhvani (sound). In the late 20th century, French philosopher Jacques Derrida distinguished between the notions of speech and writing.[11] Nomenclature[edit] Variation and Universality[edit] Lexicon[edit] The lexicon is a catalogue of words and terms that are stored in a speaker's mind.
cars
Southeast Asia
Subregion of the Asian continent The region lies near the intersection of geological plates, with both heavy seismic and volcanic activities.[6] The Sunda Plate is the main plate of the region, featuring almost all Southeast Asian countries except Myanmar, northern Thailand, northern Laos, northern Vietnam, and northern Luzon of the Philippines. The mountain ranges in Myanmar, Thailand, and Peninsular Malaysia are part of the Alpide belt, while the islands of the Philippines are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. Both seismic belts meet in Indonesia, causing the region to have relatively high occurrences of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, particularly in the Philippines and Indonesia.[7] It covers about 4,500,000 km2 (1,700,000 sq mi), which is 10.5% of Asia or 3% of Earth's total land area. Southeast Asia was home to one of the few regions across Eurasia that did not get subsumed by the Mongol Empire. Definitions[edit] States and regions of Southeast Asia Political divisions[edit]
Chinese characters
logographic writing system used in the Sinosphere region Chinese characters (simplified Chinese: 汉字; traditional Chinese: 漢字; pinyin: hànzì; literally: 'Han characters') are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese.[2][3][4] They have been adapted to write a number of other Asian languages. They remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as kanji. Chinese characters constitute the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world.[5] By virtue of their widespread current use in East Asia, and historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users. Chinese characters number in the tens of thousands, though most of them are minor graphic variants encountered only in historical texts. Unlike an alphabet, a character-based writing system associates each logogram with an entire sound and thus may be compared in some aspects to a syllabary. Function[edit] Rebus[edit]
Brain Hacks
...For answer Holmes clapped the hat upon his head. It came right over the forehead and settled upon the bridge of his nose. "It is a question of cubic capacity, " said he; "a man with so large a brain must have something in it. " ... Sherlock Holmes - The Adventure of the Blue Carbuncle. Not everyone is born with a big brain. If you’re looking to improve mental cognition, increase your memory, and enhance your alertness, here are 15 easy ways to give your brain a six-pack. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. First, know how you learn. Second, the most effective way to remember facts is by forming multiple associations. Third, rinse and repeat. 14. 15.
Understand your online social capital



by raviii Nov 18